Chapter 2
ANIMAL BODY AND THE BODY STRUCTURE MH38 - 02
In this Chapter
Objectives:
By the end of the Chapter, learners are able to
Know how many regions the animal body can be divided. Learn about viscera and the functions of the digestive organs, the respiratory organs, the urinary organs and genital organs.
Give the names of internal organs.
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
 Giáo trình Anh văn chuyên ngành dùng chung Nghề Dịch vụ thú y và chăn nuôi - Cao đẳng - Trường Cao đẳng Cộng đồng Đồng Tháp - 1
Giáo trình Anh văn chuyên ngành dùng chung Nghề Dịch vụ thú y và chăn nuôi - Cao đẳng - Trường Cao đẳng Cộng đồng Đồng Tháp - 1 -
 Giáo trình Anh văn chuyên ngành dùng chung Nghề Dịch vụ thú y và chăn nuôi - Cao đẳng - Trường Cao đẳng Cộng đồng Đồng Tháp - 2
Giáo trình Anh văn chuyên ngành dùng chung Nghề Dịch vụ thú y và chăn nuôi - Cao đẳng - Trường Cao đẳng Cộng đồng Đồng Tháp - 2 -
 Reading: Read The Following Text And Do The Exercises That Follow.
Reading: Read The Following Text And Do The Exercises That Follow. -
 Reading: Read The Following Words And Do The Exercise That Follow.
Reading: Read The Following Words And Do The Exercise That Follow. -
 Vocabulary: Translate The Following Words Into Vietnamese And Learn By Heart Them.
Vocabulary: Translate The Following Words Into Vietnamese And Learn By Heart Them.
Xem toàn bộ 75 trang tài liệu này.
Chapter 2
Bài 1: ANIMAL BODY

1. Vocabulary: Translate the following words into Vietnamese and learn by heart them.
Tissues (n) :
Epithelium (n) :
Connective tissue (n) :
Muscular tissue (n) :
Nervous tissue (n) :
Viscera (n) :
Trunk (n) :
Thorax (n) :
Abdomen (n) :
Diaphragm (n) :
Limb (n) :
Digestive organ (n) :
Mastication (n) :
Absorption (n) :
Expulsion (n) :
Accessory gland (n) :
Respiratory organ (n) :
Urinary organ (n) :
Genital organ (n) :
Germ cell (n) :
Blood vascular (n) : Lymphatic system (n) : Endocrine gland (n) :
Caudal (adj) :
Pelvis (n) :
Serous membrane (n) :
Lumen (n) :
Internal duct system (n) : Urogenital opening (n) :
2. Reading: Read the following text and do the exercises that follow.
ANIMAL BODY
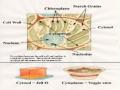
The animal body is made up of millions of cells which have all developed from one cell by a process of division during which they gradually become more specialized. The specialized cells group together to form the various tissues of the body. There are four basic types of tissue in the animal
body: epithelium, connective tissue, muscular tissue and nervous tissue. From these tissues, the different organs or viscera are formed. The organs are the well defined parts of the animal which perform particular functions. Groups of organs having a particular common function are referred to as organs systems.
In general, the body can be divided into the following regions: The head
The neck
The trunk, which is further subdivided into two parts: the thorax and the
abdomen.
The two parts are separated from each other by an arched partition called
diaphragm.
The four limbs
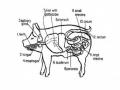
The viscera of the body include:
- The digestive organs are concerned with the nutrition of the animal. This function includes the prehension of food, its mastication, digestion, and absorption, and the initial storage of the nutrients released during digestion. The digestive organs also provide for the expulsion of the unabsorbed portion of the food, and those substances that are added to the digestive tract by its large accessory glands.
- The respiratory organs provide for the exchange of gases between the blood and the atmosphere, and produce the voice.
- The urinary organs, notably the kidneys, eliminate fluid wasted and foreign substances from the blood, and regulate the water and salt metabolism of the body.
- The genital organs are concerned with reproduction. Except for the production of the germ cells, the male and female organs have different functions to perform and consequently differ markedly in their morphology.
These four organ systems are closely related functionally to the blood vascular and lymphatic systems, to the nervous system which controls their functioning, and to the system of endocrine glands.
Most of the viscera are contained in the large body cavities of the trunk.
Some of them, however, are embedded in the tissues of the head, neck, and in the caudal part of the pelvis, where special cavities for them do not develop. The viscera occupying the body cavities are covered with the same serous membrane that lines the cavities, and are separated from one another and from the walls of the cavities allows them a certain amount of mobility.
All viscera have either a lumen or an internal duct system with which they communicate either directly or indirectly with the outside, through the mouth, nose, anus, or the urogenital openings, as the case maybe.
Exercise 1: Answer the following questions.
1. What is the animal body made up of?
2. How many basic types of tissue are there in the animal body? What are they?
3. How many parts can the body be divided? What are they?
4. How many parts can the viscera of the body include? What are they?
5. Where are most of the viscera contained?
Exercise 2: Work in groups. Translate the text about Animal Body into Vietnamese.
3. Further Practice
Exercise 1: Find the names of the words mentioned below. The first one has been done as an example.
body
gases released
viscera
system animals
nutrition cells
blood
substances
divided functions
productive
Whole physical structure, including the bones, flesh, and organs, of a person or an animal, whether dead or alive. body.
1. The process of providing and receiving food necessary for health.
.
2. The red liquid flowing through the bodies of humans and animals.
.
3. The large internal organs of the body, eg… the heart, the lungs, the bowels, etc..
4. A special activity or purpose of a person or thing.
.
5. A particular type of matter; a poisonous / chemical substance.
.
6. Producing or able to produce goods or crops, esp. in large quantities.
.
7. To allow a person or an animal to come out of a place; to set sb/sth free.
.
8. Any substance like air (i.e. not a solid or liquid) that moves freely to fill any available space..
9. Any living thing, other than a human being, that can feel and move, e.g. a lion, bird, snake, fish or fly..
10. A group of things or parts working together as a whole.
.
11. To separate or make sth separate into parts..
12. A smallest structural and functional unit of living matter, consisting of cytoplasm and a nucleus enclosed in a membrane..
Exercise 2: Complete each sentence with the words in Exercise 1.
1. They also want factories to store toxic.
2. Today he is looking for dangerousand other toxic substances.
3. The eukaryotes are represented by the protozoa, fungi, plants, and
.
4. This food provides all theyour dog needs.
5. Aerobic exercise sends moreto the brain.
6. Wethe work between us.
7. The wateron that farm is very good.
8. Happy people work better and are morethan unhappy people.
9. The digestive organs, the respiratory organs, the urinary organs, and genital organs are called theof the body.
10. The “powerhouse of the cell” is the place where energy is stored and
.
Chapter 2
Bài 2: THE BODY STRUCTURE
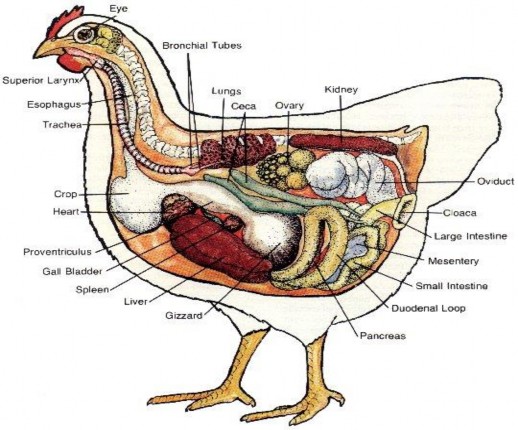
1. Vocabulary: Translate the following words into Vietnamese and learn by heart them.
Respiratory system (n) : Circulatory system and Haemopoiesis (n): Digestive system (n) :
Nervous system (n) :
Urinary system (n) :
Genital system (n) :
Integumentary system (n) :
Skeleton system (n) :
Muscular system (n) :
2. Reading: Translate the following words into Vietnamese and learn by heart them. Then, do the exercises that follow.
THE BODY STRUCTURE
INTERNAL ORGANS
2.1. Respiratory system Nose (n), nostril (n) Larynx (n)
Trachea (n) Lung (n)
Bronchus (n)/bronchi (pl) Bronchiole (n)
Alveolar sac (n) =alveolus (n) Pleura (n)
Diaphragm (n) Air sac (n)
2.2. Circulatory system and Haemopoiesis
Blood vessel (n): Artery (n), Vein (n), Capillary (n).
Heart (n): endocardium (n), myocardium (n), pericardium (n). Lymphatic vessel (n)
Lymph (n), blood (n) Lymph node (n) Spleen (n)
Bone marrow (n) Bursa (n) Thymus (n)