[15] Ngô Tất Hoạt (2011). Nâng cao hiệu quả dạy học Xác suất - Thống kê ở trường Đại học sư phạm kĩ thuật theo hướng bồi dưỡng một số thành tố năng lực kiến tạo kiến thức cho sinh viên, Luận án tiến sĩ giáo dục học, Đại học Vinh.
[16] Võ Thị Huyền (2016). Dạy học Thống kê ở Trường Đại học Cảnh sát nhân dân theo hướng gắn với thực tiễn nghề nghiệp, Luận án tiến sĩ giáo dục học, Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội.
[17] Lê Thị Bạch Liên, Trần Kiêm Minh (2020). Đánh giá và nâng cao kiến thức toán để dạy học cho sinh viên ngành sư phạm toán trong các cơ sở đào tạo giáo viên ở Việt Nam. Tạp chí khoa học Trường Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội, 65(9), 14–21.
[18] Đào Hồng Nam (2014). Dạy học Xác suất - Thống kê ở Trường Đại học Y, Luận án tiến sĩ giáo dục học, Đại học Sư phạm Tp HCM.
[19] Đoàn Quỳnh (2010). Đại số 10 nâng cao, Nhà xuất bản Giáo dục.
[20] Đặng Hùng Thắng (2008). Thống kê và ứng dụng. Nhà xuất bản Giáo dục.
[21] Mai Đức Thắng (2006). Máy tính bỏ túi trong dạy học thống kê ở lớp 10, Luận văn thạc sĩ, Đại học Sư phạm Tp HCM.
[22] Trần Văn Thương (2019). Kiến thức của giáo viên để dạy học ứng dụng thực tế của đạo hàm, Luận văn thạc sĩ giáo dục học, Đại học Sư phạm – Đại học Huế.
[23] Dương Thiệu Tống (2000). Thống kê ứng dụng trong nghiên cứu khoa học giáo dục (thống kê mô tả), NXB Đại học quốc gia Hà Nội.
[24] Nguyễn Thanh Tùng (2016). Dạy học Xác suất - Thống kê theo hướng vận dụng vào nghiệp vụ Y tế cho sinh viên ngành Y - Dược, Luận án tiến sĩ giáo dục học, Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội.
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
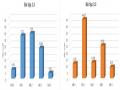
 Biểu Đồ Biểu Diễn Dữ Liệu Về Sck32 Của Gvttl Trong Thực Nghiệm 3 Kết Quả Của Bài Tập 2.3 Và 3.3 Thể Hiện Ở Hình 5.13 Cho Thấy Tỉ Lệ Các Gvttl
Biểu Đồ Biểu Diễn Dữ Liệu Về Sck32 Của Gvttl Trong Thực Nghiệm 3 Kết Quả Của Bài Tập 2.3 Và 3.3 Thể Hiện Ở Hình 5.13 Cho Thấy Tỉ Lệ Các Gvttl -
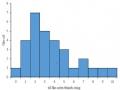
 Sự Tiến Triển Tiến Triển Kiến Thức Để Dạy Học Độ Phân Tán Của Dữ Liệu Trên Biểu Đồ Cột Và Biểu Đồ Histogram Của Gvttl Qua Nghiên Cứu
Sự Tiến Triển Tiến Triển Kiến Thức Để Dạy Học Độ Phân Tán Của Dữ Liệu Trên Biểu Đồ Cột Và Biểu Đồ Histogram Của Gvttl Qua Nghiên Cứu -
 Những Đề Xuất Về Đổi Mới Đào Tạo Nghiệp Vụ Cho Giáo Viên Toán Tương Lai Hiện Nay
Những Đề Xuất Về Đổi Mới Đào Tạo Nghiệp Vụ Cho Giáo Viên Toán Tương Lai Hiện Nay -
 Phát triển kiến thức và thực hành nghiệp vụ của giáo viên Toán tương lai để dạy học thống kê - 22
Phát triển kiến thức và thực hành nghiệp vụ của giáo viên Toán tương lai để dạy học thống kê - 22 -
 Phát triển kiến thức và thực hành nghiệp vụ của giáo viên Toán tương lai để dạy học thống kê - 23
Phát triển kiến thức và thực hành nghiệp vụ của giáo viên Toán tương lai để dạy học thống kê - 23 -
 Phát triển kiến thức và thực hành nghiệp vụ của giáo viên Toán tương lai để dạy học thống kê - 24
Phát triển kiến thức và thực hành nghiệp vụ của giáo viên Toán tương lai để dạy học thống kê - 24
Xem toàn bộ 277 trang tài liệu này.
[25] Hoa Ánh Tường (2014). Sử dụng nghiên cứu bài học để phát triển năng lực giao tiếp toán học cho học sinh trung học cơ sở, Luận án tiến sĩ khoa học giáo dục, trường Đại học Sư phạm thành phố Hồ Chí Minh.
[26] Trần Thị Hoàng Yến (2012). Dạy học theo dự án môn xác suất và thống kê ở trường đại học (chuyên ngành kinh tế - kĩ thuật), Luận án tiến sĩ giáo dục học, Viện Khoa học giáo dục Việt Nam.

Tài liệu tiếng Anh
[27] Arnold, P. (2008). Developing new statistical content knowledge with secondary school mathematics teachers. In Batanero, C., G. Burrill, C. Reading, and A. Rossman (Eds.), Joint ICMI/IASE Study: Teaching Statistics in School Mathematics. Challenges for Teaching and Teacher Education. Proceedings of the ICMI Study 18 and 2008 IASE Round Table Conference, ICMI and IASE, Monterrey.
[28] Baba, T. (2007). Japanese Education and Lesson Study: An Overview Section 1.1: “How is Lesson Study Implemented?”. In Isoda, M., Stephens, M., Ohara, Y. & Miyakawa, T. (Eds.): Japanese Lesson Study in Mathematics: Its Impact, Diversity and Potential for Educational Improvement. World Scientific Publishing Co, 2-7.
[29] Bakker, A., & Gravemeijer, K. P. (2004). Learning to reason about distribution. In The challenge of developing statistical literacy, reasoning and thinking, Springer, Dordrecht, 147-168.
[30] Bakogianni, D. (2015). Studying the process of transforming a statistical inquiry- based task in the context of a teacher study group. In CERME 9-Ninth Congress of the European Society for Research in Mathematics Education, 615-621.
[31] Ball, D. L., M. Thames., G. Phelps (2008). Content knowledge for teaching: What makes it special?. Journal of Teacher Education, 59(5), 389–407.
[32] Ball, D. L., & Cohen, D. K. (1996). Reform by the book: What is or might be the role of curriculum materials in teacher learning and instructional reform?. Educational Researcher, 25(9), 6–8.
[33] Batanero, C., Burrill, G., & Reading, C. (2011). Overview: challenges for teaching statistics in school mathematics and preparing mathematics teachers. Teaching statistics in school mathematics-challenges for teaching and teacher education: a joint ICMI/IASE study, 407-418.
[34] Batanero, C., & Díaz, C. (2010). Training teachers to teach statistics: what can we learn from research?. Statistique et enseignement, 1(1), 5-20.
[35] Baumert, J., Kunter, M., Blum, W., Brunner, M., Voss, T., Jordan, A., et al. (2010). Teachers’ mathematical knowledge, cognitive activation in the classroom, and student progress. American educational research journal, 47(1), 133-180.
[36] Ben‐Zvi, D., & Garfield, J. (2008). Introducing the emerging discipline of statistics education. School Science and Mathematics, 108(8), 355-361.
[37] Berry, A., Depaepe, F., & van Driel, J. (2016). Pedagogical content knowledge in teacher education. In International handbook of teacher education (pp. 347-386). Springer, Singapore.
[38] Blömeke, S., Felbrich, A., Müller, C., Kaiser, G., & Lehmann, R. (2008). Effectiveness of teacher education. ZDM-The International Journal on Mathematics Education, 40, 719-734.
[39] Borko, H., & Putnam, R. (1996). Learning to teach. In D. Berliner & R. Calfee (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology, New York: Macmillan, 673–708.
[40] Bromme, R. (1995). What exactly is pedagogical content knowledge? Critical remarks regarding a fruitful research program. In S. Hopmann, & K. Riquarts (Eds.) IPN Schriftenreihe: Vol. 147. Didaktik and/or curriculum (pp. 205-216). Kiel: IPN.
[41] Bruno, A., & Espinel, M. C. (2009). Construction and evaluation of histograms in teacher training. International journal of mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 40(4), 473-493.
[42] Burton, M., Daane, C. J., & Giessen, J. (2008). Infusing mathematics content into a methods course: impacting content knowledge for teaching. Issues in the Undergraduate Mathematics Preparation of School Teachers, 1, 1-12.
[43] Burgess, T. A. (2011). Teacher knowledge of and for statistical investigations. In Teaching statistics in school mathematics-challenges for teaching and teacher education, Springer, Dordrecht, 259-270.
[44] Casey, S. A. (2010). Subject matter knowledge for teaching statistical association. Statistics Education Research Journal, 9(2), 50–68.
[45] Chen, X. & Yang, F. (2013). Chinese teachers’ reconstruction of the curriculum reform through lesson study. International Journal for Lesson and Learning Studies, Vol. 2 No. 3, 218-236.
[46] Chokshi, S., & Fernandez, C. (2004). Challenges to improving Japanese lesson study: Concerns, misconceptions, and nuances. Phi Delta Kappan, 85(7), 520–525.
[47] Cobb, G. W., & Moore, D. S. (1997). Mathematics, statistics, and teaching. The American mathematical monthly, 104(9), 801-823.
[48] Cooper, L. L., & Shore, F. S. (2010). The effects of data and graph type on concepts and visualizations of variability. Journal of Statistics Education, 18(2), pp 1-16.
[49] Corcoran D., Pepperell S. (2011). Learning to teach mathematics using lessonstudy. In: Rowland T., Ruthven K. (eds) Mathematical Knowledge in Teaching.Mathematics Education Library, vol 50,pp. 213–230. Springer, Dordrecht.
[50] National Research Council. (2002). Studyingclassroom teachingas amedium for professional development: Proceedings of a U.S.–Japan Workshop. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
[51] Darling-Hammond, L., & Bransford, J. (with LePage, P., Hammerness, K., & Duffy, H.). (2005). Preparing teachers for a changing world: What teachers should learn and be able to do. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
[52] delMas, R., Garfield, J., Ooms, A., & Chance, B. (2007). Assessing students’ conceptual understanding after a first course in statistics. Statistics education research journal, 6(2), pp 28-58.
[53] delMas, R, Garfield, J., & Ooms, A. (2005). Using assessment items to study students’ difficulty reading and interpreting graphical representations of distributions. In Fourth Forum on Statistical Reasoning, Thinking, and Literacy (SRTL-4), pp 1-17.
[54] delmas, R., & Liu, Y. (2005). Exploring students’ conceptions of the standard deviation. Statistics Education Research Journal, 4(1), 55-82.
[55] delMas, R. C. (2004). A comparison of mathematical and statistical reasoning. In D. Ben-Zvi & J. Garfield (Eds.), The challenge of developing statistical literacy, reasoning, and thinking (pp. 79–95). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer
[56] Depaepe, F., Verschaffel, L., & Kelchtermans, G. (2013). Pedagogical content knowledge: A systematic review of the way in which the concept has pervaded mathematics educational research. Teaching and Teacher Education, 34(0), 12–25.
[57] Desrosières, A. (1998). The politics of large numbers: A history of statistical reasoning. Harvard University Press.
[58] Döhrmann, M., G. Kaiser, and S. Blömeke (2012). The conceptualisation of mathematics competencies in the international teacher education study TEDS-
M. ZDM - International Journal on Mathematics Education, 44(3), 325–340.
[59] Eichler, A., Zapata-Cardona, L. (2016). Empirical Research in StatisticsEducation. In: Empirical Research in Statistics Education. ICME-13 TopicalSurveys, Springer, Cham, 1-37.
[60] English, L. D. (2013). Reconceptualizing statistical learning in the early years. In Reconceptualizing early mathematics learning (pp. 67-82). Springer, Dordrecht.
[61] Escudero, I., & Sánchez, V. (2007). How do domains of knowledge integrate into mathematics teachers’ practice? The Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 26, 312-327.
[62] Espinel, C., Bruno, A., & Plasencia, I. (2008). Statistical graphs in the training of teachers. In C. Batanero; G. Burrill; R. Reading; A. Rossman. (2008). Proceedings of the Joint ICMI/IASE Study Teaching Statistics in School Mathematics. Challenges for Teaching and Teacher Education.
[63] Fauskanger, J. (2015). Challenges in measuring teachers’ knowledge.
Educational studies in Mathematics, 90(1), 57-73.
[64] Fennema, E., & Franke, M. L. (1992). Teachers' knowledge and its impact. In D. A. Grouws (Ed.), Handbook of research on mathematics teaching and learning: A project of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (p. 147–164). Macmillan Publishing Co, Inc.
[65] Fernandez, C. (2005). Lesson study: A means for elementary teachers to develop the knowledge of mathematics needed for reform-minded teaching? Mathematical thinking and learning, 7(4), 265–289.
[66] Fernandez, C., and M. Yoshida. (2004). Lesson study: A case of a Japanese approach to improving instruction through school-based teacher development. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
[67] Franklin, C., Kader, G., Mewborn, D. S., Moreno, J., Peck, R., Perry, M. & Scheaffer, R. (2005). A curriculum framework for K-12 statistics education. GAISE report. American Statistical Association.
[68] Franklin, C., Bargagliotto, A., Case, C., Kader, G., Scheaffer, R., & Spangler, D. (2015). The statistical education of teachers. Alexandria, VA: American Statistical Association. Retrieved January 27, 2020, from http://www.amstat.org/education/SET/SET.pdf.
[69] Friedrichsen, P., Driel, J. H. V., & Abell, S. K. (2011). Taking a closer look at science teaching orientations. Science Education, 95(2), 358-376.
[70] Fujii, T. (2014). Implementing Japanese Lesson study in foreign countries: Misconceptions revealed. Mathematics Teacher Education and development, 16(1), 65–83.
[71] Garfield, J., & Ben-Zvi, D. (2009). Helping students develop statistical reasoning: Implementing a Statistical Reasoning Learning Environment. Teaching Statistics, 31(3), 72–77.
[72] Gfeller, M. K., Niess, M. L., & Lederman, N. G. (1999). Preservice teachers’ use of multiple representations in solving arithmetic mean problems. School Science and Mathematics, 99(5), 250-257.
[73] Godino, J. D., Font, V., Wilhelmi, M. R., & Lurduy, O. (2011). Why is the learning of elementary arithmetic concepts difficult? Educational Studies in Mathematics, 77(2), 247–265.
[74] González, O. (2014). Secondary mathematics teachers' professional competencies for effective teaching of variability-related ideas: A Japanese case study. Statistique et Enseignement, 5(1), 31-51.
[75] Graeber, A., & Tirosh, D. (2008). Pedagogical content knowledge: Useful concept or elusive notion. In International Handbook of Mathematics Teacher Education: Volume 1 (pp. 115-132). Brill Sense.
[76] Grossman, P. L. (1990). The making of a teacher. Teacher knowledge and teacher education. New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
[77] Groth, R. E. (2007). Toward a conceptualization of statistical knowledge for teaching. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 38(5), pp. 427–437.
[78] Groth, R. E. (2013). Characterizing key developmental understandings and pedagogically powerful ideas within a statistical knowledge for teaching framework. Mathematical Thinking and Learning, 15(2), 121-145.
[79] Randall E. Groth & Jennifer A. Bergner (2006). Preservice Elementary Teachers' Conceptual and Procedural Knowledge of Mean, Median, and Mode, Mathematical Thinking and Learning, 8:1, 37-63.
[80] Groth, R. E., & Xu, S. (2011). Preparing teachers through case analyses. In
C. Batanero, G. Burrill, and C. Reading (eds.), Teaching statistics in school mathematics. Challenges for teaching and teacher education: A Joint ICMI/IASE Study (pp. 371-382). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer.
[81] Hashweh, M. Z. (2005). Teacher pedagogical constructions: A reconfiguration of pedagogical content knowledge. Teachers and Teaching: Theory and Practice, 11(3), 273–292.
[82] Hill, H. C., Sleep, L., Lewis, J. M., & Ball, D. L. (2007). Assessing teachers’ mathematical knowledge. Second handbook of research on mathematics teaching and learning: A project of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics, 112-155.
[83] Hill, H. C., Blunk, M. L., Charalambous, C. Y., Lewis, J. M., Phelps, G. C., Sleep, L., & Ball, D. L. (2008). Mathematical knowledge for teaching and the mathematical quality of instruction: An exploratory study. Cognition and instruction, 26(4), 430-511.
[84] Heather C. Hill, D. L. Ball, S. G. Schilling (2008), Unpacking Pedagogical Content knowledge: Conceptualizing and measuring Teachers’ Topic- Specific Knowledge of Students. Journal for Reseach in Mathematics Education, 39(4), 372-400.
[85] Hill, H. C., Ball, D. L., & Schilling, S. G. (2004). Developing measures of teachers' mathematics knowledge for teaching. Elementary School Journal, 105(1), 11-30.
[86] Hodgen, J. (2011). Knowing and identity: a situated theory of mathematics knowledge in teaching. In T. Rowland, & K. Ruthven (Eds.), Mathematical knowledge in teaching (pp. 27-42). Dordrecht: Springer.
[87] Huang, R., (2014). Prospective Mathematics Teachers’ Knowledge of Algebra–A Comparative Study in China and the United States of America. Springer.
[88] Huang, R., & Shimizu, Y. (2016). Improving teaching, developing teachers and teacher educators, and linking theory and practice through lesson study in mathematics: an international perspective. ZDM, 48(4), 393-409.
[89] Jacobbe, T. (2008). Elementary school teachers’ understanding of the meanand median,International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 10(5), pp. 1143–1161.
[90] Jacobbe, T., & Horton, R. M. (2010). Elementary school teachers’ comprehension of data displays. Statistics Education Research Journal, 9(1), 27-45.
[91] Jacobbe, T., & Carvalho, C. (2011). Teachers’ understanding of averages. In Teaching statistics in school mathematics-Challenges for teaching and teacher education (pp. 199-209). Springer, Dordrecht.
[92] Jakobsen, A., Thames, M. H. and Ribeiro, C. M. (2013). Delineating issues related to horizon content knowledge for mathematics teaching, Eight Congress of European Research in Mathematics Education (CERME-8), (2009), pp. 3125–3134.
[93] Kaiser, G., Blomeke, S., Konig, J., Busse, A., Dohrmann, M., Hoth, J. (2016). Professional competencies of (prospective) mathematics teachers - cognitive versus situated approaches. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 0(15), pp. 83–99.
[94] Kaplan, J. J., Gabrosek, J. G., Curtiss, P., & Malone, C. (2014). Investigating student understanding of histograms. Journal of Statistics Education, 22(2), 1-30.
[95] Kieran, C., Krainer, K., & Shaughnessy, J. M. (2012). Linking research to practice: Teachers as key stakeholders in mathematics education research. In Third international handbook of mathematics education (pp. 361-392). Springer, New York, NY.
[96] Koleza, E., & Kontogianni, A. (2013). Assesing statistical literacy: What do freshmen know? In B. Ubuz, C. Haser, & M. A. Mariotti (Eds.), Proceedings of the Eighth Congress of the European Society for Research in Mathematics Education (pp. 840–849). Antalya, Turkey: Middle East Technical University and ERME.
[97] Langrall, C. W. et al. (2017). Teaching and learning probability and statistics: An integrated perspective. Compendium for Research in Mathematics Education. Reston: National Council of Teachers of Mathematics, pp. 490–525.
[98] Leavy, A. M. (2006). Using data comparison to support a focus on distribution: Examining preservice teacher’s understandings of distribution when engaged in statistical inquiry. Statistics Education Research Journal, 5(2), 89-114.
[99] Leavy A & Hourigan M. (2018). Using lesson study to support the teaching of early number concepts: Examining the development of prospective teachers’ specialized content knowledge. Early Childhood Education Journal, 46(1), 47–60.
[100] Leavy, A. M., & Hourigan, M. (2016). Using lesson study to support knowledge development in initial teacher education: Insights from early number classrooms. Teaching and Teacher Education, 57, 161-175.
[101] Leavy, A. M. & O’Loughlin, N. (2006). Moving beyond the arithmetic average: Preservice teachers understanding of the mean. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 9(1), 53-90.
[102] Lewis, C., Perry, R., Hurd, J., & O'Connell, M. P. (2006). Lesson study comes of age in North America. Phi delta kappan, 88(4), 273-281.
[103] Lewis, C. (2009). What is the nature of knowledge development in lesson study?. Educational Action Research, 17(1), 95-110.
[104] Lewis, C., Perry, R., & Hurd, J. (2009). Improving mathematics instruction through lesson study: A theoretical model and North American case. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 12(4), 285–304.
[105] Lewis, C., & Tsuchida, I. (1998). A lesson is like a swiftly flowing river: How research lessons improve Japanese education. American Educator, 22(4), 48-56.
[106] Lewis, C., & Perry, R. (2017). Lesson study to scale up research-based knowledge: A randomized, controlled trial of fractions learning. Journal for research in mathematics education, 48(3), 261-299.