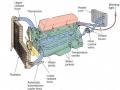
the side to facilitate the intake of fresh air. Some fuel-injected engines also have a round air cleaner; others use a rectangular one.

Figure 6.2 An air filter
Inside the air cleaner is an air filter that removes dirt and particles before they can get into the fuel injectors or carburetor. To keep the car functioning efficiently, be sure to change the air filter at least once a year or every 20,000 miles.
Task 1 Match the underlined words from the text with the correct definitions
……………… ……………… ……………… ……………… ……………… ……………… ……………… ……………… |
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
 The Starter Motor Draws A Great Deal Of Current From The………….. A Large Starter Motor Might Require 250 Or More Amperes Of Current. This Current Flows
The Starter Motor Draws A Great Deal Of Current From The………….. A Large Starter Motor Might Require 250 Or More Amperes Of Current. This Current Flows -
 The Liquid Gets Into The Radiator Through…………….. It Is Usually Mounted On The Top Of The Radiator.
The Liquid Gets Into The Radiator Through…………….. It Is Usually Mounted On The Top Of The Radiator. -
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 5
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 5 -
 A Very Thin Oil Called Transmission Fluid Fills The Transmission System And Generates Hydraulic Pressure. As The Engine Speed Changes, The Pump That Pumps The Transmission Fluid To Develop
A Very Thin Oil Called Transmission Fluid Fills The Transmission System And Generates Hydraulic Pressure. As The Engine Speed Changes, The Pump That Pumps The Transmission Fluid To Develop -
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 8
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 8 -
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 9
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 9
Xem toàn bộ 97 trang tài liệu này.
Task 2 Read the text and choose the best option to complete these following sentences
1. The fuel tank in a car is made of metal or ………………. A-liquid B-plastic composite C-alloy
2. Its function is sending messages to the fuel gauge on the dashboard. It is a…………..
A-fuel tank B-fuel pump C-float
3. The fuel is pumped through the fuel lines to the fuel injection system by means of a ……………
A-fuel pump B-fuel tank C-fuel filter
4. Those cars that use mechanical fuel pump driven by engine are the old cars that have ………………..
A-fuel-injected engines B-carbureted engines C-electronic fuel-injected engines
5. The function of the ………………..in a car is to filter the fuel. A- fuel filter B-carburetor C-fuel injection
6. The fuel filter can filter the fuel thanks to a …………..inside it. A-screen B-pump C-fuel line
7. The air is cleaned by the …………..before it’s mixed with fuel. A-fuel filter B-air cleaner C-snorkel
8. The shapes of the air cleaners are often …………….
A-round B-rectangular C- both A & B
Task 3 Write short answers for these questions using NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS
1. Where is the fuel gauge mounted in a car? …………………………
2. What kind of automotive engines uses the electric fuel pump for pumping the fuel? …………………………
3. Which part of the air cleaner clear the dirt and small particles from the air? …………………………
4. How often should we change the air cleaners? …………………………
Task 4 Fill in each blank with a suitable word or phrase
fuel injectors | injection system | fuel pump | |
fuel filters | fuel | fuel tank |
1. The fuel system in today’s vehicles is designed to prevent fuel vapors from entering the atmosphere. In older systems, a fuel pump delivered fuel under pressure to the fuel injectors. A pressure regulator at the……………. controlled the fuel pressure by sending excess fuel back to the…………. This is a return fuel system.
2. A fuel filter is connected in the……………..between the fuel tank and the engine. Many of these …………..are mounted under the vehicle, and others are mounted in the engine compartment.
3. A fuel pump draws ……………from the fuel tank and pushes it through fuel lines to the engine’s ………………. All current vehicles use an electric………….. Older vehicles with carburetors had mechanical pumps
Task 5 Translate into Vietnamese
1. Inside the fuel tank is a little float that bobs up and down on the surface of the fuel, sending messages to the fuel gauge on your dashboard so that you can tell when you have to buy more gasoline
………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
2. The fuel pump pumps the gasoline through the fuel lines, which run under your car from the fuel tank to the carburetor or fuel injectors. Older cars with carburetors use a mechanical fuel pump that’s driven by the engine.
………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
3. A small screen inside the fuel filter traps the dirt and rust that would otherwise enter your fuel if you ride around most of the time with a nearly-empty tank. Some vehicles have additional fuel filters between the fuel tank and fuel pump.
………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
4. Inside the air cleaner is an air filter that removes dirt and particles before they can get into the fuel injectors or carburetor. To keep the car functioning efficiently, be sure to change the air filter at least once a year or every 20,000 miles.
………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
Vocabulary
+ air cleaner (n) bộ lọc gió + clean the air (v) lọc gió + pass along (v) chạy dọc theo + screen (n) màng + trap the dirt and rust (v) giữ bụi và gỉ + mix (v) pha trộn + snorkel (n) ống thông hơi + stick out of (v) nhô ra ngoài + facilitate (v) làm cho thuận tiện + intake (n) việc lấy vào + fuel-injected engine (n) động cơ phun nhiên liệu + carbureted engine (n) động cơ dùng bộ chế hòa khí + location (n) vị trí + bob up and down (v) nẩy lên xuống |
Giới thiệu:
UNIT 7 ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
Mã bài: MH09-07
Trong bài này sinh viên được cung cấp một số thuật ngữ cơ bản liên quan đến cấu tạo và nguyên lý hoạt động của hệ thống phun nhiên liệu điện tử. Sinh viên đọc hiểu bài khóa nói về cấu tạo và nguyên lý hoạt động của hệ thống phun nhiên liệu điện tử và thực hành các bài tập để rèn luyện kỹ năng đọc hiểu.
Mục tiêu:
- Kiến thức:
+ Nhận biết các thuật ngữ cơ bản liên quan đến cấu tạo và nguyên lý hoạt động của hệ thống phun nhiên liệu điện tử như mô đun điều khiển, kim phun, vòi phun, thân bướm ga, chạy ra lăng ti, các loại cảm biến, ống nạp nhiên liệu, bộ diều chỉnh áp xuất…
+ Hiểu được nội dung chính của bài khóa tiếng Anh nói về cấu tạo và nguyên lý hoạt động của hệ thống phun nhiên liệu điện tử.
- Kỹ năng:
+ Đọc hiểu được nội dung bài khóa tiếng Anh nói về cấu tạo và nguyên lý hoạt động của hệ thống phun nhiên liệu điện tử.
- Năng lực tự chủ và trách nhiệm:
+ Phát triển khả năng làm việc độc lập và làm việc theo cặp/nhóm.
+ Tự đánh giá kết quả của bản thân hoặc của các thành viên trong cặp/nhóm sau khi hoàn thành bài tập.
ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
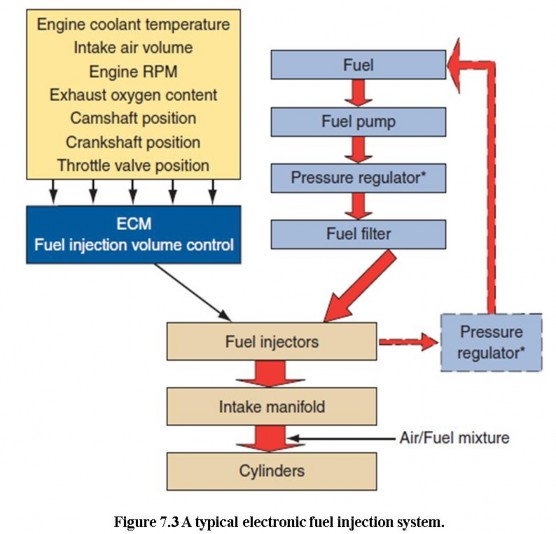
In an EFI system, the computer must know the amount of air entering the engine so it can supply the correct amount of fuelfor that amount of air. In systems with a MAP sensor, the computer calculates the amount of intake air based on MAP and rpm input signals. This type of EFI system is referred to as a speed density system, because the computer calculates the air intakeflow according to engine speed and intake manifold vacuum. Because air density changes with air temperature, an intake air temperature sensoris also used.
Today the most commonly used EFI system is the mass airflow (MAF) system. This system relies on a MAF sensor that directly measures the amount of intake air. The most common type of MAF sensor is the hot wire design. MAF systems are very responsive to changes in operating conditions because they actually measure, rather than compute, airflow.
During closed loop, EFI systems rely on the input from a variety of sensors before adjusting the air-fuel ratio. Based on all of the inputs, the PCM is able to determine the current operating conditions of the engine such as starting, idle, acceleration, cruise, deceleration, and operating temperature. The PCM gathers the inputs and refers to the look-up tables in its memory to determine the ideal air-fuel ratio for the current conditions. During open loop, fuel is delivered according to predetermined parameters held in the PCM’s memory
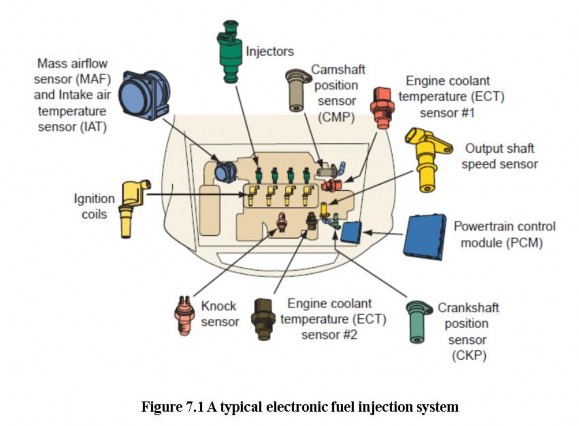
Fuel Injectors
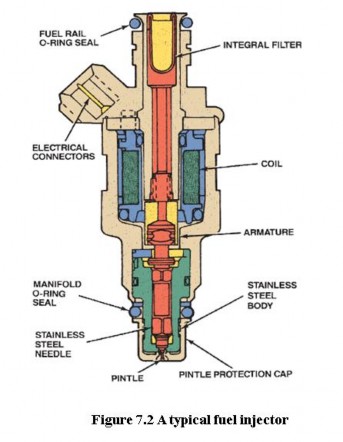
Fuel injectors are electromechanical devices that meter and atomize fuel so it can be sprayed into the intake manifold. Fuel injectors resemble a spark plug in size
and shape. O-rings are used to seal the injector at the intake manifold, throttle body. These O-rings provide thermal insulation to prevent the formation of vapor bubbles. They also reduce potentially damaging vibration. When the injector is electrically energized, a fine mist of fuel sprays from the injector tip. Most injectors consist of a solenoid, a needle valve, and a nozzle. The solenoid is attached to the nozzle valve. The PCM controls the injector by controlling its ground circuit through a driver circuit. When the solenoid winding is energized, it creates a magnetic field that draws the armature back and pulls the needle valve from its seat. Fuel then sprays out of the nozzle. When the solenoid is de-energized, the magnetic field collapses and a helical spring forces the needle valve back on its seat, shutting off fuel flow.
Idle Speed Control
Idle speed control is a function of the PCM. Based on operating conditions and inputs from various sensors, the PCM regulates the idle speed. In throttle body and port EFI systems, engine idle speed is controlled by bypassing a certain amount of airflow past the throttle valve in the throttle body housing. Two types of air by- pass systems are used: auxiliary air valves and idle air control (IAC) valves. IAC valve systems are more common. Most TBI units are fitted with an idle speed motor.
Inputs
The ability of the fuel injection system to control the air-fuel ratio depends on its ability to properly time the injector pulses with the compression stroke of each cylinder and its ability to vary the injector “on” time, according to changing engine demands. Both tasks require the use of sensors that monitor the operating conditions of the engine. The PCM receives these signals from the CAN bus and inputs sent directly to the computer.
Task 1 Match the underlined words from the text with the correct definitions
……………….. ……………….. ……………….. ……………….. ……………….. ……………….. ……………….. ……………….. |
Task 2 Read the text and decide if these statements are TRUE (T) or FALSE (F)
……….. |
……….. ……….. ……….. ……….. ……….. ……….. ……….. |
MAP and rpm input signals are always calculated by the MAP
Task 3 Answer these questions with NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/ OR A NUMBER
1. What is an indispensable part of the mass airflow system?
…………………………………………………………………
2. What helps the PCM determine the current operating conditions of the engine?
………………………………………………………………..
3. After collecting the inputs from various sensors, what does the PCM rely on to determine the ideal air-fuel ratio for the current conditions?
……………………………………………………………….
4. What are used to seal the injector at the intake manifold, throttle body?
……………………………………………………………….
5. What is the idle speed controlled by?
……………………………………………………………….
Task 4 Read the text again and have a look at the pictures again. Fill in each blank with a suitable type of sensors
1. The ………………sensor converts air flowing past a heated sensing element into an electronic signal.
2. The signals from the exhaust gas ……………sensor are used to monitor the air fuel mixture.
3. The ……………..sensor measures air temperature and sends an electronic signal to the PCM.
4. The ………………..sensor signals the PCM when the engine needs cold enrichment, as it does during warm up.
5. The ……………..sensor allows the PCM to monitor throttle position. The signals from this sensor are used to clarify load and operating conditions.
6. The ………………sensor is used to monitor engine speed. This signal advises the PCM to adjust the pulse width of the injectors for engine speed.
7. The signals from the CKP are often used with the signals from the ………….. to determine which cylinders are on the compression stroke.
Vocabulary
+ needle valve (n) van kim phun + nozzle (n) vòi phun, lỗ phun + auxiliary air valve (n) van khí phụ + idle air control (IAC) (n) điều khiển khí chạy ra lăng ti + fuel injector (n) kim phun + electromechanical device (n) thiết bị cơ điện tử + meter (v) đo; (n) máy đo + atomize (v) phun, tán nhỏ + spray (v) phun + O-ring (n) vòng chữ o + seal (v) đóng kín + throttle body (n) thân bướm ga + thermal insulation (n) lớp cách nhiệt + formation (n) sự hình thành + vapor bubble (n) bóng khí + energize (v) kích hoạt, cấp điện + de-energize (v) ngắt nguồn + fine mist (n) lớp sương mịn + solenoid winding (n) cuộn solenoid + armature (n) cái lõi, phần ứng điện + helical spring (n) lò xo xoắn + force (v) ép + shut off (v) đóng +CAN = controller area network: mạng điều khiển khu vực |