99. Fifth Edition. 2013. "Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders",
Am Psychiatric Assoc. 21.
100. Ellis, A., & Dryden, W. (2007). The practice of rational emotive behavior therapy: Springer publishing company.
101. Eschenauer, R., & Chen-Hayes, S. F. J. P. S. C. (2005). The transformative individual school counseling model: An accountability model for urban school counselors. 244-248.
102. Feizy, F., Sadeghian, E., Shamsaei, F., & Tapak, L. (2020). The relationship between internet addiction and psychosomatic disorders in Iranian undergraduate nursing students: a cross-sectional study. Journal of Addictive Diseases, 38(2), 164-169.
103. Fengqiang, G., Jie, X., Yueqiang, R., & Lei, H. (2016). The relationship between internet addiction and aggression: multiple mediating effects of life events and social support. Psychology research, 6(1), 42-49.
104. Flexner, A. (1915). Proceedings of the National Conference of Charities and Correction. School and Society, 1, 901-911.
105. Frey, A. J., Alvarez, M. E., Sabatino, C. A., Lindsey, B. C., Dupper, D. R., Raines, J. C., . . . Schools. (2012). The development of a national school social work practice model. In (Vol. 34, pp. 131-134): Oxford University Press.
106. riedlander, F. (1963). Underlying sources of job satisfaction. Journal of Applied Psychology, 47(4), 246.
107. Deepak Goel, Alka Subramanyam và Ravindra Kamath. 2013. "A study on the prevalence of internet addiction and its association with psychopathology in Indian adolescents", Indian Journal of Psychiatry. 55(2), tr. 140.
108. Minmin Gu. 2013. A study of adolescents' Internet use and Internet addiction in Shanghai, China: Implications for social work practice, Chinese University of Hong Kong.
109. Alex S Hall và Jeffrey Parsons. 2001. "Internet addiction: College student case study using best practices in cognitive behavior therapy", Journal of mental health counseling. 23(4), tr. 312.
110. Hanson, B. G. (2014). General Systems Theory-Beginning With Wholes: Beginning with Wholes: Taylor & Francis.
111. Hinojo-Lucena, F.-J., Aznar-Díaz, I., Cáceres-Reche, M.-P., Trujillo-Torres, J.-M., & Romero-Rodríguez, J.-M. (2019). Problematic Internet Use as a Predictor of Eating Disorders in Students: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis Study. Nutrients, 11(9), 2151.
112. Holliman, D. C., Dziegielewsk, S. F., & Datta, P. J. S. W. i. H. C. (2001). Discharge planning and social work practice. 32(3), 1-19.
113. Jaffee, K. D., Dessel, A. B., Woodford, M. R. J. J. o. G., & Services, L. S. (2016). The nature of incoming graduate social work students' attitudes toward sexual minorities. 28(4), 255-276.
114. Jang, K. S., Hwang, S. Y., & Choi, J. Y. (2008). Internet addiction and psychiatric symptoms among Korean adolescents. Journal of School Health, 78(3), 165-171.
115. Javaeed, A., Bint Zafar, M., Iqbal, M., & Ghauri, S. K. (2019). Correlation between Internet addiction, depression, anxiety and stress among undergraduate medical students in Azad Kashmir. Pakistan journal of medical sciences, 35(2), 506.
116. Javaeed, A., Jeelani, R., Gulab, S., & Ghauri, S. K. (2020). Relationship between internet addiction and academic performance of undergraduate medical students of Azad Kashmir. Pakistan journal of medical sciences, 36(2), 229.
117. Durkee, T., Kaess, M., Carli, V., Parzer, P., Wasserman, C., Floderus, B., . . . Bobes, J. (2012). Prevalence of pathological internet use among adolescents in E urope: demographic and social factors. Addiction, 107(12), 2210-2222.
118. Yusuf Karaer và Devrim Akdemir. 2019. "Parenting styles, perceived social support and emotion regulation in adolescents with internet addiction", Comprehensive psychiatry. 92, tr. 22-27.
119. Kasiram, M. I. (1993). School social work service delivery: models for future practice.
120. Kheyri, F., Azizifar, A., Valizadeh, R., Veisani, Y., Aibod, S., Cheraghi, F., & Mohamadian, F. (2019). Investigation the relationship between internet dependence with anxiety and educational performance of high school students. Journal of Education and Health Promotion, 8.
121. Kormas, G., Critselis, E., Janikian, M., Kafetzis, D., & Tsitsika, A. (2011). Risk factors and psychosocial characteristics of potential problematic and problematic internet use among adolescents: a cross-sectional study. BMC public health, 11(1), 595.
122. Li, Y., Zhang, X., Lu, F., Zhang, Q., & Wang, Y. (2014). Internet addiction among elementary and middle school students in China: A nationally representative sample study. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17(2), 111-116.
123. Lim, J.-A., Gwak, A. R., Park, S. M., Kwon, J.-G., Lee, J.-Y., Jung, H. Y., . . . Choi, J.-S. (2015). Are adolescents with internet addiction prone to aggressive behavior? The mediating effect of clinical comorbidities on the predictability of aggression in adolescents with internet addiction. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 18(5), 260-267.
124. Lin, P.-H., Lee, Y.-C., Chen, K.-L., Hsieh, P.-L., & Yang, S.-Y. (2019). The Relationships Between Sleep Quality and Internet Addiction among Female College Students. Frontiers in neuroscience, 13, 599.
125. Machado, M. d. R., Bruck, I., Antoniuk, S. A., Cat, M. N. L., Soares, M. C., & Silva, A. F. d. (2018). Internet addiction and its correlation with behavioral problems and functional impairments–A cross-sectional study. Jornal Brasileiro de Psiquiatria, 67(1), 34-38.
126. Kwok-Kei Mak và các cộng sự. 2014. "Psychometric properties of the revised chen internet addiction scale (CIAS-R) in Chinese adolescents", Journal of abnormal child psychology. 42(7), tr. 1237-1245.
127. Kwok-Kei Mak và các cộng sự. 2014. "Epidemiology of internet behaviors and addiction among adolescents in six Asian countries", Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking. 17(11), tr. 720-728.
128. Mancoske, R. J. J. S., & Welfare, S. (1981). Sociological perspectives on the ecological model. 8, 710.
129. Maree, J. G., & Care. (2021). The psychosocial development theory of Erik Erikson: critical overview. Early Child Development, 191(7-8), 1107-1121.
130. Mathew, G. (1992). Introduction to Social Case Work.
131. Miskulin, I., Rogina, K., Miskulin, M., Molnar, K., Simic, I., & Dumic, A. (2018). Risk factors of Internet addiction among Croatian university students. European Journal of Public Health, 28(suppl_4), cky214. 140.
132. Missaoui, S. G., Brahim, T., Bouriga, W., & Abdelaziz, A. B. (2014). Prevalence and consequences of internet addiction in a cohort of Tunisian adolescents: A Pilot Study. Journal of Child and Adolescent Behavior.
133. Mohamed, G., & Bernouss, R. (2020). A cross-sectional study on Internet addiction among Moroccan high school students, its prevalence and association with poor scholastic performance. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 25(1), 479-490.
134. Morahan-Martin. 2005. "Internet abuse: Addiction? disorder? symptom? alternative explanations?". 23(1), tr. 39-48.
135. Subramaniam Mythily, Shijia Qiu và Munidasa Winslow. 2008. "Prevalence and correlates of excessive Internet use among youth in Singapore", Annals Academy of Medicine Singapore. 37(1), tr. 9.
136. Nalwa, K., & Anand, A. P. (2003). Internet addiction in students: A cause of concern. Cyberpsychology & behavior, 6(6), 653-656.
137. Newsome, W. S., Anderson-Butcher, D., Fink, J., Hall, L., & Huffer, J. J. S. S.
W. J. (2008). The impact of school social work services on student absenteeism and risk factors related to school truancy. 32(2), 21-38.
138. Pavlov, I. P. (1904). Conditioned reflexes: an investigation of the physiological activity of the cerebral cortex: London University Press.
139. Mirko Pawlikowski, Christine Altstötter-Gleich và Matthias Brand. 2013. "Validation and psychometric properties of a short version of Young’s Internet Addiction Test", Computers in Human Behavior. 29(3), tr. 1212-1223.
140. Ramirez-Valles, J., Dirkes, J., & Barrett, H. A. J. J. o. G. S. W. (2014). GayBy boomers’ social support: Exploring the connection between health and emotional and instrumental support in older gay men. 57(2-4), 218-234.
141. Ross, M. G., & Lappin, B. W. (1955). Community organization: Theory and principles. Retrieved from
142. Royse, D., Dhooper, S. S., & Rompf, E. L. (2016). Field instruction: A guide for social work students: Waveland Press.
143. Ryding, F. C., & Kaye, L. K. (2018). “Internet addiction”: A conceptual minefield. International journal of mental health and addiction, 16(1), 225- 232.
144. Santos, V. A., Freire, R., Zugliani, M., Cirillo, P., Santos, H. H., Nardi, A. E., & King, A. L. J. J. r. p. (2016). Treatment of Internet addiction with anxiety disorders: Treatment protocol and preliminary before-after results involving pharmacotherapy and modified cognitive behavioral therapy. 5(1), e5278.
145. Şaşmaz, T., Öner, S., Kurt, A. Ö., Yapıcı, G., Yazıcı, A. E., Buğdaycı, R., & Şiş, M. (2014). Prevalence and risk factors of Internet addiction in high school students. The European Journal of Public Health, 24(1), 15-20.
146. Siddiqi, S., & Memon, Z. A. (2016). Internet addiction impacts on time management that results in poor academic performance. Paper presented at the 2016 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT).
147. Singh, L. K., Suchandra, K. H. H., Pattajoshi, A., Mamidipalli, S. S., Kamal, H., Singh, S., . . . Mehta, V. (2019). Internet addiction and daytime sleepiness among professionals in India: A web-based survey. Indian journal of psychiatry, 61(3), 265.
148. Siporin, M. J. J. S., & Welfare, S. (1980). Ecological systems theory in social work. 7, 507.
149. Siste, K., Hanafi, E., Sen, L. T., Murtani, B. J., Christian, H., Limawan, A. P., & Siswidiani, L. P. J. F. i. P. (2021). Implications of COVID-19 and Lockdown on Internet Addiction Among Adolescents: Data From a Developing Country. 12.
150. Siste, K., Hanafi, E., Sen, L. T., Murtani, B. J., Christian, H., Limawan, A. P., & Siswidiani, L. P. J. F. i. P. (2021). Implications of COVID-19 and Lockdown on Internet Addiction Among Adolescents: Data From a Developing Country. 12.
151. Skinner, C. E. (1938). The “tyrosinase reaction” of the actinomycetes. Journal of bacteriology, 35(4), 415-424.
152. Staples, J. (2016). Understanding School Social Workers’ Roles in Bullying Prevention and Intervention. 10.
153. Teater, B. (2014). Contemporary Social Work Practice: A Handbook for Students: McGraw-Hill Education (UK).
154. Thomas, M., & Pierson, J. (2010). Dictionary of social work: the definitive a to z of social work and social care: The definitive a to z of social work and social care: McGraw-Hill Education (UK).
155. Tomas, G. J. N. D. I. T. P. s. U. (2010). Social Work Intervention with Individuals and Groups.
156. Toseland, R. W., & Rivas, R. F. (2005). An introduction to group work practice.
157. Wolpe, J. (1952). Experimental neuroses as learned behaviour. British journal of psychology, 43(4), 243.
158. Work, I. A. o. S. o. S. (2018). Global social work statement of ethical principles.
159. Ageing, I. A. o. S. W. J. S. I. G. o. (2011). The role of the social worker with older persons.
160. Young, K., Pistner, M., O'MARA, J., & Buchanan, J. (1999). Cyber disorders: The mental health concern for the new millennium. Cyberpsychology & behavior, 2(5), 475-479.
161. Young, K. S. (1996). Psychology of computer use: XL. Addictive use of the Internet: a case that breaks the stereotype. Psychological reports, 79(3), 899- 902.
162. Young, K. S. (1998). Internet addiction: The emergence of a new clinical disorder. Cyberpsychology & behavior, 1(3), 237-244.
163. Young, K. S. (1999). Internet addiction: symptoms, evaluation and treatment.
Innovations in clinical practice: A source book, 17, 19-31.
164. Young, K. S. (2004). Internet addiction: A new clinical phenomenon and its consequences. American behavioral scientist, 48(4), 402-415.
165. Young, K. S.. 2009. "Internet addiction: The emergence of a new clinical disorder".
166. Young, K. S. (2013). Treatment outcomes using CBT-IA with Internet- addicted patients. Journal of behavioral addictions, 2(4), 209-215.
167. Zheng, S., Guan, W., Li, B., & Qin, D.-z. (2015). Social Work in Teen Addiction Correction Services Research under the New Situation. Paper presented at the 2015 4th National Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering.
Một số trang Web trên mạng Internet
168. Hiền Minh. 2020. "Hiện thực hóa khát vọng chuyển đổi số của Việt Nam",<https://baochinhphu.vn/print/hien-thuc-hoa-khat-vong-chuyen-doi-so- cua-viet-nam-102284478.htm>.
169. Hashimoto Yoshiaki. "Limited by web: Internet addiction in Japan",
170. Cổng thông tin điện tử Bình Định.
171. Đức Hoàng. 2017. "20 năm thay đổi cùng Internet tại Việt Nam",<https://vnexpress.net/20-nam-thay-doi-cung-internet-tai-viet-nam- 3673784.html>.
172. https://skhdt.binhdinh.gov.vn/vi/tong-quan-kinh-te-xa-hoi/tong-quan-kinh-te- xa-hoi-tinh-binh-dinh.html.
173. Lê Hương. 2009. "Internet và những vụ trọng án ở Bình Định",
174. Phúc Lộc. 2014. "Bất ổn các quán game gần trường học",
175. World Health Organization (WHO). 2018. "Addictive behaviours: Gaming disorder",
PHỤ LỤC 1
Chào bạn!
PHỤ LỤC
TRẮC NGHIỆM VỀ MỨC ĐỘ SỬ DỤNG INTERNET
(Dựa theo tiểu chuẩn của Kimberly Young)
Chúng tôi đang thực hiện cuộc khảo sát về việc sử dụng internet ở học sinh trên địa bàn tỉnh Bình Định và một số thông tin về hoạt động hỗ trợ của công tác xã hội đối với học sinh. Chúng tôi rất mong sự hợp tác và chia sẻ của bạn để chúng tôi thực hiện tốt công trình nghiên cứu này. Chúng tôi cam đoan mọi thông tin các bạn cung cấp đều được giữ bí mật và chỉ phục vụ cho mục đích nghiên cứu khoa học.
Sau đây là một số câu hỏi về mức độ sử dụng internet, em vui lòng khoanh tròn vào các lựa chọn phù hợp nhất với bản thân em. Trong đó:
3 = Thường xuyên | |
1 = Hiếm khi | 4 = Rất thường xuyên |
2 = Thỉnh thoảng | 5 = Luôn luôn |
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
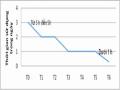
 Thời Gian Sử Dụng Internet Của Q Trước Và Sau Can Thiệp
Thời Gian Sử Dụng Internet Của Q Trước Và Sau Can Thiệp -
 Đổi Mới Nội Dung Và Các Phương Thức Thực Hiện Các Hoạt Động Công Tác Xã Hội Đối Với Hs Nghiện Internet
Đổi Mới Nội Dung Và Các Phương Thức Thực Hiện Các Hoạt Động Công Tác Xã Hội Đối Với Hs Nghiện Internet -
 Công tác xã hội đối với học sinh nghiện internet từ thực tiễn tỉnh Bình Định - 22
Công tác xã hội đối với học sinh nghiện internet từ thực tiễn tỉnh Bình Định - 22 -
 Phiếu Trưng Cầu Ý Kiến Phần I: Một Số Thông Tin Cá Nhân
Phiếu Trưng Cầu Ý Kiến Phần I: Một Số Thông Tin Cá Nhân -
 Công tác xã hội đối với học sinh nghiện internet từ thực tiễn tỉnh Bình Định - 25
Công tác xã hội đối với học sinh nghiện internet từ thực tiễn tỉnh Bình Định - 25 -
 Câu Hỏi Phỏng Vấn Sâu Cán Bộ, Giáo Viên Làm Công Tác Kiêm Nhiệm Ctxh Trong Trường Học
Câu Hỏi Phỏng Vấn Sâu Cán Bộ, Giáo Viên Làm Công Tác Kiêm Nhiệm Ctxh Trong Trường Học
Xem toàn bộ 238 trang tài liệu này.

CÂU HỎI | LỰA CHỌN CỦA BẠN | ||||||
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
1 | Bạn có thường ở trên mạng lâu hơn dự định? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
2 | Bạn có thường xuyên sao nhãng việc học tập và một số công việc nhà để dành nhiều thời gian lên mạng? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
3 | Bạn có thường thích ở trên mạng hơn so với dành thời gian để nói chuyện với người thân, bạn bè của bạn không? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
4 | Bạn có thường xuyên thiết lập các mối quan hệmới với những thành viên trên mạng không? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
5 | Những người thân của bạn có thường than phiền về thời gian mà bạn dành cho việc lên mạng không? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
6 | Việc học của bạn có thường bị ảnh hưởng bởi số thời lượng mà bạn dành cho việc lên mạng không? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
7 | Bạn có thường xuyên phải kiểm tra email và các tài khoản trên internet trước khi làm việc khác nào đó mà bạn cần thiết phải làm không? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
8 | Công việc hay năng suất lao động của bạn có thường biểu hiện kém hiệu quả chỉ vì mạng Internet? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
9 | Bạn có thường trở nên đề phòng hoặc giấu giếm khi có bất cứ ai hỏi bạn làm gì trên mạng khổng? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
10 | Bạn có thường ngăn chặn những suy nghĩ lo âu về cuộc sống của mình bằng những suy nghĩ dễ chịu về mạng Internet? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
11 | Bạn có thường dự đoán về thời gian của lần lên mạng tiếp theo? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
12 | Bạn có thường lo lắng cuộc sống không có internet sẽ trở nên buồn chán, trống rỗng, không có niềm vui? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
13 | Bạn có thường cáu kỉnh, kêu la, hoặc bực mình nếu có ai đó làm phiền bạn trong khi bạn đang trực tuyến trên mạng không? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
14 | Bạn có thường mất ngủ vì thức khuya để trực tuyến trên mạng | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |