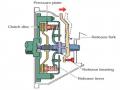
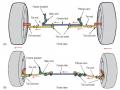
lateral stability than the single-pivot arm, which is lighter and requires less space than the wishbone.
Stabilizer bars
Most vehicles have a front stabilizer bar associated with linkage that is designed to prevent the car from leaning when it corners.
These stabilizers improve high speed stability. Some cars also include a rear stabilizer bar. The stabilizer connects one side of the suspension to the other through the frame. As your car begins to dip on one side, the stabilizer bar restricts that side’s movement, depending on the diameter of the bar. Larger diameter stabilizers restrict more than smaller ones do.
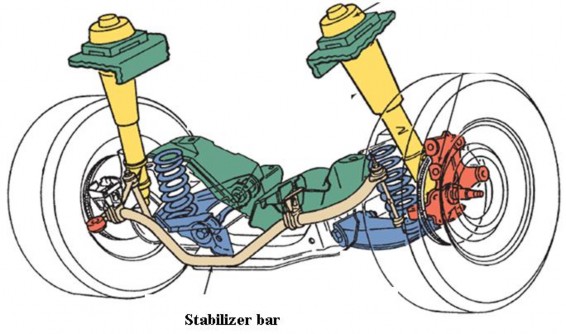
Figure 11.3 A stabilizer bar
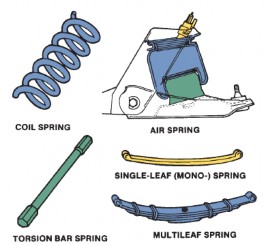
Springs
Figure 13.4 Types of spring |
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 8
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 8 -
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 9
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 9 -
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 10
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 10 -
 Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 12
Anh văn chuyên ngành Nghề Công nghệ ô tô - CĐ TC - Trường Cao đẳng nghề Đồng Tháp - 12
Xem toàn bộ 97 trang tài liệu này.
Shock absorbers and struts
Shock absorbers and MacPherson struts do most work of protecting the passenger compartment from bumps. When a wheel hits a bump, it tends to keep bouncing up and down long after the bump has been left behind unless the movement is controlled. The bouncing effect is due to the inflated rubber tire on the wheel, and so the fact is that a coil spring that is either pulled or compressed doesn’t just snap back into its former shape but keeps moving up and down for some time afterward. Shock absorber and struts allow the springs to compress freely and to return slowly – like the door that opens quickly and easily but closes gently.
Task 1 Match the underlined words from the text with the correct definitions
1. a damping device that uses compressed air, as in suspension systems 2. A spring made of a number of strips of metal curved slightly upwards and clamped together one above the other 3. a helical spring made from metal wire 4. a thing used to keep something steady or stable 5. suspension systems that use a short upper control arm and longer lower control arm to hold the wheels to the frame 6. the system of springs and shock absorbers by which a vehicle is supported on its wheels 7. an elastic device, usually a helical metal coil, that can be pressed or pulled but returns to its former shape when released, used chiefly to exert constant tension or absorb movement 8. move or cause to move in a circle round an axis or center 9. an A frame on a suspension or steering system |
Task 2 Read the text and circle the correct answers
1. The majority of cars have ………………………. A-independent rear suspension systems
B-independent front suspension systems
C-independent front and rear suspension systems
2. On the double-wishbone suspensions, the wheels are held to the frame thanks to ……..
A-a short upper control arm B-longer lower control arm C-both A and B
3. The wheel can rotate and pivot because …………
A-there are rubber bushings at the inboard end of the control arms, B-there is a ball joint at the outboard end of the control arm
C-both and b
4. Upper control arm …………………..on MacPherson strut suspension A-is not used B-is often used C-is rarely used
5. The function of the front stabilizer bar with associated linkage is
………………………
A-preventing the car from leaning when it corners
` B-absorbing the shock
C-stabilizing the high speed
6. ………………have two stabilizers: front stabilizer and rear stabilizer A-all cars B-some cars C-most cars
7. A coil spring cannot return its former shape immediately, but it keeps moving up and down for some time afterward.
A-True B-False C-Not mentioned
Task 3 Read the text and answer the questions
1. How many types of common suspensions are there? What are they?
…………………………………………………………………………………
2. What are features of double-wishbone suspensions?
…………………………………………………………………………………
3. What is the function of the control arms on double-wishbone suspensions?
…………………………………………………………………………………
4. How many types of strut suspensions are there? What are they?
…………………………………………………………………………………
5. What features does a conventional strut suspension have?
…………………………………………………………………………………
6. What types of springs are used to absorb the bumps?
…………………………………………………………………………………
Task 4 Fill in each blank with a suitable word or phrase
weight | leaf springs spring | |
control arms | stabilizer | steering knuckle |
1. A ……………..is the core of all suspension systems. Springs carry the
……………..of the vehicle and absorb shock forces while maintaining correct riding height.
2. Although ……………….were the first type of suspension spring used on automobiles, today they are generally found only on light-duty trucks, vans, and some passenger cars. There are three basic types of leaf springs: multiple leaf, mono-leaf, and fiber composite.
3. Shock absorbers can be mounted either vertically or at an angle. Angle mounting of …………………improves vehicle stability and dampens accelerating and braking torque.
4. Nearly all suspension systems have a ……………….which is also known as the anti-sway bar. This bar, like the shock absorbers, provides directional stability.
5. Each wheel is independently connected to the frame by a……………….., ball joint assemblies, and short upper and longer lower………………...
Vocabulary
+lean (v) nghiêng +corner (v) rẽ, quẹo +improve (n) cải thiện +high speed (n) tốc độ cao +stability (n) sự ổn định |
+dip (v) bật đèn cốt, dìm xuống +restrict (v) hạn chế +diameter (n) đường kính +spring (n) lò xo +core (n) cái lõi, nòng cốt +absorb (v) hấp thu +leaf spring (n) lò xo lá +torsion bar (n) thanh xoắn +air spring (n) lò xo khí +shock absorber (n) phuộc nhún +bump (n,v) va chạm +bounce up and down (v) nảy lên xuống +inflated rubber tire (n) lốp bơm đầy không khí +compress (v) nén +return (v) trở lại +inboard (a) ở vùng giữa, vào phía trong +outboard (a) về phía ngoài +rotate (v) xoay +pivot (v) xoay trên một cái trụ +damp (v) làm cho bớt rung, hãm lại |
+short-long arm suspension (n) hệ thống
Giới thiệu:
UNIT 14 PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
Mã bài: MH09-14
Trong bài này sinh viên được cung cấp một số thuật ngữ cơ bản liên quan đến các công việc bảo trì xe ô tô. Sinh viên đọc hiểu bài khóa nói về các công việc bảo trì xe các bài tập để rèn luyện kỹ năng đọc hiểu.
Mục tiêu:
- Kiến thức:
+ Nhận biết các thuật ngữ cơ bản liên quan đến các công việc bảo trì xe như kiểm tra các đai truyền động, kiểm tra ắc quy, kiểm tra bộ lọc gió...
+ Hiểu được nội dung chính của bài khóa tiếng Anh nói về các công việc bảo trì xe như kiểm tra các đai truyền động, kiểm tra ắc quy, kiểm tra bộ lọc gió...
- Kỹ năng:
+ Đọc hiểu được nội dung bài khóa tiếng Anh nói về các công việc bảo trì xe ô
tô.
- Năng lực tự chủ và trách nhiệm:
+ Phát triển khả năng làm việc độc lập và làm việc theo cặp/nhóm.
+ Tự đánh giá kết quả của bản thân hoặc của các thành viên trong cặp/nhóm sau khi hoàn thành bài tập.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
1. Check the Air Filter
In carbureted engines, the air cleaner is usually large and round with a snorkel sticking out of the side to facilitate the intake of fresh air. Some fuel-injected engines also have a round air cleaner; others use a rectangular one. Because the air filterextracts dirt and dust particles from the air, you should change it at least once a year or every 20,000 miles. If you do most of your driving in a dusty or sandy area, you may need to replaceyour air filter more often

Figure 14.1 A dirty & clean air filter
2. Check the Accessory Belts
Take a look at all the belts that drive the fan, the alternator, and other parts of your car. If any of belts “gives” more than half an inch when you press on it, you may be able to adjust it if it is in good condition.
If the belt is cracked inside or outside, or if the inside surface is glazed, you should replace it.
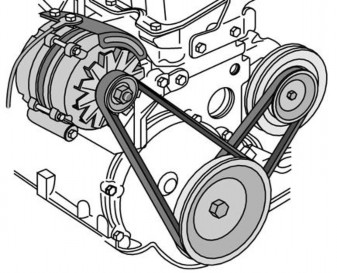
Figure 14.2 Accessory belts
3. Check the Oil Dipstick
Oil reduces the frictionin your engine and keeps it running smoothly. You should check your oil at least once a month to make sure that there’s enough oil and that it isn’t contaminated. To find out whether your car needs oil, do the following:
+ When the engine is cold, pull out the dipstick and wipe it off on a clean rag.
+ Shove the stick back in again.

Figure 14.3 Checking the oil
+ Pull the dipstickout again and look at the film of oil on the end of the stick.
+ Notice how high the oil film reaches on the dipstick and the condition of the oil. If your oil looks clean enough but only reaches the “Add” level on the dipstick, you need to add oil. If the oil is dirty and grimy or has a smell of gasoline, it probably needs to be changed.
+ Put the dipstick back in.
3. Check the Battery
The battery is part of the ignition system and stores electrical current that your car uses to start. The battery also passes electricity along to the parts of your vehicle that need electricity to function. A battery, like other parts of your car, should be checked regularly. A battery that's kept clean and filled with water will last a long time.
To check your battery, follow these steps:
+ If you have a battery with removable caps on the top, remove them.
+ If the liquid inside the battery doesn’t reach the tops of the plates, add distilled water or water with a low mineral content until it covers them.
+ If you see powdery deposits on the terminals, clean them off.
+ Dry everything off with a clean rag.
+ To prevent these corrosive deposits from forming again on the terminals, coat them with grease or petroleum jelly.
+ Examine the battery cables and clamps to see whether they are badly frayed or corroded. If the damage looks bad, the cables and clamps should probably be replaced.
+ If you’ve been having trouble starting your car, if your headlights seem dim, or if the battery is old and has bars or caps that you can remove and look inside, buy a
battery tester and use it to check whether the battery acid concentration is high enough.
+ Check the battery case and the terminals. If you see major cracks in the battery case or obvious terminal damage, the battery should be replaced.

Figure 14.4 Checking the battery
Task 1 Match the underlined words from the text with the correct definitions
1. A device for filtering particles from the air passing through it, especially one protecting the air inlet of an internal combustion engine 2. A piece of old cloth, especially one torn from a larger piece, used typically for cleaning things 3. A rod for measuring the depth of a liquid, especially oil in a vehicle's engine 4. a clasp for holding things together 5. A powerful light at the front of a motor vehicle 6. The resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over another 7. provide a substitute for something that is broken, old, or inoperative 8. a dynamo that generates an alternating current |
Task 2 Read the text and circle the correct answers
1. The air cleaners have ……………shapes.
A-round B- rectangular C-A and B are correct
2. You should change the air filters ………………
A-once every twelve months B-twice a year C-three times a year
3. You should replace the accessory belt if it is
A-cracked and worn B-glazed C-broken
4. You should check the oil at least once a month to ……………