98. Malagu C., Guidi., Stefancich M., Carotta M. C., Mertinelli G. (2002), “Model for Schottky barrier and surface states in nanostructured n-type semiconductors”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 91, pp. 808-814.
99. Malyshev V. V., & Pislyakov A. V. (2008), "Investigation of gas-sensitivity of sensor structures to hydrogen in a wide range of temperature, concentration and humidity of gas medium", Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, Vol. 134(2), pp. 913-921.
100. Mantzavinos D., Lauer E., Hellenbrand R., Livingston A. G., I. Metcalfe S. (1997), “Wet oxidation as a pretreatment method for wastewaters contaminated by bioresistant organics”, Water Sci. Technol., Vol. 36, pp. 109–116.
101. McQuarrie D. A. (1983), “Quantum chemistry, University Science Books”, Sausalito, California, pp. 436-437.
102. Mehrabian M., Azimirad R., Mirabbaszadeh K., Afarideh H., Davoudian M. (2011), “UV detecting properties of hydrothermal synthesized ZnO nanorods”, Phys. E: Low-dimension. Syst. Nanostruct., Vol. 43, pp. 1141-1145.
103. Merriman T. R., Dalbeth N. (2011), “The genetic basis of hyperuricaemia and gout”, Joint Bone Spine, Vol. 78, pp. 35–40.
104. Miller J. C., Miller J. N. (2010), Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, Ed. 6th, Pearson Education Limited, England.
105. Mishra V. S. (1995), “Wet air oxidation”, Ind Eng Chem Res, Vol. 34(1), pp. 2–48.
106. Mitra P., Maiti H. S. (2004), “A wet-chemical process to form palladium oxide sensitiser layer on thin film zinc oxide based LPG sensor”, Sens. Actuators B, Vol. 97, pp. 49–58.
107. Moss T. S. (1954), "The interpretation of the properties of indium antimonide",
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
 Ảnh Hưởng Của Biên Độ Xung (Δe) Đến Tín Hiệu Ip
Ảnh Hưởng Của Biên Độ Xung (Δe) Đến Tín Hiệu Ip -
 Hàm Lượng Ua Trong 3 Mẫu Nt2, Nt4 Và Nt5 Sau 3 Đo Lần Lặp Lại
Hàm Lượng Ua Trong 3 Mẫu Nt2, Nt4 Và Nt5 Sau 3 Đo Lần Lặp Lại -
 Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 22
Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 22 -
 Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 24
Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 24 -
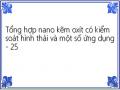
 Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 25
Tổng hợp nano kẽm oxít có kiểm soát hình thái và một số ứng dụng - 25
Xem toàn bộ 207 trang tài liệu này.
Proceedings of the Physical Society of London, Vol. 67, pp. 775–782
108. Mutschall D., Holzner K. (1996), “Obermeier E”., Sens. Actuators B, Vol. 36, pp. 320–324.

109. Nakagawa T., Kang D. H., Feig D., Sanchez-Lozada L. G., Srinivas T. R., Sautin Y., Ejaz A. A., Segal M., Johnson R. J. (2006), “Unearthing uric acid: An ancient factor with recently found significance in renal and cardiovascular disease”, Kidney Int., Vol. 69, pp. 1722–1725.
110. Ngoc Tien Huynh, Van Hoang Luan, Thuy Hoa Le, Tri Khoa Nguyen, Hahn
S. H., Chung J. S., Shin E. W., Hur S. H. (2013), “One-pot synthesis of a reduced graphene oxide–zinc oxide sphere composite and its use as a visible light photocatalyst”, Chemical Engineering Journal, Vol. 229, pp. 126–133.
111. Nia Y. H., Wei X. W., Ma X. & Hong J. M. (2005), "CTAB assisted one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of columnar hexagonal-shaped ZnO crystals", Journal of crystal growth, Vol. 283(1), pp. 48-56.
112. Novakova J. (1971), “Isotopic exchange of oxygen 18O between the gaseous phase and oxide catalysts”, Catal. Rev.-Sci. Eng., Vol. 4, pp. 77–113.
113. Nyhan W. L. (1997), “The recognition of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome as an inborn error of purine metabolism”, J. Inher. Metab. Dis., Vol. 20, pp. 171–178.
114. Ozgur U., Alivov Y. I., Liu C., Teke A., M. Reshchikov A., Dogan S., Avrutin V., Cho S. J., Morkoc H. (2005), “A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 98, pp. 041301-041301.
115. Pacholski C., Kornowski A., Weller H. (2002), “Self-Assembly of ZnO: From Nanodots to Nanorods”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Vol. 41, pp. 1188-1191.
116. Pal U., Serrano J. G., Santiago P., Xiong G., Ucer K. B., Williams R. T. (2006), “Synthesis and optical properties of ZnO nanostructures with different morphologies”, Opt. Mater., Vol. 29, pp. 65-69.
117. Park H. Y., Go H. Y., Kalme S., Mane R. S., Han S. H., Yoon M. Y. (2009), “Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications”, Anal. Chem., Vol. 81, pp. 4280-4284.
118. Patil D. R., Patil L. A. (2006), “Preparation and study of NH3 gas sensing behavior of Fe2O3 doped ZnO thick film resistors, Sens. Transducers, Vol. 70, pp. 661–670.
119. Peiró A. M., Ayllo´n J. A., Peral J., Dome`nech X., Domingo C. (2005), “Microwave activated chemical bath deposition (MW-CBD) of zinc oxide: Influence of bath composition and substrate characteristics”, J. Crystal Growth, Vol. 285, pp. 6-16.
120. Peng Y., Xu A. W., Deng B., Antonietti M., H. Coă lfen (2006), “Polymer- Controlled Crystallization of Zinc Oxide Hexagonal Nanorings and Disks”, J. Phys. Chem. B, Vol. 110, pp. 2988-2993.
121. Perello J., Sanchis P., Grases F. (2005), “Determination of uric acid in urine, saliva and calcium oxalate renal calculi by high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry”, J. Chromatogr, B 824, pp. 175–180.
122. Prabakar K., Kim H. (2010), “Growth control of ZnO nanorod density by sol–gel method”, Thin Solid Films, Vol. 518, pp.136–138.
123. Raj C. R., Ohsaka T. (2003), “Voltammetric detection of uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid at a gold electrode modified with a self-assembled monolayer of heteroaromatic thiol”, J. Electroanal. Chem., Vol. 540, pp. 69–77.
124. Rajalakshmi M., Arora A. K., B. Bendre S., Mahamuni S. (2000), “Optical phonon confinement in zinc oxide nanoparticles”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 87, pp. 2445-2448.
125. Raju A. R., & Rao C. N. R. (1991), "Gas-sensing characteristics of ZnO and copper-impregnated ZnO", Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, Vol. 3(4), pp. 305-310.
126. Rao B. B. (2000), “Zinc oxide ceramic semi-conductor gas sensor for ethanol vapour”, Materials Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 64, pp. 62–65.
127. Rao G. S. T., Rao D. T. (1999), “Gas sensitivity of ZnO based thick film sensor to NH3 at room temperature”, Sens. Actuators B, Vol. 55, pp. 166– 169.
128. Rautio J., Perọmọki P., Honkamo J., Jantunen H. (2009), “Effect of synthesis method variables on particle size in the preparation of homogeneous doped nano ZnO material”, Microchemical Journal, Vol. 91, pp. 272–276.
129. Ren X., Chen D., Meng X., Tang F., Hou X., Han D., Zhang L. (2009), “Zinc oxide nanoparticles/glucose oxidase photoelectrochemical system for the farbrication of biosensor”, Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, Vol. 334, pp. 183 – 187.
130. Robert R., Barbati S., Ricq N., Ambrosio M., “Intermediates in wet oxidation of cellulose: identification of hydroxyl radical and characterization of hydrogen peroxide”, Water Res., Vol. 36 (2002) 4821–4829.
131. Rocha D. L., Rocha F. R. P. (2010), “A flow-based procedure with solenoid micro-pumps for the spectrophotometric determination of uric acid in urine”, Microchem. J., Vol. 94, pp. 53–59.
132. Saito S., Miyayama M., Koumoto K. & Yanagida, H. (1985), "Gas sensing characteristics of porous ZnO and Pt/ZnO ceramics", Journal of the American Ceramic Society, Vol. 68(1), pp. 40-43.
133. Sauer M. L., Ollis D. F. (1996), “Photocatalyzed oxidation of ethanol and acetaldehyde in humidified air”, J. Catal., Vol. 158, pp. 570–582.
134. Sermon A. P., Bond G. C. (1974), “Hydrogen spillover”, Catal. Rev., Vol. 8, pp. 211-239.
135. Shimizu N., Ogin, C., Dadjour M. F., Murata T. (2007), “Sonocatalytic degradation of methylene blue with TiO2 pellets in water”, Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, Vol. 14 (2), pp. 184 - 190.
136. Slunecko J., Kosec M. (1998), “Morphology and Crystallization Behavior of Sol-Gel-Derived Titania”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., Vol. 81, pp. 1121-1133.
137. Sounart T. L., Liu J., Voigt J. A., Hsu J. W. P., Spoerke E. D., Tian Z. R., Jiang Y. (2006), “Sequential Nucleation and Growth of Complex Nanostructured Films”, Adv. Funct. Mater., Vol. 16, pp. 335-344.
138. Stoyanova A., Ivanov S., Tsakova V., Bund A. (2011), “Au nanoparticles – polyaniline nanocomposite layers obtained through layer – by – layer adsorption for the simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid”, Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 56, pp. 3693-3699.
139. Sun X. W., Wang J. X., Wei A. (2008), “Zinc oxide nanostructured biosensor for glucose detection”, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., Vol. 24, pp. 649-656.
140. Suwanboon S., Amornpitoksuk P. (2011), “Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline La-doped ZnO powders through a mechanical milling and their optical properties”, Ceramics International, Vol. 37, pp. 3515–3521.
141. Takita Y., Sano K., Muraya T., Nishiguchi H., Kawata N., Ito M., Akbay T., Ishihara T. (1998), “Oxidative dehydrogenation of iso-butane to iso-butene II. Rare earth phosphate catalysts”, Appl. Catal. A: Gen., Vol. 170, pp. 23–31.
142. Tang C.F., Kumar S.A., Chen S.M. (2008), “Zinc oxide/redox mediator composite films – based sensor for electrochemical detection of important biomolecules”, Analytical Biochemistry, Vol. 380, pp. 174 – 183.
143. Tang H., Yan M., Zhang H., Li S., Ma X., Wang M., Yang D. (2006), “A selective NH3 gas sensor based on Fe2O3–ZnO nanocomposites at room temperature”, Sensors and Actuators B, Vol. 114, pp. 910–915.
144. The International Institute of Ammonia Refrigeration, http://www.iiar.org
145. Tian Z. R., Voigt J. A., Liu J., Mckenzie B., Mcdermott M. J. (2002), “Biomimetic Arrays of Oriented Helical ZnO Nanorods and Columns”, J. Am. Chem. Soc., Vol. 124, pp. 12954-12955.
146. Timmer B. H., Thesis Ph. D., Twente U. (2004), “AMINA-chip : a miniaturized measurement system for ambient ammonia”, The Netherlands.
147. Vijayan B. K., Dimitrijevic N. M., Wu J., Gray A. (2010), “The effects of Pt doping on the structure and visible light photoactivity of titania nanotubes”, J. Phys. Chem. C, Vol. 114 pp. 21262–21269.
148. Wagh M. S., Jain G. H., Patil D. R., Patil S. A. , Patil L. A. (2006), “Modified zinc oxide thick film resistors as NH3 gas sensor”, Sens. Actuators, B 115, pp. 128–133.
149. Wang C. C., Akbar S. A., Madou M. J. (1998), "Ceramic based resistive sensors", J. Electroceram, Vol. 2, pp. 273–282.
150. Wang D., Yang J., Xing G., Yang L., Lang J., Gao M., Yao B., Tom W. (2009), “Abnormal blueshift of UV emission in single-crystalline ZnO nanowires”, Journal of Luminescence, Vol. 129, pp. 996–999.
151. Wang H., Li C., Zhao H., Li R., Liu J. (2013), “Synthesis, characterization, and electrical conductivity of ZnO with different morphologies”, Powder Technology, Vol. 239, pp. 266-271.
152. Wang J., Jiang. Y. F., Zhang Z. H., Zhang. X. D., Ma. T., Zhang. G., et al., (2007), “Investigation on the sonocatalytic degradation of acid red B in the presence of nanometer TiO2 catalysts and comparison of catalytic activities of anatase and rutile TiO2 powders”, Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, Vol. 14 (5), pp. 545 - 555
153. Wang J., Zhang W. D. (2011), “Sputtering deposition of gold nanoparticles onto vertically aligned carbon nanotubes for electroanalysis of uric acid”, J. Electroanal. Chem., Vol. 654, pp. 79–84.
154. Wang M., Hahn S. H., Kim J. S., Chung J. S., Kim E. J., Koo K.-K. (2008), “Solvent-controlled crystallization of zinc oxide nano(micro) disks”, Journal of Crystal Growth, Vol. 310, pp. 1213–1219.
155. Wang W., Li Z., Zheng W., Huang H., Wang C., Sun J. (2010), “Cr2O3- sensitized ZnO electrospun nanofibers based ethanol detectors”, Sensors and Actuators B, Vol. 143, pp. 754–758.
156. Wang W., Qiao X., Chen J., Tan F., Li H. (2009), "Influence of titanium doping on the structure and morphology of MgO prepared by copre method", Mater. Charact, Vol. 60, pp. 858–862.
157. Wang X., Wu M., Tang W., Zhu Y., Wang L., Wang Q., He P., Fang Y., (2013), “Simultaneous electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid using a palladium nanoparticle/graphene/chitosan modified electrode”, Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Vol. 695, pp. 10–16.
158. Wang Y. (2011), “The electrochemistry of uric acid at a gold electrode modified with L-cysteine, and its application to sensing uric urine”, Microchim. Acta., Vol. 172, pp. 419–424.
159. Wang Y., Wu X., Su Q., Lee Y., Zhou Z. (2001), “Ammonia-sensing characteristics of Pt and SiO2 doped SnO2”, Materials, Solid-State Electron., Vol. 45, pp. 347–350.
160. Wang Z. L. (2004), “Zinc oxide nanostructures: growth, properties and applications”, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, Vol. 16, R829.
161. Wei A., Sun X. W., Wang J. X., Lei Y., Cai X. P., Li C. M., Dong Z. L., Huang W. (2006), “Enzymatic glucose biosensor based on ZnO nanorod array grown by hydrothermal decomposition”, Appl. Phys. Lett., Vol. 89, pp. 123902-123902.
162. Williams D. E. (1999), "Semiconducting oxides as gas-sensitive resistors",
Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, Vol. 57(1), pp. 1-16.
163. Wongrat E., Pimpang P., Choopun S. (2009), “Comparative study of ethanol sensor based on gold nanoparticles: ZnO nanostructure and gold: ZnO nanostructure”, Applied Surface Science, Vol. 256, pp. 968–971.
164. Wu C., Liu X., Wei D., Fan J., Wang J. (2001), “Photosonochemical degradation of phenol in water”, Water Res., Vol. 35, pp. 3927–3933.
165. Wu F., Huang Y., Li Q. (2005), “Animal tissue-based chemiluminescence sensing of uric acid”, Anal. Chim. Acta, Vol. 536, pp. 107–113.
166. Xu J., Han J., Zhang Y., Sun Yu’an, Xie B. (2008), “Studies on alcohol sensing mechanism of ZnO based gas sensors”, Sensors and Actuators, B 132, pp. 334–339.
167. Yamazoe N., Kurokawa Y., Seiyama T. (1983), “Effects of additives on semiconductor gas sensors”, Sensors Actuat., Vol. 4, pp. 283-289.
168. Yang S., Qu L., Yang R., Li J., Yu L. (2010) “Modified glassy carbon electrode with Nafion/MWNTs as a sensitive voltammetric sensor for the determination of paeonol in pharmaceutical and biological samples”, Journal of Applied Electrochemistry , Vol. 40, pp. 231-243.
169. Yang Z., Huang Y., Chen G., Guo Z., Cheng S., Huang S. (2009), “Ethanol gas sensor based on Al-doped ZnO nanomaterial with many gas diffusing channels”, Sensors and Actuators B, Vol. 140, pp. 549–556.
170. Yang Z., Ye Z., Zhao B., Zong X., Wang P. (2010), “Synthesis of ZnO nanobundles via Sol–Gel route and application to glucose biosensor”, J. Sol- Gel Sci. Technol., Vol. 54, pp. 282-285.
171. Yang Z., Zong X., Ye Z., Zhao B., Wang Q., Wang P. (2010), “The application of complex multiple forklike ZnO nanostructures to rapid and ultrahigh sensitive hydrogen peroxide biosensors”, Biomaterials, Vol. 31, pp. 7534-7541.
172. Ye C. H., Bando Y., Shen G. Z., Golberg D. (2006), “Thickness-dependent photocatalytic performance of ZnO nanoplatelets”, J. Phys. Chem. B, Vol. 110, pp. 15146–15151.
173. Yu C. L., Yang K., Yu J., Peng P., Cao F., Li X., Zhou X. C. (2011), “Effects of Rare Earth Ce Doping on the Structure and Photocatalytic Performance of ZnO”, Acta. Phys. Chim. Sin., Vol. 27, pp. 505–512.
174. Zamiri R., Lemos A. F., Reblo A., Ahangar H. A., Ferreira J. M. F. (2013), “Effects of rare-earth (Er, La and Yb) doping on morphology and structure properties of ZnO nanostructures prepared by wet chemical method”, Ceramics International, Vol. 40, pp. 523-529.
175. Zhang H., Yang D., Li S., Ma X., Ji Y., Xu J., Que D. (2005), “Controllable growth of ZnO nanostructures by citric acid assisted hydrothermal process”, Mater. Lett., Vol. 59, pp. 1696-1700.
176. Zhang J., Sun L., Yin J., Su H., Liao C., Yan C. (2002), “Control of ZnO Morphology via a Simple Solution Route”, Chem. Mater., Vol. 14, pp. 4172-4177.
177. Zhang L., Zhao J., Zheng J., Li L., Zhu Z. (2011), “Shuttle-like ZnO nano/microrods: Facile synthesis, optical characterization and high formaldehyde sensing properties”, Applied Surface Science, Vol. 258, pp. 711– 718.
178. Zhang R., Liu S., Wang L., Yang G. (2013), “Electroanalysis of ascorbic acid using poly(bromocresol purple) film modified glassy carbon electrode”, Measurement, Vol. 46, pp. 1089 – 1093.