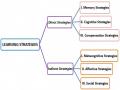
style, and aspects of personality). Thereby, the two versions of Oxford's Strategy Inventory for Language Learning (SILL) were taken in the two contexts: one for English speakers who learn a new language and another for the speakers of other languages learning English. They proposed that cognitive styles were about the conceptualization of the world while the personality traits were characterized by one’s learning environment, and LLS can be modified via training. However, most researchers have emphasized the essential role of language learning strategies. The study result showed that high proficient learners frequently used compensation strategies but low proficient learners used metacognitive strategies, followed by memory strategies and affective strategies. Surely, most of the overseas research now and then has been acknowledged all over the world and has brought big values to the educational foundation of human beings from the forward directions. Therefore, each study contributed to the most modern and effective teaching method of a language or a field of major, leading the similar or opposite ideas to be unavoidable. Starting from the earlier studies of the decade 1970s to now, it seems without changing the unique role of “Reading Comprehension” – a baseline of other patterns or elements. Besides the individual attitudes and motivation, the success in language learning (bilingual or trilingual) of a person has been always nurtured by that person’s comprehensive reading ability, LLS, and LLS instruction that later on being represented via the salient study in LLS from Oxford (1990), Oxford et al. and the others afterward. The researchers could recognize the importance of LLS through the learner’s reading strategies or ability in which one’s reading performance involved both mental and physical actions, as well as that one’s use of LLS.
Language reading comprehension is a first success of a child. Berg, Paige, & Lou (2012) identified the importance of fluent, expressive reading and
referred reading fluency as a successful element in learners’ literacy, especially for elementary school students. There were two components of fluency: the automaticity of word recognition and expressive oral reading that related to the secondary school students’ overall reading proficiency. He detected the relationship between “prosody and silent reading comprehension” in which the majority of secondary school students did not reach at. Like this, reading is a process for struggling readers: from initial reading (disfluent reading) to “deep” reading (by repeated reading), later forming language fluency and reading comprehension. Akkakoson (2013) investigated the relationship between L2- based strategic reading instruction and Thai students’ English reading achievement. There is a reciprocal relationship inside, if the reading strategies to students are instructed, the student’s L2 or English learning process becomes better. However, this FL reading context is researched in Thailand via the experimental approach employing a pre-test/ post-test design in their daily classrooms with diversified reading programs, and the students at low level of reading competence were provided reading strategy instruction. An English reading course took about 16 weeks under the two different approaches: one uses a teacher-centered method (control group) and another uses a portfolio (experimental group). As a result, the experimental group achieved effective reading strategy use better than the rest of Thai university students. From here, we can see the strength of learning strategies during the learner’s text reading outside the classroom. This showed that the more effective language reading strategies, the higher reading proficiency of students. However, Akkakoson retained two limitations in its implications needed discussing: the use of standardized tests for English reading comprehension measures, the use of portfolios for student’s reading investigation.
Anyways, how students perform their reading comprehension ability will describe how effective they use the strategies. According to Lai, Wilson, McNaughton & Hsiao (2014), the Literacy Project has an impact on reading comprehension and secondary school qualification. The quasi-experimental design was employed in the study of that literacy project (e.g. a design-based approach and classroom observations) which was implemented in seven schools with low secondary school qualification rates. On the basis of teacher and student surveys, the study stated that teachers themselves implement suitable reading tests to their students, in which before that the literacy intervention and literacy components through the reading strategies helped improve secondary school students’ achievement, despite the implemented selection being on the secondary schools with low qualification rates. Besides the Literacy Project, the study also insisted the value of the Learning Schools Model (LSM), the literacy skills may be attained by this support. Secondary school students used comprehension strategies for vocabulary acquisition. Instruction outside the classroom was a bit different from Primary school because whenever students wanted to read a basic material (from simple to complex texts), they just accessed an LSM available on the Internet. Generally, the intervention of literacy across secondary schools has a concurrent attainment in students’ reading contexts thanks to LSM. Therefore, teachers need to design instruction on LSM effectively, collect and analyze the database timely to easily make changes in reading teaching practice. Loh & Hu (2018) explained STELLAR® as a contraction of “Strategies for English Language Learning and Reading”, a national literacy program which was implemented by the Ministry of Education in Singapore (MOE) in 2010 across primary schools starting with Primary 1-students made premises for student’s secondary school eligibility. STELLAR® uses random sampling in about ten primary schools for 5 years, and there are two dimensions for the STELLAR®: The
designed program reflects materials and its teaching strategies, the implementation was supported properly and timely. Dimension 1 had the aim of intensifying student’s speaking ability and literacy skills, then promoting their positive learning attitude (STELLAR, 2008). The harmonious combination of reading and writing as an integrated skill in language learning brings the strengths in primary education. For example, they used strategies such as Shared reading (Holdaway, 1982); The language experience approach, sustained silent reading; Supported reading; K‐W‐L (Know-Want to know- Learned; Ogle, 1986). The used teaching strategies here are student‐centered in which have a mutual interaction between teacher and students during the teaching and learning time, otherwise aim to encourage students’ learning as well as to strengthen their oral ability (MOE, 2012). Dimension 2 was being started with the English curriculum of the nation and met its requirements, language teachers were given development chances, schools can be in charge of nominating two STELLAR® teacher mentors or STMs (e.g. for lower and upper primary levels). Finally, STELLAR® offered the three future directions for the educational implementation of students’ language skills after finishing a primary level of 6 schooling years through the national Primary School Leaving Examination (PSLE). These future directions include Critical Components, Principled Adaptation, and Empowering Internal Change Agents. Hereby, Vietnam may learn the same way to apply in elementary education as a preparation to secondary education. None better than teachers, who should know the program components, make changes for any material or curriculum, coach and mentor other teachers for teaching professional development. The ultimate goal is to stipulate student’s speaking and reading for the next upper level of curriculum.
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
 The use of language learning strategies in English reading at Doan Ket secondary school - An investigation - 3
The use of language learning strategies in English reading at Doan Ket secondary school - An investigation - 3 -
 Significance Of English Reading Strategy Use At Secondary Schools
Significance Of English Reading Strategy Use At Secondary Schools -
 Reading Strategy Instructions In Secondary Schools
Reading Strategy Instructions In Secondary Schools -
 The use of language learning strategies in English reading at Doan Ket secondary school - An investigation - 7
The use of language learning strategies in English reading at Doan Ket secondary school - An investigation - 7 -
 The use of language learning strategies in English reading at Doan Ket secondary school - An investigation - 8
The use of language learning strategies in English reading at Doan Ket secondary school - An investigation - 8 -
 The Research Objectives And Research Questions
The Research Objectives And Research Questions
Xem toàn bộ 140 trang tài liệu này.
Reading strategy use and the application of reading programs in secondary schools make language benefits in these students’ proficient achievement. Baye (2018) had synthesized a quantitative research which highlighted “the effectiveness of secondary school students’ reading programs, especially programs for struggling readers” in the USA and UK. To do this experimental research, the authors used random assignment (n = 62) or high-quality quasi- experiments (n = 7) to evaluate outcomes of measuring reading programs. To increase the positive outcomes, these reading programs were categorized into group tutoring (from small to large), cooperative learning, whole-school approaches (e.g. reforming teacher teams, and focusing on writing procedures). The individuals’ learning effort created more positive impacts (e.g. the social studies/science programs, structured strategies, and group/personalization rotation for readers’ exciting struggles). Reading programs with an extra resource and using technology somehow decides a student’s reading effect. Nevertheless, the benefits from those programs are just a bit more effective than the ones without resources, but secondary school student readers absorb mostly from social and cognitive engagements more than from the additional reading. In the U.S. educators concern students' reading performance in both middle and high schools. As a result, they have found organizations specializing in educational care. The National Center for Education Statistics (2016) itself reported that secondary school students’ reading performance was not high. It only took the proficient or above proficient rates for the eighth graders scored at National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) with 34% and for the 12th grade level with 37% in 2015. Therefore, the problem here is that a strong focus on reading strategies, via the multi-forms in different manifestations (e.g. the insertional technology with pictures/visuals, cooperative learning, other social engagements, etc.) to speed up students’ literacy proficiency and support

to other language skills or language areas, and Vietnam education may follow their successful strategies.
The LLS application in reading comprehension has been at different levels depending on the conditional areas or countries, but similar to a focus on cognitive and metacognitive awareness in language apprehension. According to Gunning & Oxford (2014), children’s LLS use and the effects of strategy instruction brought success on oral interaction tasks among the sixth graders. Despite the goal of detecting children’s oral interaction of competency development, the theories of metacognition value the strategy instruction to children and their language learning in any other skills. The research by Ter Beek, Brummer, Donker, Anouk, & Marie-Christine Opdenakker (2018) has provided learners with cognitive and metacognitive aspects through their comprehensive reading from computer environments. This research used a mix of quantitative and qualitative approaches to emphasize the digital interventions (modern method) and the importance of applying these mechanisms in teaching as well. Most studies concentrated on learning products or a combination of learning processes because only when being cognitive and metacognitive prefabrication with assistance from computers. All have brought a positive effect on comprehensive reading output and created learning motivation to students. There is a comparison between primary education and secondary education. It is signified that the most important thing to language learners is the regulatory learning skill for secondary education, in which their self-learning and autonomous learning started taking shape at this stage. While Parson (2015) before insisted that “teachers at primary level will be the ones who regulate, direct and guide the student’s learning” because mostly students at this age cannot be aware of their own learning. Therefore, the journal concluded that secondary school students are much more authority
than primary school students. Researcher Irena Kuzborska (2018) noted his research about Interactive Reading Strategies in which the outstanding factor was metacognitive awareness as every reader’s ultimate aim. Metacognitive awareness was defined as an involvement of cognitive knowledge and its regulation and through this, readers’ cognitive knowledge could help them meet the various situations in reading. Beyond that research, Oxford & Gkonou (2018) also identified “culture, language, and learning strategies drawn together to form a grand tapestry”. Consciously, learners with regulated thoughts can benefit from their strategy employment, developing their specific skills and general proficiency because whenever a learner is learning culture and language means including one’s learning strategies. A recent research by Wolsey (2020) assumed that “learners’ self‐assessment in reading helps establish the suitable learning criteria themselves or adapt to the established ones, then control over their learning better through metacognitive awareness (e.g. the particular skills, learning strategies, or used language, multiple learning tasks, etc.). As a natural force for the secondary education system and as an advanced trend in language learning, these secondary school students need directing and speeding up their learning cognition to become good strategic readers.
The previous international studies have strongly considered both lower and upper secondary education soon. Dubé, Bessette, Ouellet, Dufour, Paviel, Bruchesi, Cloutier & Landry (2019) showed that teaching practices have promoted the development of students’ reading skills in secondary schools. This research used both quantitative and qualitative approaches with the main purpose of assisting curriculum/ material designers, authoritative leaders, pedagogical advisors/ teachers in making decisions for the results of teaching practice adoption or adaptation. Literacy skills development has made changes
in secondary school students. Their study displayed the importance of the two skills Reading and Writing. Dubé et al. claimed that a person who are good at reading will intensify one’s writing styles and skill, and it synthesized the such four objectives in the study as: (1) Establishing core knowledge to students for the development of writing and reading texts; (2) Describing the teaching practice contexts related to education (for example, school types); (3) Analyzing the results or effects of literacy skills on students’ progress and success; (4) Identifying what practices need transferring and what conditions in the present context correspond to the respective education program. The three steps in a sequence of teaching writing strategies as before reading (self- questioning about text themes), during reading (analysis of text types/ structure), and after reading (summarizing) were mentioned to make reading skill become the decisive factor in a student's learning process (Fagella-Luby et al., 2007, also cited in this Chapter 5 of Dubé et al., 2019). Obviously, reading is the initial considerable element in training programs or special education, and particularly language classes in secondary schools. For this reason, the need of teaching reading comprehension courses in all subjects at secondary education is also increasing. All is synthesized to raise the metacognition in each student individually, and students can be aware of their thoughts in the learning process and easily comprehend the reading contents they have done. That research compared the reading outcomes between the middle grades (6-8) and the high school ones (9-12) to see that writing makes positive effects on language reading contrary to several good reading programs intensifying writing ability. Most programs of the middle grades have concentrated on practices from teachers in regular classrooms, but reading comprehension requires students to employ the multiple strategies flexibly. People attach special importance to the high school performance rather than the middle grades, then a course of both writing and reading is prepared for helping