21. Bulger H. A., Johns H. E. J. (1941), “The detemination of plasma uric acid”,
Biol. Chem., Vol. 140, pp. 427–440.
22. Burstein E. (1954), "Anomalous optical absorption limit in InSb", Physical Review, Vol. 93(3), pp. 632-633.
23. Calleja J. M., Cardona M., “Resonant Raman scattering in ZnO”, Phys. ReV. B, Vol. 16 (1977) pp. 3753-3761.
24. Cannon P. J., Stason W. B., Demartini F. E., Sommers S. C., Laragh J. H. (1966), “Hyperuricemia in primary and renal hypertension”, N. Engl. J. Med., Vol. 275, pp. 457–464.
25. Cao B., Li Y., Duan G., Cai W. (2006), “Growth of ZnO nanoneedle arrays with strong ultraviolet emissions by an electrochemical deposition method”, Cryst. Growth Des., Vol. 6, pp 1091-1095.
26. Carneiro J. T., Moulijn J. A., Mul G. (2010), “Photocatalytic oxidation of cyclohexane by titanium dioxide: catalyst deactivation and regeneration”, J. Catal., Vol. 273, pp 199–210.
27. Cavani F., Trifiro F. (1997), “Classification of industrial catalysts and catalysis for the petrochemical industry”, Catal. Today, Vol. 34, pp 269–279.
28. Chakinala A. G., Gogate. P. R., Burgess. A. E., Bremner D. H. (2008), “Treatment of industrial wastewater effluents using hydrodynamic cavitation and the advanced Fenton process”, Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, Vol. 15, 49-54.
29. Chang S. C. (1980), “Oxygen chemisorption on tin oxide: correlation between electrical conductivity and EPR measurements”, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., Vol. 17, pp 366-369.
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
 So Sánh Độ Cảm Biến Ammonia Của Vật Liệu Zno Và La – Zno Với Một Số Nghiên Cứu Khác
So Sánh Độ Cảm Biến Ammonia Của Vật Liệu Zno Và La – Zno Với Một Số Nghiên Cứu Khác -
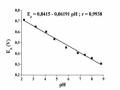
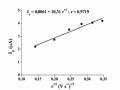
 Ảnh Hưởng Của Biên Độ Xung (Δe) Đến Tín Hiệu Ip
Ảnh Hưởng Của Biên Độ Xung (Δe) Đến Tín Hiệu Ip -
 Hàm Lượng Ua Trong 3 Mẫu Nt2, Nt4 Và Nt5 Sau 3 Đo Lần Lặp Lại
Hàm Lượng Ua Trong 3 Mẫu Nt2, Nt4 Và Nt5 Sau 3 Đo Lần Lặp Lại -
 Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 23
Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 23 -
 Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 24
Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 24 -
 Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 25
Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 25
Xem toàn bộ 207 trang tài liệu này.
30. Charpentier C., Prod’homme P., Maurin I., Chaigneau M., and Roca i Cabarrocas P. (2011), “X-Ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy for a better understanding of ZnO:Al growth process”, European Physical Journa Photovoltaics, Vol. 2, pp. 25002-25010.
31. Srivastava R. , Dwivedi R. and Srivastava S. K. (1998), “Development of high sensitivity based tin oxide gas sensors for gas/odour detection at room temperature”, Sensors and Actuators, Vol. 50, pp.175–180.

32. Chaudhari G. N., Jagtap S. V., Gedam N. N., Pawar M. J., Sangawar V. S. (2009), “Sol–gel synthesized semiconducting LaCo0.8Fe0.2O3 -based powder for thick film NH3 gas sensor”, Talanta, Vol. 78, pp 1136–1140.
33. Chawla S., Rawal R., Kumar D., Pundir C.S. (2012), “Amperometric determination of total phenolic content in wine by laccase immobilized onto silver nanoparticles/zinc oxide nanoparticles modified gold electrode”, Analytical Biochemistry, Vol. 430, pp. 16-23.
34. Chen Y. W., Qiao Q., Liu Y. C., Yang G. L. (2009), “Size-controlled synthesis and optical properties of small-sized ZnO nanorods”, J. Phys. Chem. C, Vol. 113, pp 7497–7502.
35. Clesceri L.S., Greenberg A.E., Eaton A.D. (1998), Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th Ed., APHA, USA.
36. Colussi S., de Leitenburg C., Dolcetti G., & Trovarelli A. (2004), "The role of rare earth oxides as promoters and stabilizers in combustion catalysts", Journal of alloys and compounds, Vol. 374(1), pp. 387-392.
37. Crum L. A., Mason. T. J., Reisse J. L., Suslick K. S. (Eds.) (1999), “Sonochemistry and Sonoluminescence”, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht. pp. 191-204.
38. Dai Z.H., Liu K., Tang Y.W., Yang X.D., Bao J.C., Shen J 2008, “A novel tetragonal pyramid-shaped porous ZnO nanostructure and its application in the biosensing of horseradish peroxidase”, J. Mater. Chem., Vol. 18, pp 1919–1926
39. Dai Z. H., Shao G. J., Hong J. M., Bao J. C., Shen J. (2009), “Immobilization and direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase on a tetragonal pyramid-shaped porous ZnO nanostructure for a glucose biosensor”, Biosens. Bioelectron., Vol. 24, pp. 1286–1291.
40. Daneshvar N., Salari D., Khataee, A. R (2004). "Photocatalytic degradation of azo dye acid red 14 in water on ZnO as an alternative catalyst to TiO2", Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, Vol. 162 (2–3), pp. 317-322.
41. Decremps F., Porres J. P., Saitta A. M., Chervin J. C., Polian A. (2002), “High pressure Raman spectroscopy study of wurtzite ZnO”, Phys. ReV. B., Vol. 65, pp. 092101-092104.
42. Deng S. H., Duan M. Y., Xu M., He L. (2011), “Effect of La doping on the electronic structure and optical properties of ZnO”, Physica B, Vol. 406, pp. 2314–2318.
43. Dole B. N., Mote V. D., Huse V. R., Purushotham Y., Lande M. K., Jadhav
K. M., & Shah S. S. (2011), "Structural studies of Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles", Current Applied Physics, Vol. 11(3), pp. 762-766.
44. Dong L., Jiao J., Tuggle D. W., Petty J. M., Elliff S. A., & Coulter M. (2003), "ZnO nanowires formed on tungsten substrates and their electron field emission properties", Applied physics Letters, Vol. 82(7), pp. 1096-1098.
45. Du J., Yue R., Ren F., Yao Z., Jiang F., Yang P., Du Y. (2013), “Simultaneous determination of uric acid and dopamine using a carbon fiber electrode modified by layer – by – layer assembly of graphene and gold nanoparticles”, Vol. 33, pp. 452–465.
46. Dutta P. K., Gallagher P. K. (1992), “Raman spectroscopic and thermoanalytical studies of the reaction of barium hydroxide with anatase and titanium oxide gels”, J. Chem. Mater., Vol. 4, pp. 847-851.
47. Ekaterina V. Rokhina, Repo E., Virkutyte J. (2010), “Comparative kinetic analysis of silent and ultrasound-assisted catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenol”, Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, Vol. 17, pp. 541–546
48. Eren Z. (2012), “Ultrasound as a basic and auxiliary process for dye remediation: A review”, Journal of Environmental Management, Vol. 104, pp. 127-141.
49. Falasca G. F. (2006), “Metabolic diseases: gout”, Clin. Dermatol., Vol. 24, pp. 498–508.
50. Farbod M., Zargar Shoushtari M., & Parhoodeh S. (2011), "Fabrication and characterization of Zn1−xAlxO nanoparticles by DC arc plasma", Physica B: Condensed Matter, Vol. 406(2), pp. 205-210.
51. Farrauto R. J., Bartholomew C. H. (1997), “Fundamentals of industrial catalytic processes”, Blackie Academic and Professional, pp. 151-153.
52. Fogg A. G. (1994), “Adsorptive stripping voltammetry or cathodic stripping voltammetry methods of accumulation and determination in stripping voltammetry”, Analytical Proceeding Including Analytical Communication, Vol. 31, pp. 313 – 317.
53. Frindell K. L., Bartl M. H., Robinson M. R., Bazan G. C., Popitsch A., & Stucky G. D. (2003), "Visible and near-IR luminescence via energy transfer in rare earth doped mesoporous titania thin films with nanocrystalline walls", Journal of Solid State Chemistry, Vol. 172(1), pp 81-88.
54. Fu Y. Q., Luo J. K., Du X. Y., Flewitt A. J., Li Y., Markx G. H., Walton A. J., Milne W. I. (2010), “Recent developments on ZnO films for acoustic wave based bio-sensing and microfluidic applications: a review”, Sens. Actuat. B: Chem., Vol. 143, pp. 606-619.
55. Galban J., Andreu Y., Almenara M. J., Marcos S., Castillo J. R. (2001), “Direct determination of uric acid in serum by a fluorometric-enzymatic method based on uricase”, Talanta, Vol. 54, pp. 847–854.
56. Gao S., Zhang H., Wang X., Deng R., Sun D., Zheng G. (2006), “ZnO-based hollow microspheres: biopolymer-assisted assemblies from ZnO nanorods”, J. Phys. Chem. B, Vol. 110, pp. 15847-15852.
57. Ge C., Xie C., Hu M., Gui Y., Bai Z., Zeng D. (2007), “Structural characteristics and UV-light enhanced gas sensitivity of La-doped ZnO nanoparticles”, Materials Science and Engineering B, Vol. 141, pp. 43–48.
58. Ge J. T., Qu J. H., (2003), “Degradation of azo dye acid red B on manganese dioxide in the absence and presence of ultrasonic irradiation”, Journal of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 100 (1e3), pp. 197-207.
59. Ge L., Huang Q. H., Zhang Y. F., Shen Z. (2000), “Ring-opening polymerization of styrene oxide with rare earth coordination catalysts", Eur. Polym. J. , Vol. 36(12), pp. 2699-2705
60. Geiger J. F., Beckmann P., Schierbaum K. D., Gopel W. (1991), “Interaction of Pd-overlayers with SnO2 : comperative comperative XPS, SIMS, and SNMS studies”, Fres. J. Anal. Chem., Vol. 341, pp. 25-30.
61. Gogate P. R, Aniruddha B. P. (2004), “A review of imperative technologies for wastewater treatment II: hybrid methods”, Advances in Environmental Research, Vol. 8, pp. 553–597
62. Grabowska I., Chudy M., Dybko A., Brzozka Z. (2008), “Uric acid determination in a miniaturized flow system with dual optical detection”,
Sens. Actuators B, Vol. 130, pp. 508–513.
63. Groot T. T., Sense of Contact 6 Keynote, Sensor Research at Energy Research Center Netherlands (ECN), March, 2004.
64. Gu B. X., . Xu C. X, Zhu G. P., Liu S. Q., Chen L. Y., Li X. S. (2009), “Tyrosinase Immobilization on ZnO Nanorods for Phenol Detection”, J. Phys. Chem. B, Vol. 113, pp. 377-381.
65. He M., Jiu H., Liu Y., Tian Y., Li D., Sun Y., Zhao G. (2013), “Controllable synthesis of ZnO microstructures with morphologies from rods to disks Materials”, Letters, Vol. 92, pp. 154–156.
66. Hu H., Deng C., Huang X. (2010), “Hydrothermal growth of center-hollow multigonal star-shaped ZnO architectures assembled by hexagonal conic nanotubes”, Mater. Chem. Phys., Vol. 121, pp. 364-369.
67. Hubert T., Boon-Brett L., Black G., Banach U., “Hydrogen sensors – A review”, Sensors and Actuators B, Vol. 157, pp. 329–352.
68. Ince N. H., Tezcanli G. (2011), “Reactive dyestuff degradation by combined sonolysis and ozonation”, Dyes and Pigments, Vol. 49 (3), pp. 145-153
69. Israr M. Q., Sadaf J. R., Asif M. H., Nur O., Willander M., Danielsson B. (2010), “Potentiometric cholesterol biosensor based on ZnO nanorods chemically grown on Ag wire”, Thin Solid Films, Vol. 519, pp. 1106-1109.
70. Ivanovskaya M., Kotsikau D., Faglia G., & Nelli P. (2003), "Influence of chemical composition and structural factors of Fe2O3/In2O3 sensor on their selectivity and sensitivity to ethanol", Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, Vol. 93(1), pp. 422-430.
71. Jia T., Wang W., Long F., Fu Z., Wang H., Zhang Q. (2009), “Fabrication, characterization and photocatalytic activity of La-doped ZnO Nanowires”, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, Vol. 484, pp. 410–415.
72. Jiang H., Hu J. Q. , Gu F. , Li C. Z. (2008), “Large-Scaled, Uniform, Monodispersed ZnO Colloidal Microspheres”, J. Phys Chem., Vol. 112, pp. 12138–12141
73. Karthigeyan A., Gupta R. P., Scharnagl K., Burgmair M., Sharma S. K., Eisele I. (2002), “A room temperature HSGFET ammonia sensor based on iridium oxide thin film”, Sens. Actuators B: Chemical, Vol. 85, pp. 145-153
74. Khatamian M., Khandar A. A., Divband B., Haghighi M., Ebrahimias S. (2012), “Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol in aqueous suspension by Ln (La3+, Nd3+ or Sm3+) doped ZnO nanoparticles”, Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, Vol. 1, pp. 120-127.
75. Kim C., Kim Y. J., Jang E. S., Yi G. C., Kim H. H. (2006), “Whispering- gallery-modelike-enhanced emission fromZnO nanodisk”, Appl. Phys. Lett., Vol. 88, pp. 093104-093104.
76. Kiomarsipour N., Razavi R. S. (2012), “Characterization and optical property of ZnO nano-submicro- and microrods synthesized by hydrothermal method on a large-scale, Superlattices and Microstructures, Vol. 52, pp. 704–710.
77. Kiomarsipour N., Razavi R. S. (2013), “Hydrothermal synthesisand optical property of scale-and spindle-like ZnO”, Ceramics International, Vol. 39, pp. 813–818 .
78. Kong J. Z., Li A. D., Zhai H. F., Gong Y. P., Li H., Wu D. (2009), “Preparation, characterization of the Ta-doped ZnO nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity under visible-light illumination”, J. Solid State Chem., Vol. 182, pp. 2061–2067.
79. Krishnamoorthy S., Iliadis A. A. (2008), “Properties of high sensitivity ZnO surface acoustic wave sensors on SiO2/(1 0 0) Si substrates”, Solid-State Electron., Vol. 52, pp. 1710-1716.
80. Kruusma J., Benham A. M., Williams J. G. & Kataky R. (2006), "An introduction to thiol redox proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and a review of current electrochemical methods of detection of thiols", Analyst, Vol. 131(4), pp. 459-473.
81. Kumar P. S., Paik P., Raj A. D., Mangalaraj D., Nataraj D., Gedanken A., Ramakrishna S. (2012), “Biodegradability study and pH influence on growth and orientation of ZnO nanorods via aqueous solution process”, Applied Surface Science, Vol. 258, pp. 6765– 6771.
82. Kumar S. A., Cheng H.W., Chen S.M., (2009) “Electroanalysis of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) using nano – ZnO/poly(luminol) hybrid film modified electrode”, Reactive and Functional Polymers, Vol. 69, pp. 364 – 370.
83. Lan W., Liu Y. P., Zhang M., Wang B., Yan H., Wang Y. Y. (2007), “Structural and optical properties of La-doped ZnO films prepared by magnetron sputtering”, Mater. Lett., Vol. 61, pp. 2262-2265.
84. Lee H. J. (2009) , “Gas sensors using hierarchical and hollow oxide nanostructures: Overview”, Sensors and Actuators B, Vol. 140, pp. 319–336.
85. Lei Y., Yan X., Zhao J., Liu X., Song Y., Luo N., Zhang Y. (2011), “Improved glucose electrochemical biosensor by appropriate immobilization of nano-ZnO”, Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfac., Vol. 82, pp. 168-172.
86. Li Y. F., Liu Z. M., Liu Y. L., Yang Y. H., Shen G. L., Yu R. Q. (2006), “A mediator-free phenol biosensor based on immobilizing tyrosinase to ZnO nanoparticles”, Anal. Biochem., Vol. 349, pp. 33-40.
87. Liao X., Zhang X. (2007), “Zinc Oxide Nanostructures and Their Core−Shell Luminescence Properties”, J. Phys Chem., Vol. 111, pp. 9081–9085.
88. Li-Jian B. , Xiao-Yan N., Yin J., Yue-Duan Q., Zhi-Yuan H. (2007), “Nanopillar ZnO gas sensor for hydrogen and ethanol” , Sensors and Actuators B, Vol. 126, pp. 604–608.
89. Lin J. J., Zhao X. S., Liu D., Yu Z. G., Zhang Y., Xu H. (2008), “The decoloration and mineralization of azo dye CI Acid Red 14 by sonochemical process: rate improvement via Fenton’s reactions”, Journal of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 157 (2-3), pp. 541 - 546.
90. Lippi G., Montagnana M., Franchini M., Favaloro E. J., Targher G. (2008), “The paradoxical relationship between serum uric acid and cardiovascular disease”, Clin. Chim. Acta, Vol. 392, pp.1–7.
91. Liu J. P., Huang X. T., Li Y. Y., Ji X. X., Li Z. K., He X., Sun F. L. (2007), “Vertically Aligned 1D ZnO Nanostructures on Bulk Alloy Substrates: Direct Solution Synthesis, Photoluminescence, and Field Emission”, J. Phys. Chem., Vol. 111, pp. 4990-4997
92. Liu Y. L., Yang Y. H.,Yang H. F., Liu Z -M., Shen G. L., Yu R. Q. (2005), “Nanosized flower-like ZnO synthesized by a simple hydrothermal method and applied as matrix for horseradish peroxidase immobilization for electro- biosensing”, J. Inorg. Biochem., Vol. 99, pp. 2046-2053.
93. Loudon R. (1964), “The Raman effect in crystals”, AdV. Phys., Vol. 13, pp. 423-482.
94. Lu L., Li R., Peng T., Fan K., Dai K. (2011), “Effects of rare earth ion modifications on the photoelectrochemical properties of ZnO-based dye- sensitized solar cells”, Renewable Energy, 36, pp. 3386 - 3393.
95. Lucovsky G., Phillips J. C. (2005), “Defects and defect relaxation at internal interfaces between high-k transition metal and rare earth dielectrics and interfacial native oxides in metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) structures”, Thin Solid Films, Vol. 486, pp. 200–204.
96. Lupan O., Chai G., Chow L. (2008), “Novel hydrogen gas sensor based on single ZnO nanorod”, Microelectronic Engineering, Vol. 85, pp. 2220–2225.
97. Ma Y., Wang W.L., Liao K.L., Kong Y. J. (2002), "Study on sensitivity of nano-grain ZnO gas sensor", Journal of Wide Bandgap Materials, Vol. 10, pp. 113–120.