them are the same.
A-True B-False C-Not Mentioned
2. The brake pedal is connected to a shaft leading to ……………..
A-small pistons B-master cylinder C-small pistons in the master cylinder
3. What happens when you step on the brake pedal?
A-brake fluid is forced out of the master cylinder and into the brake lines B-the small pistons in master cylinder begin to move.
C-both A and B
4. There is a brake booster between the brake pedal and the master cylinder in cars with power brakes.
A-True B-False C-Not mentioned
5. The cars that have anti-lock brake systems (ABS) often use
…………………to create pressure for booster operation
A-electronic pump B-vacuum pump C-hydraulic pump
6. There is ………………….in the master cylinder from which it runs to the four wheels of the car thanks to fluid lines.
A-brake fluid B-gasoline C-vacuum
7. The brake lines are only made of steel.
A-True B-False C-Not mentioned
Task 3 Read the text again and answer these questions
1. Where is the brake booster located? What is its function?
…………………………………………………………………………………
2. How many types of common power brakes are there? What are they?
…………………………………………………………………………………
3. What is the hydraulic pump in the cars with ABS used for?
…………………………………………………………………………………
4. What happens when you step on the brake pedal? What happens when you release it?
…………………………………………………………………………………
5. What are the brake lines?
…………………………………………………………………………………
Task 4 Fill in each blank with a suitable word or phrase
master cylinder, brake pedal, brake lines,
anti-lock brake, hydraulic pressure, brake fluid,
1. A hydraulic system uses a brake fluid to transfer pressure from the
……………to the pads or shoes.
2. …………….serves as a lubricant for many parts to ensure smooth and even operation. In addition, brake fluid must fight corrosion and rust in the
………….and other components.
3. …………………systems are designed to prevent skidding and enable you to keep controlling your car until it can stop safely.
4. The brake lines run from the………………, along your car’s frame, to each wheel.
5. In a brake system, hydraulic systems provide……………. used to move brake pads or brake shoes against spinning rotors or drums mounted to the wheels.
Vocabulary
+ rear axle (n) cầu sau + steer (v) lái +self-adjusting (a) tự điều chỉnh +manually adjusted (a) điều chỉnh bằng tay + increase (v) tăng lên + vacuum-assisted booster (n) trợ lực phanh chân không + atmospheric pressure (n) áp xuất khí + hydraulic-assisted booster (n) trợ lực phanh thủy lực + hydraulic pressure (n) thủy lực +anti-lock brake systems (ABS) (n) hệ thống phanh chống hãm cứng + brake shoes (n) guốc phanh + brade pad (n) má phanh |
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 6
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 6 -
 A Very Thin Oil Called Transmission Fluid Fills The Transmission System And Generates Hydraulic Pressure. As The Engine Speed Changes, The Pump That Pumps The Transmission Fluid To Develop
A Very Thin Oil Called Transmission Fluid Fills The Transmission System And Generates Hydraulic Pressure. As The Engine Speed Changes, The Pump That Pumps The Transmission Fluid To Develop -
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 8
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 8 -
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 10
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 10 -
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 11
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 11 -
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 12
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 12
Xem toàn bộ 97 trang tài liệu này.
Giới thiệu:
UNIT 11 DRUM BRAKES & DISC BRAKES
Mã bài: MH09-11
Trong bài này sinh viên được cung cấp một số thuật ngữ cơ bản liên quan đến các chi tiết cấu tạo của phanh trống và phanh đĩa trên xe ô tô. Sinh viên đọc hiểu bài khóa nói về các chi tiết cấu tạo của phanh trống và phanh đĩa và thực hành các bài tập để rèn luyện kỹ năng đọc hiểu.
Mục tiêu:
- Kiến thức:
+ Nhận biết các thuật ngữ cơ bản liên quan đến các chi tiết cấu tạo của phanh trống và phanh đĩa như má phanh, guốc phanh, xi lanh phanh, trống phanh, đĩa phanh, bộ phận điều chỉnh phanh...
+ Hiểu được nội dung chính của bài khóa tiếng Anh nói về chi tiết cấu tạo của phanh trống và phanh đĩa trên xe ô tô.
- Kỹ năng:
+ Đọc hiểu được nội dung bài khóa tiếng Anh nói về chi tiết cấu tạo của phanh trống và phanh đĩa trên xe ô tô.
- Năng lực tự chủ và trách nhiệm:
+ Phát triển khả năng làm việc độc lập và làm việc theo cặp/nhóm.
+ Tự đánh giá kết quả của bản thân hoặc của các thành viên trong cặp/nhóm sau khi hoàn thành bài tập.
DRUM BRAKES & DISC BRAKES
1. DRUM BRAKES
Drum brakes are the oldest type of brakes still on the road. Their main advantage is that they require less hydraulic pressure to stop your car because the brake shoes tend to screw themselves into the brake drums after the pistons in the wheel cylinders push them there.
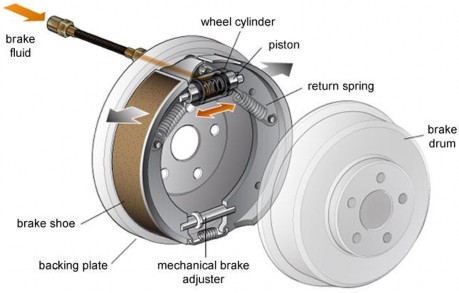
Figure 11.1 A typical drum brake
Brake drums
Brake drums are hollow steel cylinders located in the back of each wheel. Because the lug bolts that go through them are the same as the ones that go through the wheels of your car, they turn when the wheel turn. If you keep your brakes in good condition and replace your brake linings before they become too worn, your brake drums will last for the life of your vehicle.
Wheel cylinders
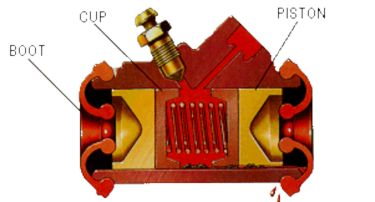
Figure 11.2 A wheel cylinder cutaway
Wheel cylinders are small, but powerful mechanisms located inside each brake drum on the brake backing plate. The brake fluid that is forced through the brake lines into the wheel cylinders. The fluid then activates the two small pistons located inside each wheel cylinder by forcing them farther apart. The pistons emerge from either end of the wheel cylinder and push against the brake shoes. Seals from the wheel cylinder called cups keep the brake fluid from leaking out. Dust boots on each end of the cylinder prevent dirt and dust from entering and fouling the cylinder.
Brake shoes
Brake shoesare curved pieces of metal that stop the car when the pistons in the wheel cylinders push them against the inside of the brake drum. The brake shoes are attached to a set of springs that draw them back into place when you take your foot off the brake pedal.
Brake linings
When the brake shoes are forced against the insides of the brake drum, the brake liningscreate friction that causes the brake drum to stop turning. This in turn forces the wheels to stop turning, which stops the car.
Adjusting devices
At the bottom of the brake backing plate is a manual adjusting wheel or a self- adjusting device. These are used to adjust the distancebetween the surface of the brake lining and the inside of the brake drum when you step on the brake pedal. As your brake linings become worn, the distance increases, and this adjustment compensates for that.
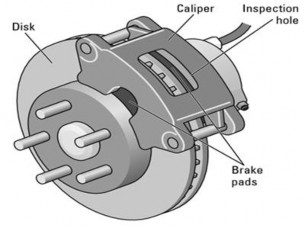
2. DISC BRAKES
Figure 11.3 A disc brake |
Disc brakes have advantages and disadvantages. Because they operate in open air, they are less prone to overheating. They’re also affected less by water because the edge of each brake pad scrapes the water away before it can get between the pads and the disc. Disadvantages include the difficulty of attaching a parking brake to the rear disc brakes and the fact that disc brakes usually need to be powered-assisted. In the past, some manufacturers produced vehicles with disc brakes on the front wheels
and drum brakes on the rear wheels. Today nearly all vehicles have four wheel disc brakes, with the parking brake integrated into the rear discs.
Task 1 Match the bold italic words in the text above with the correct definitions
1. a layer of hard material attached to a brake shoe or brake pad to increase friction against the drum or disc 2. a long curved block, typically one of a pair, which presses on to the drum in a drum brake 3. grip the wheel harshly 4. not smooth or level 5. a broad, very short cylinder attached to a wheel, against which the brake shoes press in a drum brake 6. a thin block, typically one of a pair, which presses on to the disc in a disc brake 7. the length of the space between two points 8. a part of an engine that consists of a short cylinder that fits inside a tube and moves up and down or backwards and forwards to make other parts of the engine move |
Task 2 Read the text and circle the correct answers
1. Brake drums are hollow steel cylinders. They are placed ………………… A-in the front of each wheel B- in the back of each wheel
C-in the middle of each wheel
2. People place the wheel cylinders inside …………………..on the brake backing plate.
A-each brake drum B-each hollow steel cylinder C-each wheel of the car
3. Brake shoes are curved pieces of metal. The brake shoes can stop the car when
………
A-the pistons in the wheel cylinders push them away from the inside of the brake drum
B-the pistons in the wheel cylinders push them towards the inside of the brake drum
C-the pistons in the wheel cylinders pull them away from the inside of the brake drum
4. The brake shoes are attached to a set of springs. These springs help ………… A-draw brake shoes back into place when you press the brake pedal.
B-draw brake shoes back into place when you push the brake pedal.
C-draw the brake shoes back into place when you release the brake pedal.
5. There is a ………….at the bottom of the brake backing plate. A-manual adjusting wheel B-self-adjusting device
C-both a and b
6. Disc brakes are composed of a flat steel disc. It is placed ………… A- between a pair of calipers B-beside a pair of calipers
C-in the front of a pair of calipers
7. There is …………………..in the calipers of the brake disc. These pistons force the brake fluid in the brake lines into the disc.
A-only one piston B- more than one piston
C-both A and B
Task 3 Read the text again and answer the questions
1. What is the main advantage of the drum brakes?
…………………………………………………………………………………
2. What is the shape of a brake shoe?
…………………………………………………………………………………
3. What is the function of the brake linings?
…………………………………………………………………………………
4. What are adjusting devices used for?
…………………………………………………………………………………
5. What is the function of brake pads of the disc brakes?
…………………………………………………………………………………
6. What are the disadvantages of disc brakes?
…………………………………………………………………………………
Task 4 Fill in each blank with a suitable word or phrase
hydraulic pressure, | emergency brake, | |
drum brake, | brake drum, | linings, |
1. The parking brake or………………..is usually attached to the rear wheels of the car.
2. The most important feature contributing to the effectiveness of the braking force supplied by the drum brake is the ………………pressure or force directed against the …………..
3. Brake shoes are the backbone of a……………... They must support the lining and carry it into the drum so the pressure is distributed across the lining surface during brake application.
4. Wheel cylinders convert ……………..from the master cylinder into a mechanical force at the brakes.
5. Brake pads are metal plates with the ……………..bonded to them. Pads are placed at each side of the caliper and straddle the rotor.
*Vocabulary
+parking brake (n) phanh đậu xe, phanh khẩn cấp +distance (n) khoảng cách +become worn (v) bị mòn +compensate (v) bù lại, bồi thường +composed of (a) gồm có +sandwich (v) kẹp giữa +operate (v) hoạt động +require (v) đòi hỏi +tend to (v) có khuynh hướng +screw into (v) siết chặt vào +hollow (a) lõm vào, rỗng +curved (a) hình cung, cong +push against (v) đẩy ngược lại |
+draw back (v) kéo lại +take off (v) tháo ra, cỡi ra +create (v) tạo ra +cause (v) gây ra +inside (n) mặt trong, phần bên trong +adjust (v) điều chỉnh +adjustment (n) sự điều chỉnh + prone (a) dễ bị hỏng + straddle (v) ôm từ 2 phía |
+bolt (n) bu lông