[36] Kurisinkel J. L., Zhang Y., and Varma V. (2017). Abstractive multi-document summarization by partial tree extraction, recombination and linearization. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Vol. 1: Long Papers), pp. 812-821. Asian Federation of Natural Language Processing.
[37] Genest P. E., and Lapalme G. (2012). Fully abstractive approach to guided summarization. In Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Vol. 2: Short Papers), pp. 354-358. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[38] Khan A., Salim N., and Jaya Kumar Y. (2015). A framework for multi- document abstractive summarization based on semantic role labelling. Applied Soft Computing, Vol. 30, pp. 737–747. DOI: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.01.070.
[39] Hou L., Hu P., and Bei C. (2018). Abstractive document summarization via neural model with joint attention. In Proceedings of the Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing. Dalian, China. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319- 73618-1_28.
[40] Cai T., Shen M., Peng H., Jiang L. and Dai Q. (2019). Improving transformer with sequential context representations for abstractive text summarization. In Proceedings of the Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 11838, pp. 512-524. Springer, Cham. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-32233-5_40.
[41] Chopra S., Auli M., and Rush M. (2016). Abstractive sentence summarization with attentive recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pp. 93-98. Association for Computational Linguistics. DOI: 10.18653/v1/N16-1012.
[42] Jiang X. J., Mao X. L., Feng B. S., Wei X., Bian B. B., and Huang H. (2019). HSDS: An Abstractive Model for Automatic Survey Generation. Database Systems for Advanced Applications. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 11446. Springer, Cham. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-18576-3_5.
[43] See A., Liu P. J., and Manning C. D (2017). Get to the point: Summarization with pointer generator networks. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Vol. 1: Long Papers), pp. 1073–1083.
[44] Clarke J. and Lapata M. (2006). Models for sentence compression: A comparison across domains, training requirements and evaluation measures. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Computational Linguistics and 44th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 377–384.
[45] Clarke J. and Lapata M. (2008). Global inference for sentence compression: An integer linear programming approach. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, Vol. 31, pp. 399-429.
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
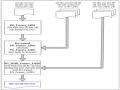
 Các Giai Đoạn Huấn Luyện Mô Hình Tóm Tắt Đa Văn Bản Hướng Tóm Lược Đề Xuất Pg_Feature_Amds
Các Giai Đoạn Huấn Luyện Mô Hình Tóm Tắt Đa Văn Bản Hướng Tóm Lược Đề Xuất Pg_Feature_Amds -
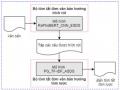
 Mô Hình Tóm Tắt Đơn Văn Bản Hỗn Hợp Ext_Abs_Asds
Mô Hình Tóm Tắt Đơn Văn Bản Hỗn Hợp Ext_Abs_Asds -
 Nghiên cứu, phát triển một số phương pháp tóm tắt văn bản sử dụng kỹ thuật học sâu - 19
Nghiên cứu, phát triển một số phương pháp tóm tắt văn bản sử dụng kỹ thuật học sâu - 19 -
 Nghiên cứu, phát triển một số phương pháp tóm tắt văn bản sử dụng kỹ thuật học sâu - 21
Nghiên cứu, phát triển một số phương pháp tóm tắt văn bản sử dụng kỹ thuật học sâu - 21 -
 Nghiên cứu, phát triển một số phương pháp tóm tắt văn bản sử dụng kỹ thuật học sâu - 22
Nghiên cứu, phát triển một số phương pháp tóm tắt văn bản sử dụng kỹ thuật học sâu - 22 -
 Nghiên cứu, phát triển một số phương pháp tóm tắt văn bản sử dụng kỹ thuật học sâu - 23
Nghiên cứu, phát triển một số phương pháp tóm tắt văn bản sử dụng kỹ thuật học sâu - 23
Xem toàn bộ 185 trang tài liệu này.
[46] Nguyen M.L. and Horiguchi S. (2003). A Sentence Reduction Using Syntax Control. In Proceedings of the 6th Information Retrieval with Asian Language, pp. 139-146.
[47] Nguyen M.L. and Horiguchi S. (2004). Example-Based Sentence Reduction Using the Hidden Markov Model. ACM Transactions on Asian Language Information Processing, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp. 146-158.

[48] Turner J. and Charniak E (2005). Supervised and unsupervised learning for sentence compression. In Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 290–297.
[49] Nguyễn Nhật An (2015). Nghiên cứu, phát triển các kỹ thuật tự động tóm tắt văn bản tiếng Việt. Luận án Tiến sỹ, Viện khoa học và Công nghệ quân sự.
[50] Lê Thanh Hương (2014). Nghiên cứu một số phương pháp tóm tắt văn bản tự động trên máy tính áp dụng cho tiếng Việt. Báo cáo tổng kết đề tài Khoa học và công nghệ cấp bộ, Đại học Bách khoa Hà Nội.
[51] Nguyễn Thị Thu Hà (2012). Phát triển một số thuật toán tóm tắt văn bản Tiếng Việt sử dụng phương pháp học bán giám sát. Luận án Tiến sỹ, Học viện Kỹ thuật quân sự.
[52] Nguyễn Trọng Phúc, Lê Thanh Hương (2008). Tóm tắt văn bản tiếng Việt sử dụng cấu trúc diễn ngôn. Hội thảo ICT.rda 2008.
[53] Trương Quốc Định, Nguyễn Quang Dũng (2012). Một giải pháp tóm tắt văn bản tiếng Việt tự động. Hội thảo quốc gia lần thứ XV: Một số vấn đề chọn lọc của Công nghệ thông tin và truyền thông- Hà Nội.
[54] Nguyen Quang Uy, Pham Tuan Anh, Truong Cong Doan, and Nguyen Xuan Hoai (2012). A Study on the Use of Genetic Programming for Automatic Text Summarization. In Proceedings of the 2012 Fourth International Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering (KSE), pp. 93-98.
[55] Thanh Le Ha, Quyet Thang Huynh, and Chi Mai Luong (2005). A Primary Study on Summarization of Documents in Vietnamese. In Proceedings of the First International Congress of the International Federation for Systems Research, Kobe, Japan, pp. 234-239. JAIST Press.
[56] M. L. Nguyen, Shimazu Akira, Xuan Hieu Phan, Tu Bao Ho, Horiguchi, and Susumu (2005). Sentence Extraction with Support Vector Machine Ensemble. In Proceedings of the First World Congress of the International Federation for Systems Research: The New Roles of Systems Sciences For a Knowledge- based Society. JAIST Press.
[57] Lâm Quang Tường, Phạm Thế Phi và Đỗ Đức Hào (2017). Tóm tắt văn bản tiếng Việt tự động với mô hình sequence-to-sequence. Tạp chí khoa học Trường Đại học Cần Thơ. Số chuyên đề: Công nghệ thông tin, trang 125-132.
[58] Ha N.T.T and Quynh N.H (2010). A novel important word based sentence reduction method for Vietnamese text. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd International Conference on Intellectual Technology in Industrial Practice, Vol. 2, pp. 401-406.
[59] Ha N.T.T, Quynh N.H, and Tao N.Q (2010). A Semi - Supervised Learning Approach for Generating Vietnamese Sentence Redution. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer and Software Modeling, pp. 127- 131.
[60] Makoto Hirohata, Yousuke Shinnaka, Koji Iwano, and Sadaoki Furui (2005). Sentence extraction – based presentation summarization techniques and evaluation metrics. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '05), pp. 1065-1068. DOI: 10.1109/ICASSP.2005.1415301.
[61] Daniel Jurafsky and James H. Martin (2008). Speech and Language Processing: An introduction to natural language processing, computational linguistics, and speech recognition. Chap. 6, Chap. 17, Chap. 22, Chap. 23. Prentice Hall.
[62] Edmundson H. P. (1969). New methods in automatic extracting. Journal of the ACM 16, pp. 264-285.
[63] Ronald Brandow, Karl Mitze, and Lisa F. Rau (1995). Automatic condensation of electronic publications by sentence selection. Information Processing and Management: an International Journal, Special issue: summarizing text, Vol. 31, pp. 675-685. DOI: 10.1016/0306-4573(95)00052-I.
[64] Salton G. and Buckley C. (1997). Term-weighting approaches in automatic text retrieval. Information Processing and Management: an International Journal, Vol. 24, No. 5, pp. 513-523. DOI: 10.1016/0306-4573(88)90021-0.
[65] Mohamed Abdel Fattah and Fuji Ren (2008). Automatic Text Summarization. In Proceedings of World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, Vol. 27, pp. 192-195.
[66] Salton G. (1989). Automatic Text Processing. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company.
[67] Dragomir R. Radev et al (2003). Evaluation Challenges in Large-scale Document Summarization. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 375-382. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[68] Lin C.Y. (2004). ROUGE: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In Text Summarization Branches Out, pp. 74-81. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[69] Ting K. M. (2011). Precision and Recall. In: Sammut C., Webb G.I. (eds) Encyclopedia of Machine Learning. Springer, Boston, MA. DOI: 10.1007/978-0-387-30164-8_652.
[70] Goutte C. and Gaussier E. (2005). A Probabilistic Interpretation of Precision, Recall and F-Score, with Implication for Evaluation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Information Retrieval. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol 3408, pp. 345–359. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540- 31865-1_25.
[71] Karl Moritz Hermann, Tomas Kocisky, Edward Grefenstette, Lasse Espeholt, Will Kay, Mustafa Suleyman, and Phil Blunsom (2015). Teaching machines to
read and comprehend. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vol. 1, pp. 1693–1701.
[72] https://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/duc/guidelines/2001.html.
[73] https://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/duc/guidelines/2002.html.
[74] Paul Over and James Yen (2004). An introduction to DUC-2004. National Institute of Standards and Technology.
[75] DUC 2007: Task, Documents, and Measures. url: https://duc.nist.gov/duc2007/tasks.html.
[76] Trần Mai Vũ (2012). Thiết kế và cài đặt chương trình tóm tắt đa văn bản tiếng Việt. Đề tài cấp Bộ Giáo dục và Đào tạo (Mã số: B2012-01-24).
[77] Nhi-Thao Tran, Minh-Quoc Nghiem, Nhung T. H. Nguyen, N. Nguyen, Nam Van Chi, Dinh Dien (2020). ViMs: a high-quality Vietnamese dataset for abstractive multi-document summarization. Language Resources and Evaluation, pp. 893–920.
[78] Christian M. Meyer, Darina Benikova, Margot Mieskes, and Iryna Gurevych (2016). MDSWriter: Annotation Tool for Creating High-Quality Multi- Document Summarization Corpora. In Proceedings of ACL-2016 System Demonstrations, pp. 97-102. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[79] Shalin Savalia and Vahid Emamian (2018). Cardiac Arrhythmia Classification by Multi-Layer Perceptron and Convolution Neural Networks, Bioengineering 2018, 5(2), 35 (Special Issue Advanced Biomaterials for Cardiovascular Tissue Engineering Applications). DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering5020035.
[80] Werbos P.J. (1990). Backpropagation Through Time: What It Does and How to Do It. In Proceedings of the IEEE, Vol. 78, No. 10, pp. 1550-1560. DOI:10.1109/5.58337.
[81] Patrice Y. Simard, Dave Steinkraus, and John C. Platt (2003). Best Practices for Convolutional Neural Networks Applied to Visual Document Analysis. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR), Scotland, UK. DOI: 10.1109/ICDAR.2003.1227801.
[82] Samer C. H., Rishi K., and Rowen (2015). Image Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Cadence White paper, 1–12.
[83] Nguyễn Đắc Thành (2017). Nhận dạng và phân loại hoa quả trong ảnh màu. Luận văn thạc sĩ Kỹ thuật phần mềm. Trường Đại học Công nghệ - Đại học Quốc Gia Hà Nội.
[84] Niitsoo A., Edelhauber T., and Mutschler C (2018). Convolutional Neural Networks for Position Estimation in TDoA-Based Locating Systems. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Nantes, France, pp. 1-8.
[85] Kim Y. (2014). Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 1746–1751. Association for Computational Linguistics. DOI:10.3115/v1/D14-1181.
[86] Collobert R., Weston J., Bottou L., Karlen M., Kavukcuglu K., and Kuksa P. (2011). Natural Language Processing (Almost) from Scratch. Journal of Machine Learning Research, Vol. 12, pp. 2493–2537.
[87] Hochreiter S. and Schmidhuber J. (1997). Long short-term memory. Neural computation, Vol. 9, No. 8, pp. 1735-1780. DOI: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735.
[88] Mike Schuster and Kuldip K. Paliwal (1997). Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Networks, Vol. 45, No. 11, pp. 2673–2681. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing. DOI: 10.1109/78.650093.
[89] Kyunghyun Cho, Bart van Merrienboer, Caglar Gulcehre, Dzmitry Bahdanau, Fethi Bougares, Holger Schwenk, and Yoshua Bengio (2014). Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Doha, Qatar, pp. 1724-1734.
[90] Junyoung Chung, Kyung Hyun Cho, and Yoshua Bengio (2014). Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.3555.
[91] Alex Graves, Abdel-rahman Mohamed, and Geoffrey Hinton (2013). Speech Recognition with Deep Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, pp. 6645-6649.
[92] Ilya Sutskever, Oriol Vinyals, and Quoc V. Le (2014). Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS'14), Vol. 2, pp. 3104–3112.
[93] Dzmitry Bahdanau, Kyunghyun Cho, and Yoshua Bengio (2015). Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2015), San Diego, CA, USA.
[94] Graves A., Wayne G., and Danihelka I. (2014). Neural turing machines. CoRR, abs/1410.5401.
[95] Thang Luong, Hieu Pham, and Christopher D. Manning (2015). Effective Approaches to Attention-based Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 1412–1421. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[96] Kelvin Xu, Jimmy Ba, Ryan Kiros, Kyunghyun Cho, Aaron Courville, Ruslan Salakhudinov, Rich Zemel, and Yoshua Bengio (2015). Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR 37, pp. 2048–2057.
[97] Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N Gomez, Łukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin (2017). Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 6000–6010.
[98] Phạm Minh Nguyên (2020). Nghiên cứu dịch máy Trung - Việt dựa vào mô hình Transformer. Luận văn Thạc sỹ Hệ thống thông tin, Trường Đại học Công nghệ - Đại học Quốc gia Hà Nội.
[99] Mikolov T., Chen K., Corrado G., and Dean J. (2013). Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2013), pp. 1-12.
[100] Chung H., Lee S., and Park J. (2016). Deep neural network using trainable activation functions. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 348-352.
[101] Xin Rong (2014). word2vec Parameter Learning Explained. CoRR abs/1411.2738.
[102] Devlin J., Chang M.W., Lee K., and Toutanova K. (2019). Bert: Pre- training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, pp. 4171–4186.
[103] Yukun Zhu, Ryan Kiros, Richard Zemel, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Raquel Urtasun, Antonio Torralba, and Sanja Fidler (2015). Aligning books and movies: Towards story-like visual explanations by watching movies and reading books. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Vol. 1, pp. 19-27. DOI: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.11.
[104] Yonghui Wu, Mike Schuster, Zhifeng Chen, Quoc V. Le, Mohammad Norouzi, Wolfgang Macherey, Maxim Krikun, Yuan Cao, and Qin Gao (2016). Google’s neural machine translation system: Bridging the gap between human and machine translation. Technical Report.
[105] Telmo Pires, Eva Schlinger, and Dan Garrette. How multilingual is Multilingual BERT?. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 4996–5001. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[106] Yinhan Liu, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, and Veselin Stoyanov (2019). RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. In Proceedings of the 20th Chinese National Conference on Computational Linguistics, pp. 1218-1227.
[107] Trieu H. Trinh and Quoc V. Le (2018). A simple method for commonsense reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.02847.
[108] Rico Sennrich, Barry Haddow, and Alexandra Birch (2016). Neural machine translation of rare words with subword units. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Vol. 1: Long Papers), pp. 1715-1725. Association for Computational Linguistics. DOI: 10.18653/v1/P16-1162.
[109] Kingma D. and Ba J. (2015). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2015), Conference Track Proceedings, San Diego, CA, USA.
[110] Dat Quoc Nguyen and Anh Tuan Nguyen (2020). PhoBERT: Pre-trained language models for Vietnamese. In Proceedings of Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020. DOI: 10.18653/v1/2020.findings-emnlp.92.
[111] Iulia Turc, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee, and Kristina Toutanova (2019). Well-Read Students Learn Better: On the Importance of Pre-training Compact Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.08962.
[112] Cristian Bucila, Rich Caruana, and Alexandru Niculescu-Mizil (2006). Model compression. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pp. 535–541. DOI: 10.1145/1150402.1150464.
[113] Geoffrey E. Hinton, Oriol Vinyals, and Jeffrey Dean (2014). Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. NIPS Workshop 2014, Montreal, Canada.
[114] Mnih V., Kavukcuoglu K., Silver D., Graves A., Antonoglou I., Wierstra D., and Miller M. R. (2013). Playing Atari with Deep Reinforcement Learning. NIPS Deep Learning Workshop 2013.
[115] Alexander M. Rush, Sumit Chopra, and Jason Weston (2015). A Neural Attention Model for Abstractive Sentence Summarization. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 379-389.
[116] Jaime Carbonell and Jade Goldstein (1998). The Use of MMR, Diversity- Based Reranking for Reordering Documents and Producing Summaries. In Proceedings of the 21st annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval, pp. 335-336.
[117] Ming Zhong, Pengfei Liu, Yiran Chen, Danqing Wang, Xipeng Qiu, and Xuanjing Huang (2020). Extractive Summarization as Text Matching. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 6197–6208. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[118] Liu Y. (2019). Fine-tune BERT for Extractive Summarization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1903.10318.
[119] Xingxing Zhang, Furu Wei, and Ming Zhou (2019). HIBERT: Document Level Pre-training of Hierarchical Bidirectional Transformers for Document Summarization. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 5059–5069.
[120] Tom M. Mitchell (1997). Machine Learning, McGraw-Hill.
[121] Vũ Hữu Tiệp (2020). Machine Learning cơ bản (cập nhật lần cuối: 20/01/2020).
[122] Ilya Loshchilov and Frank Hutter (2019). Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization. In Proceeding of International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2019).
[123] Daniel Cer, Yinfei Yang, Sheng-yi Kong, Nan Hua, Nicole Limtiaco, Rhomni St. John, Noah Constant, Mario Guajardo-Cespedes, Steve Yuan, Chris Tar, Yun-Hsuan Sung, Brian Strope, and Ray Kurzweil (2018).
Universal Sentence Encoder for English. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations, pp. 169–174.
[124] Yinfei Yang, Daniel Cer, Amin Ahmad, Mandy Guo, Jax Law, Noah Constant, Gustavo Hernandez Abrego, Steve Yuan, Chris Tar, Yun-Hsuan Sung, Brian Strope, and Ray Kurzweil (2020). Multilingual Universal Sentence Encoder for Semantic Retrieval. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, pp. 87–94.
[125] Shashi Narayan, Shay B. Cohen, and Mirella Lapata (2018). Ranking Sentences for Extractive Summarization with Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of NAACL-HLT 2018, pp. 1747–1759.
[126] Diganta Misra and Landskape. Mish: A Self Regularized Non-Monotonic Activation Function. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.08681v3.
[127] Nal Kalchbrenner, Edward Grefenstette, and Phil Blunsom (2014). A Convolutional Neural Network for Modelling Sentences. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vol. 1: Long Papers, pp. 655–665.
[128] Nallapati R., Zhou B., Santos C. dos, Gulcehre C., and Xiang B. (2016). Abstractive text summarization using sequence-to-sequence RNNs and beyond. In Proceedings of the 20th SIGNLL Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, pp. 280–290.
[129] Leo Laugier, Evan Thompson, and Alexandros Vlissidis (2018). Extractive Document Summarization Using Convolutional Neural Networks – Reimplementation. Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley.
[130] Gu J., Lu Z., Li H., and Li V. (2016). Incorporating copying mechanism in sequence-to-sequence learning. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vol. 1: Long Papers, pp. 1631– 1640.
[131] Vinyals O., Fortunato M., and Jaitly N. (2015). Pointer networks. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vol. 2, pp. 2692–2700
[132] Chen Q., Zhu X., Ling Z., Wei S., and Jiang H. (2016). Distraction-based neural networks for modeling documents. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-16), pp. 2754- 2760.
[133] Zhaopeng Tu, Zhengdong Lu, Yang Liu, Xiaohua Liu, and Hang Li (2016). Modeling coverage for neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vol. 1, pp. 76-85. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[134] Pascanu R., Mikolov T., and Y. Bengio (2013). On the difficulty of training recurrent neural networks. In ICML'13: Proceedings of the 30th International