diabetes mellitus breath,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 205, pp. 261–267, 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2014.08.082.
[29] S. Mubeen et al., “Hybrid tin oxide-SWNT nanostructures based gas sensor,” Electrochim. Acta, vol. 92, pp. 484–490, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.01.029.
[30] M. Narjinary, P. Rana, A. Sen, and M. Pal, “Enhanced and selective acetone sensing properties of SnO2-MWCNT nanocomposites: Promising materials for diabetes sensor,” Mater. Des., vol. 115, pp. 158–164, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.11.042.
[31] U. Shaislamov and B. L. Yang, “CdS-sensitized single-crystalline TiO2 nanorods and polycrystalline nanotubes for solar hydrogen generation,” J. Mater. Res., vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 418–423, 2013, doi: 10.1557/jmr.2012.373.
[32] L. L. Xing, S. Yuan, Z. H. Chen, Y. J. Chen, and X. Y. Xue, “Enhanced gas sensing performance of SnO2/α-MoO3 heterostructure nanobelts,” Nanotechnology, vol. 22, no. 22, 2011, doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/22/22/225502.
[33] A. Chowdhuri, P. Sharma, V. Gupta, K. Sreenivas, and K. V. Rao, “H 2S gas sensing mechanism of SnO 2 films with ultrathin CuO dotted islands,” J. Appl. Phys., vol. 92, no. 4, pp. 2172–2180, 2002, doi: 10.1063/1.1490154.
[34] X. Liu, J. Zhang, X. Guo, S. Wang, and S. Wu, “Core-shell α-Fe 2O 3@SnO 2/Au hybrid structures and their enhanced gas sensing properties,” RSC Adv., vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 1650–1655, 2012, doi: 10.1039/c1ra00811k.
[35] M. S. Wagh, L. A. Patil, T. Seth, and D. P. Amalnerkar, “Surface cupricated SnO2-ZnO thick films as a H2S gas sensor,” Mater. Chem. Phys., vol. 84, no. 2–3, pp. 228–233, 2004, doi: 10.1016/S0254-0584(03)00232-3.
[36] Q. Kuang et al., “Enhancing the photon- and gas-sensing properties of a single SnO 2 nanowire based nanodevice by nanoparticle surface functionalization,” J. Phys. Chem. C, vol. 112, no. 30, pp. 11539–11544, 2008, doi: 10.1021/jp802880c.
[37] S. W. Choi, J. Y. Park, and S. S. Kim, “Synthesis of SnO2-ZnO core-shell nanofibers via a novel two-step process and their gas sensing properties,” Nanotechnology, vol. 20, no. 46, 2009, doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/20/46/465603.
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
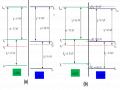
 Sơ Đồ Mức Năng Lượng Của Sno 2 Và Zno Trước (A) Và Sau Khi Biến Tính (B).
Sơ Đồ Mức Năng Lượng Của Sno 2 Và Zno Trước (A) Và Sau Khi Biến Tính (B). -
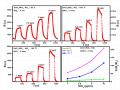
 So Sánh Thời Gian Hồi - Đáp Khí H 2 S (0,1 ÷ 1 Ppm) Của Cảm Biến Cấu Trúc Dây Nano Sno 2 Phủ Lớp Nano Wo 3 Có Bề Dày 5 Nm Tại 150, 200 Và 200 O C.
So Sánh Thời Gian Hồi - Đáp Khí H 2 S (0,1 ÷ 1 Ppm) Của Cảm Biến Cấu Trúc Dây Nano Sno 2 Phủ Lớp Nano Wo 3 Có Bề Dày 5 Nm Tại 150, 200 Và 200 O C. -
 Ảnh Hưởng Của Nhiệt Độ Đến Tính Chất Nhạy Khí Của Cảm Biến
Ảnh Hưởng Của Nhiệt Độ Đến Tính Chất Nhạy Khí Của Cảm Biến -
 Nghiên cứu chế tạo và tính nhạy khí của cấu trúc dị thể giữa dây nano SnO2 và một số oxit kim loại bán dẫn - 17
Nghiên cứu chế tạo và tính nhạy khí của cấu trúc dị thể giữa dây nano SnO2 và một số oxit kim loại bán dẫn - 17
Xem toàn bộ 143 trang tài liệu này.
[38] J.-H. Kim, A. Katoch, S.-H. Kim, and S. S. Kim, “Chemiresistive Sensing Behavior of SnO 2 ( n )–Cu 2 O ( p ) Core–Shell Nanowires,” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 2, no. 28, p. 150708132759008, 2015, doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b03224.
[39] S. Choi, A. Katoch, G. Sun, J.-H. Kim, S.-H. Kim, and S. S. Kim, “Dual Functional Sensing Mechanism in SnO 2 –ZnO Core–Shell Nanowires,” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 6, no. 11, pp. 8281–8287, 2014, doi: 10.1021/am501107c.

[40] D. R. Miller, S. A. Akbar, and P. A. Morris, “Nanoscale metal oxide-based heterojunctions for gas sensing: A review,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 204, pp. 250–272, 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2014.07.074.
[41] X. Xue, L. Xing, Y. Chen, S. Shi, Y. Wang, and T. Wang, “Synthesis and H 2 S Sensing Properties of CuO-SnO 2 Core / Shell PN-Junction Nanorods,” Energy, vol. 4, pp. 12157–12160, 2008, doi: 10.1021/jp8037818.
[42] C. Jin, S. Park, H. Kim, and C. Lee, “Ultrasensitive multiple networked Ga2O3-core/ZnO-shell nanorod gas sensors,” Sensors Actuators B Chem., vol. 161, no. 1, pp. 223–228, 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2011.10.023.
[43] T. Tharsika, A. S. M. A. Haseeb, S. A. Akbar, M. F. aizul M. Sabri, and W. Y. ew Hoong, “Enhanced ethanol gas sensing properties of SnO???-core/ZnO- shell nanostructures,” Sensors (Basel)., vol. 14, no. 8, pp. 14586–14600, 2014, doi: 10.3390/s140814586.
[44] A. Katoch, J. Kim, and S. S. Kim, “TiO 2 /ZnO Inner / Outer Double-Layer Hollow Fibers for Improved Detection of Reducing Gases,” ACS Appl. Mater. interfacesAPPLIED Mater. INTERFACES, vol. 6, no. Iv, pp. 21494–21499, 2014, doi: 10.1021/am506499e.
[45] A. Chowdhuri, V. Gupta, K. Sreenivas, R. Kumar, S. Mozumdar, and P. K. Patanjali, “Response speed of SnO2-based H2S gas sensors with CuO nanoparticles,” Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 84, no. 7, pp. 1180–1182, 2004, doi: 10.1063/1.1646760.
[46] H. R. Kim, A. Haensch, I. D. Kim, N. Barsan, U. Weimar, and J. H. Lee, “The role of NiO doping in reducing the impact of humidity on the performance of
SnO2-based gas sensors: Synthesis strategies, and phenomenological and spectroscopic studies,” Adv. Funct. Mater., vol. 21, no. 23, pp. 4456–4463, 2011, doi: 10.1002/adfm.201101154.
[47] Z. Lou, J. Deng, L. Wang, L. Wang, T. Fei, and T. Zhang, “Toluene and ethanol sensing performances of pristine and PdO-decorated flower-like ZnO structures,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 176, pp. 323–329, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2012.09.027.
[48] A. Trinchi et al., “Investigation of sol-gel prepared CeO2-TiO2 thin films for oxygen gas sensing,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 95, no. 1–3, pp. 145– 150, 2003, doi: 10.1016/S0925-4005(03)00424-6.
[49] G. Cui, L. Gao, B. Yao, S. Wang, P. Zhang, and M. Zhang, “Electrochemistry of CuO/In2O3 p-n heterojunction nano/microstructure array with sensitivity to H2 at and below room-temperature,” Electrochem. commun., vol. 30, no. 3, pp. 42–45, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2013.02.003.
[50] S. Sharma, A. Kumar, N. Singh, and D. Kaur, “Excellent room temperature ammonia gas sensing properties of n-MoS2/p-CuO heterojunction nanoworms,” Sensors Actuators B Chem., vol. 275, Dec. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.08.046.
[51] K.-R. Park, H.-B. Cho, J. Lee, Y. Song, W.-B. Kim, and Y.-H. Choa, “Design of highly porous SnO2-CuO nanotubes for enhancing H2S gas sensor performance,” Sensors Actuators B Chem., vol. 302, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.127179.
[52] M. N. Rumyantseva et al., “Sub-ppm H2S sensing by tubular ZnO-Co3O4 nanofibers,” Sensors Actuators B Chem., vol. 307, Mar. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.127624.
[53] J.-H. Kim, A. Mirzaei, H. W. Kim, and S. S. Kim, “Extremely sensitive and selective sub-ppm CO detection by the synergistic effect of Au nanoparticles and core–shell nanowires,” Sensors Actuators B Chem., 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.090.
[54] J. H. Kim, H. W. Kim, and S. S. Kim, “Ultra-sensitive benzene detection by a novel approach: Core-shell nanowires combined with the Pd-
functionalization,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 239, pp. 578–585, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.071.
[55] M. M. Arafat, B. Dinan, S. A. Akbar, and A. S. M. A. Haseeb, “Gas Sensors Based on One Dimensional Nanostructured Metal-Oxides: A Review,” Sensors, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 7207–7258, May 2012, doi: 10.3390/s120607207.
[56] C. Yu-Jin, Z. Chun-Ling, W. Li-Jiao, G. Peng, C. Mao-Sheng, and S. Xiao- Ling, “Synthesis and enhanced ethanol sensing characteristics of α-Fe 2 O 3 / SnO 2 core–shell nanorods,” Nanotechnology, vol. 20, no. 4, p. 45502, 2009, doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/20/4/045502.
[57] I.-S. Hwang et al., “Synthesis and gas sensing characteristics of highly crystalline ZnO–SnO2 core–shell nanowires,” Sensors Actuators B Chem., vol. 148, no. 2, pp. 595–600, 2010, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2010.05.052.
[58] Y.-J. Chen et al., “Synthesis and enhanced gas sensing properties of crystalline CeO2/TiO2 core/shell nanorods,” Sensors Actuators B Chem., vol. 156, no. 2, pp. 867–874, 2011, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2011.02.057.
[59] N. Singh, A. Ponzoni, R. K. Gupta, P. S. Lee, and E. Comini, “Synthesis of In2O3-ZnO core-shell nanowires and their application in gas sensing,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 160, no. 1, pp. 1346–1351, 2011, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2011.09.073.
[60] H. S. Kim, C. H. Jin, S. H. Park, and C. M. Lee, “Structural, luminescent, and NO2 sensing properties of SnO 2-core/V2O5-shell nanorods,” J. Electroceramics, vol. 30, no. 1–2, pp. 6–12, 2013, doi: 10.1007/s10832-012- 9687-6.
[61] L. F. da Silva et al., “UV-enhanced ozone gas sensing response of ZnO-SnO2 heterojunctions at room temperature,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 240, pp. 573–579, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.158.
[62] J. Kim and S. S. Kim, “Realization of abilities with Pt- functionalized SnO 2 - ZnO core-shell nanowires,” pp. 1–36.
[63] S. Bai et al., “On the construction of hollow nanofibers of ZnO-SnO2 heterojunctions to enhance the NO2 sensing properties,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 266, no. 2, pp. 692–702, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.03.055.
[64] K. Hu, F. Wang, Z. Shen, H. Liu, W. Zeng, and Y. Wang, “Ar plasma treatment on ZnO–SnO2 heterojunction nanofibers and its enhancement mechanism of hydrogen gas sensing,” Ceram. Int., vol. 46, no. 13, pp. 21439–21447, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.242.
[65] C. Lou, C. Yang, W. Zheng, X. Liu, and J. Zhang, “Atomic layer deposition of ZnO on SnO2 nanospheres for enhanced formaldehyde detection,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 329, p. 129218, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.129218.
[66] S. Qin, P. Tang, Y. Feng, and D. Li, “Novel ultrathin mesoporous ZnO-SnO2 n-n heterojunction nanosheets with high sensitivity to ethanol,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 309, no. August 2019, p. 127801, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.127801.
[67] N. X. Thai et al., “Realization of a portable H2S sensing instrument based on SnO2 nanowires,” J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 40–47, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.jsamd.2020.01.003.
[68] A. Mirzaei, S. S. Kim, and H. W. Kim, “Resistance-based H2S gas sensors using metal oxide nanostructures: A review of recent advances,” Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol. 357. pp. 314–331, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.06.015.
[69] A. Sharma, M. Tomar, and V. Gupta, “WO3 nanoclusters–SnO2 film gas sensor heterostructure with enhanced response for NO2,” Sensors Actuators B Chem., vol. 176, pp. 675–684, Jan. 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2012.09.094.
[70] J. Sukunta, A. Wisitsoraat, A. Tuantranont, S. Phanichphant, and C. Liewhiran, “WO3 nanotubes−SnO2 nanoparticles heterointerfaces for ultrasensitive and selective NO2 detections,” Appl. Surf. Sci., vol. 458, pp. 319–332, Nov. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.07.096.
[71] K. P. Yuan et al., “Precise preparation of WO3@SnO2 core shell nanosheets for efficient NH3 gas sensing,” J. Colloid Interface Sci., vol. 568, pp. 81–88, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.02.042.
[72] M. Yin, Y. Yao, H. Fan, and S. Liu, “WO3-SnO2 nanosheet composites: Hydrothermal synthesis and gas sensing mechanism,” J. Alloys Compd., vol.
736, no. 2, pp. 322–331, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.185.
[73] A. Manuscript, “Nanoscale.”
[74] Y. Gui, F. Dong, Y. Zhang, and J. Tian, “Preparation and gas sensitivity of WO3 hollow microspheres and SnO2 doped heterojunction sensors,” Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process., vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 1531–1537, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2013.05.012.
[75] L. Yin et al., “In situ formation of Au/SnO2 nanocrystals on WO3 nanoplates as excellent gas-sensing materials for H2S detection,” Mater. Chem. Phys., vol. 148, no. 3, pp. 1099–1107, 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.09.025.
[76] J. H. Kim, J. H. Lee, A. Mirzaei, H. W. Kim, and S. S. Kim, “SnO2 (n)-NiO
(p) composite nanowebs: Gas sensing properties and sensing mechanisms,”
Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 258, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.11.063.
[77] N. D. Hoa, D. Van Thien, N. Van Duy, and N. Van Hieu, “Facile synthesis of single-crystal nanoporous α-NiS nanosheets from Ni(OH)2 counterpart,” Mater. Lett., vol. 161, pp. 282–285, 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2015.08.123.
[78] C. J. Chen and R. K. Chiang, “Sulfidation of rock-salt-type transition metal oxide nanoparticles as an example of a solid state reaction in colloidal nanoparticles,” Dalt. Trans., vol. 40, no. 4, 2011, doi: 10.1039/c0dt00906g.
[79] N. Cattabiani et al., “Tin Oxide Nanowires Decorated with Ag Nanoparticles for Visible Light-Enhanced Hydrogen Sensing at Room Temperature: Bridging Conductometric Gas Sensing and Plasmon-Driven Catalysis,” J. Phys. Chem. C, vol. 122, no. 9, 2018, doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b09807.
[80] I. S. Hwang et al., “Facile control of C2H5OH sensing characteristics by decorating discrete Ag nanoclusters on SnO2 nanowire networks,” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 3, no. 8, 2011, doi: 10.1021/am200647f.
[81] N. Bhardwaj and S. Mohapatra, “Structural, optical and gas sensing properties of Ag-SnO2 plasmonic nanocomposite thin films,” Ceram. Int., vol. 42, no. 15, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.08.017.
[82] N. Van Hieu, P. Thi Hong Van, L. Tien Nhan, N. Van Duy, and N. Duc Hoa, “Giant enhancement of H2S gas response by decorating n-type SnO2 nanowires with p-type NiO nanoparticles,” Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 101, no. 25,
2012, doi: 10.1063/1.4772488.
[83] M. Kaur et al., “RF sputtered SnO2: NiO thin films as sub-ppm H2S sensor operable at room temperature,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 242, pp. 389– 403, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.11.054.
[84] S. C. Lee et al., “Improvement of H2S sensing properties of SnO2-based thick film gas sensors promoted with MoO3 and NiO,” Sensors (Switzerland), vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 3889–3901, 2013, doi: 10.3390/s130303889.
[85] T. Yang et al., A pulse-driven sensor based on ordered mesoporous Ag2O/SnO2 with improved H2S-sensing performance, vol. 228. Elsevier B.V., 2016.
[86] V. V. Sysoev et al., “Percolating SnO2 nanowire network as a stable gas sensor: Direct comparison of long-term performance versus SnO2 nanoparticle films,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 139, no. 2, pp. 699–703, 2009, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2009.03.065.
[87] P. S. Kolhe, P. M. Koinkar, N. Maiti, and K. M. Sonawane, “Synthesis of Ag doped SnO2 thin films for the evaluation of H2S gas sensing properties,” Phys. B Condens. Matter, vol. 524, pp. 90–96, Nov. 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2017.07.056.
[88] T. M. Ngoc et al., “Self-heated Ag-decorated SnO2 nanowires with low power consumption used as a predictive virtual multisensor for H2S-selective sensing,” Anal. Chim. Acta, vol. 1069, pp. 108–116, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.04.020.
[89] E. S. M. Duraia, Z. A. Mansorov, and S. Tokmolden, “Synthesis, characterization and photoluminescence of tin oxide nanoribbons and nanowires,” Physica B: Condensed Matter, vol. 404, no. 21. pp. 3952–3956, 2009, doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2009.07.135.
[90] L. Mazeina, Y. N. Picard, J. D. Caldwell, E. R. Glaser, and S. M. Prokes, “Growth and photoluminescence properties of vertically aligned SnO2 nanowires,” Journal of Crystal Growth, vol. 311, no. 11. pp. 3158–3162, 2009, doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2009.03.025.
[91] Y. Wang, H. Zhang, and X. Sun, “Electrospun nanowebs of NiO/SnO 2 p-n
heterojunctions for enhanced gas sensing,” Appl. Surf. Sci., vol. 389, pp. 514– 520, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.07.073.
[92] A. Martucci, D. Buso, M. De Monte, M. Guglielmi, C. Cantalini, and C. Sada, “Nanostructured sol-gel silica thin films doped with NiO and SnO2 for gas sensing applications,” J. Mater. Chem., vol. 14, no. 19, pp. 2889–2895, 2004, doi: 10.1039/b405301j.
[93] C. Wei et al., “Hydrothermal synthesis and structural characterization of NiO/SnO2 composites and hydrogen sensing properties,” J. Spectrosc., vol. 2015, 2015, doi: 10.1155/2015/450485.
[94] H. Gao et al., Ultrasensitive and low detection limit of toluene gas sensor based on SnO2-decorated NiO nanostructure, vol. 255. Elsevier B.V., 2018.
[95] D. D. Trung et al., “Effective decoration of Pd nanoparticles on the surface of SnO2 nanowires for enhancement of CO gas-sensing performance,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 265, pp. 124–132, 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.054.
[96] S. Sen et al., “Growth of SnO2/W18O49 nanowire hierarchical heterostructure and their application as chemical sensor,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 147, no. 2, pp. 453–460, 2010, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2010.04.016.
[97] J. Fang et al., “Gas sensing properties of NiO/SnO2 heterojunction thin film,” Sensors Actuators, B Chem., vol. 252, pp. 1163–1168, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.07.013.
[98] D. D. Trung, N. Van Toan, P. Van Tong, N. Van Duy, N. D. Hoa, and N. Van Hieu, “Synthesis of single-crystal SnO 2 nanowires for NO x gas sensors application,” Ceram. Int., vol. 38, no. 8, 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.05.039.
[99] K. H. Stern, “High Temperature Properties and Decomposition of Inorganic Salts Part 3, Nitrates and Nitrites,” J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, vol. 1, no. 3, 1972, doi: 10.1063/1.3253104.
[100] M. A. M. Hassan, I. R. Agool, and L. M. Raoof, “Silver oxide nanostructure prepared on porous silicon for optoelectronic application,” Appl. Nanosci., vol. 4, no. 4, 2014, doi: 10.1007/s13204-013-0215-z.
[101] N. Van Hoang et al., “Enhanced H2S gas-sensing performance of α-Fe2O3