69. Jentink J, Loane MA, Dolk H, et al. Valproic acid monotherapy in pregnancy and major congenital malformations. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2185
70. Vajda FJ, O'Brien TJ, Graham JE, et al. Dose dependence of fetal malformations associated with valproate. Neurology. 2013;81:999.
71. Jentink J, Dolk H, Loane MA, et al. Intrauterine exposure to carbamazepine and specific congenital malformations: systematic review and case-control study. BMJ. 2010;341:c6581.
72. Hernandez-Diaz S, Huybrechts KF, Desai RJ, et al. Topiramate use early in pregnancy and the risk of oral clefts: A pregnancy cohort study. Neurology. 2018;90:e342.
73. Hunt S, Russell A, Smithson WH, et al. Topiramate in pregnancy: preliminary experience from the UK Epilepsy and Pregnancy Register. Neurology. 2008; 71:272.
74. Vajda FJ, O'Brien TJ, Lander CM, et al. Antiepileptic drug combinations not involving valproate and the risk of fetal malformations. Epilepsia. 2016; 57:1048.
75. Hernández-Díaz S, McElrath TF, Pennell PB, et al. Fetal growth and premature delivery in pregnant women on antiepileptic drugs. Ann Neurol. 2017;82:457.
76. Hernández-Díaz S, Mittendorf R, Smith CR, et al. Association between topiramate and zonisamide use during pregnancy and low birth weight. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:21.
77. Mølgaard-Nielsen D, Hviid A. Newer-generation antiepileptic drugs and the risk of major birth defects. JAMA. 2011;305:1996.
78. Cunnington MC, Weil JG, Messenheimer JA, et al. Final results from 18 years of the International Lamotrigine Pregnancy Registry. Neurology. 2011; 76:1817.
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
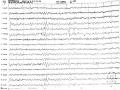
 Điện Não Đồ Ngoài Cơn: Các Kịch Phát Dạng Nhọn-Sóng Chậm Vùng Trán Thái Dương Bên Phải (Bệnh Nhân Phạm Thị Mỹ L. Trong Nghiên Cứu)
Điện Não Đồ Ngoài Cơn: Các Kịch Phát Dạng Nhọn-Sóng Chậm Vùng Trán Thái Dương Bên Phải (Bệnh Nhân Phạm Thị Mỹ L. Trong Nghiên Cứu) -
 Các Yếu Tố Ảnh Hưởng Đến Kết Cục Thai Kỳ Các Yếu Tố Ảnh Hưởng Đến Quyết Định Đẻ Mổ
Các Yếu Tố Ảnh Hưởng Đến Kết Cục Thai Kỳ Các Yếu Tố Ảnh Hưởng Đến Quyết Định Đẻ Mổ -
 Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 18
Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 18 -
 Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 20
Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 20 -
 Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 21
Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 21
Xem toàn bộ 171 trang tài liệu này.
79. Cunnington M, Ferber S, Quartey G, International Lamotrigine Pregnancy Registry Scientific Advisory Committee. Effect of dose on the frequency of major birth defects following fetal exposure to lamotrigine monotherapy in an international observational study. Epilepsia. 2007;48:1207.
80. Glaxo SmithKline. The Lamotrigine Pregnancy registry. Interim report: 1 September 1992 through 30 September 2008; Issued January 2008. http://pregnancyregistry.gsk.com/lamotrigine.html (Accessed on March 31, 2008).

81. Holmes LB, Baldwin EJ, Smith CR, et al. Increased frequency of isolated cleft palate in infants exposed to lamotrigine during pregnancy. Neurology. 2008; 70:2152.
82. Dolk H, Wang H, Loane M, et al. Lamotrigine use in pregnancy and risk of orofacial cleft and other congenital anomalies. Neurology. 2016;86:1716.
83. Mawhinney E, Craig J, Morrow J, et al. Levetiracetam in pregnancy: results from the UK and Ireland epilepsy and pregnancy registers. Neurology. 2013; 80:400.
84. Bromley RL, Calderbank R, Cheyne CP, et al. Cognition in school-age children exposed to levetiracetam, topiramate, or sodium valproate. Neurology. 2016; 87:1943.
85. Winterfeld U, Merlob P, Baud D, et al. Pregnancy outcome following maternal exposure to pregabalin may call for concern. Neurology. 2016;86:2251.
86. Patorno E, Bateman TB, Huybrechts SK et al. Pregabalin use early in pregnancy and the risk of major congenital malformations. Neurology. 2017 May 23;88(21):2020-2025.
87. Fujii H, Goel A, Bernard N, et al. Pregnancy outcomes following gabapentin use: results of a prospective comparative cohort study. Neurology. 2013; 80:1565.
88. The North American Antiepileptic Drug Pregnancy Registry. Update on monotherapy findings: Comparative safety of 11 antiepileptic drugs used during pregnancy. http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/wp-content/uploads/ 2016-newsletter-Winter-2016.pdf (Accessed on October 18, 2018).
89. McVearry KM, Gaillard WD, VanMeter J, Meador KJ. A prospective study of cognitive fluency and originality in children exposed in utero to carbamazepine, lamotrigine, or valproate monotherapy. Epilepsy Behav. 2009; 16:609.
90. Meador KJ, Baker GA, Browning N, et al. Cognitive function at 3 years of age after fetal exposure to antiepileptic drugs. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1597.
91. Meador KJ, Baker GA, Browning N, et al. Effects of fetal antiepileptic drug exposure: outcomes at age 4.5 years. Neurology. 2012;78:1207.
92. Meador KJ, Baker GA, Browning N, et al. Fetal antiepileptic drug exposure and cognitive outcomes at age 6 years (NEAD study): a prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:244-52.
93. Gaily E, Kantola-Sorsa E, Hiilesmaa V, et al. Normal intelligence in children with prenatal exposure to carbamazepine. Neurology. 2004;62:28.
94. Nadebaum C, Anderson VA, Vajda F, et al. Language skills of school-aged children prenatally exposed to antiepileptic drugs. Neurology. 2011;76:719.
95. Thomas SV, Ajaykumar B, Sindhu K, et al. Motor and mental development of infants exposed to antiepileptic drugs in utero. Epilepsy Behav. 2008;13:229.
96. Christensen J, Grønborg TK, Sørensen MJ, et al. Prenatal valproate exposure and risk of autism spectrum disorders and childhood autism. JAMA. 2013; 309:1696.
97. Bromley RL, Mawer GE, Briggs M, et al. The prevalence of neurodevelopmental disorders in children prenatally exposed to antiepileptic drugs. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013;84:637.
98. Cummings C, Stewart M, Stevenson M, et al. Neurodevelopment of children exposed in utero to lamotrigine, sodium valproate and carbamazepine. Arch Dis Child. 2011;96:643.
99. Perucca E, Tomson T. Prenatal exposure to antiepileptic drugs. Lancet. 2006; 367:1467
100. Kini U, Adab N, Vinten J, et al. Dysmorphic features: an important clue to the diagnosis and severity of fetal anticonvulsant syndromes. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2006;91:F90.
101. Holmes LB, Coull BA, Dorfman J, Rosenberger PB. The correlation of deficits in IQ with midface and digit hypoplasia in children exposed in utero to anticonvulsant drugs. J Pediatr. 2005;146:118.
102. Peljto AL, Barker-Cummings C, Vasoli VM, et al. Familial risk of epilepsy: a population-based study. Brain. 2014;137:795.
103. Teramo K, Hiilesmaa V, Bardy A, Saarikoski S. Fetal heart rate during a maternal grand mal epileptic seizure. J Perinat Med. 1979;7:3.
104. Nei M, Daly S, Liporace J. A maternal complex partial seizure in labor can affect fetal heart rate. Neurology. 1998;51:904.
105. Chen YH, Chiou HY, Lin HC, Lin HL. Affect of seizures during gestation on pregnancy outcomes in women with epilepsy. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:979.
106. Vinten J, Adab N, Kini U, et al. Neuropsychological effects of exposure to anticonvulsant medication in utero. Neurology. 2005;64:949.
107. EURAP Study Group.Seizure control and treatment in pregnancy: observations from the EURAP epilepsy pregnancy registry. Neurology. 2006;66:354
108. O'Brien MD, Guillebaud J. Contraception for women with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2006;47(9):1419.
109. Harden CL, Pennell PB, Koppel BS, et al. Practice parameter update: management issues for women with epilepsy--focus on pregnancy (an evidence-based review): vitamin K, folic acid, blood levels, and breastfeeding: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee and Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and American Epilepsy Society. Neurology. 2009;73(2):142
110. Reynolds EH, Green R. Valproate and folate: Congenital and developmental risks. Epilepsy Behav. 2020;108:107068
111. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Preconception and interconception care. In: Guidelines for Women's Health Care, 4th ed, ACOG, 2014. p.389.
112. Morrow JI, Hunt SJ, Russell AJ, et al. Folic acid use and major congenital malformations in offspring of women with epilepsy: a prospective study from the UK Epilepsy and Pregnancy Register. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009;80(5):506.
113. Ban L, Fleming KM, Doyle P, et al. Congenital Anomalies in Children of Mothers Taking Antiepileptic Drugs with and without Periconceptional High Dose Folic Acid Use: A Population-Based Cohort Study. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0131130.
114. Meador KJ, Pennell PB, May RC, et al. Effects of periconceptional folate on cognition in children of women with epilepsy: NEAD study. Neurology. 2020;94(7):e729.
115. Bjørk M, Riedel B, Spigset O, et al. Association of Folic Acid Supplementation During Pregnancy With the Risk of Autistic Traits in Children Exposed to Antiepileptic Drugs In Utero. JAMA Neurol. 2018;75(2):160.
116. Sen A, Nashef L. New regulations to cut valproate-exposed pregnancies. Lancet. 2018;392(10146):458.
117. Vajda FJ, O'Brien T, Lander C, et al.The efficacy of the newer antiepileptic drugs in controlling seizures in pregnancy. Epilepsia. 2014 Aug;55(8):1229-34.
118. Battino D, Tomson T, Bonizzoni E, et al. Seizure control and treatment changes in pregnancy: observations from the EURAP epilepsy pregnancy registry. Epilepsia. 2013 Sep;54(9):1621-7.
119. Hobbins JC. Diagnosis and management of neural-tube defects today. N Engl J Med. 1991;324(10):690.
120. Nadel AS, Green JK, Holmes LB, et al. Absence of need for amniocentesis in patients with elevated levels of maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein and normal ultrasonographic examinations. N Engl J Med. 1990;323(9):557.
121. Voinescu PE, Pennell PB. Delivery of a Personalized Treatment Approach to Women with Epilepsy. Semin Neurol. 2017;37(6):611
122. Morisky DE, Ang A, Krousel-Wood M, Ward H.J. Predictive validity of a medication adherence measure in an outpatient setting. Journal of Clinical Hypertension (Greenwich). 2008;10:348-354
123. Hirsch LJ, LaRoche SM, Gaspard N, et al. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society’s Standardized Critical Care EEG Terminology: 2012 version. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2013;30:1–27.
124. Hirsch LJ, Fong WK, Leitinger M, et al. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society’s Standardized Critical Care EEG Terminology: 2021 Version. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2021;38: 1–29.
125. Wellmer J, Quesada CM, Rothe L, et al. Proposal for a magnetic resonance imaging protocol for the detection of epileptogenic lesions at early outpatient stages. Epilepsia. 2013;54(11):1977-87.
126. Sukumaran SC, Sarma PS, Thomas SV. Polytherapy increases the risk of infertility in women with epilepsy. Neurology. 2010;75(15):1351.
127. Wallace H, Shorvon S, Tallis R. Age-specific incidence and prevalence rates of treated epilepsy in an unselected population of 2,052,922 and age-specific fertility rates of women with epilepsy. Lancet. 1998;352(9145):1970.
128. McGrath A, Sharpe L, Lah S, Parratt K. Pregnancy-related knowledge and information needs of women with epilepsy: a systematic review. Epilepsy Behav. 2014;31:246.
129. Greene ND et al, 2014. Neural tube defects. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2014;37:221- 42.
130. Blom HJ et al, 2006. Neural tube defects and folate: case far from closed. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006 Sep;7(9):724-31.
131. Abe K et al. Impact of planning of pregnancy in women with epilepsy on seizure control during pregnancy and on maternal and neonatal outcomes. Seizure. 2014 Feb;23(2):112-6.
132. Lamberink HJ, Otte WM, Geerts AT, et al. Individualised prediction model of seizure recurrence and long-term outcomes after withdrawal of antiepileptic drugs in seizure-free patients: a systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16(7):523.
133. Park S, Lee DH, Kim SW, Roh YH. Prognostic analysis of patients with epilepsy according to time of relapse after withdrawal of antiepileptic drugs following four seizure-free years. Epilepsia. 2017 Jan;58(1):60-67.
134. Lossius MI, Hessen E, Mowinckel P, et al. Consequences of antiepileptic drug withdrawal: a randomized, double-blind study (Akershus Study). Epilepsia. 2008;49(3):455.
135. Tomson T, Marson A, Boon P, et al. Valproate in the treatment of epilepsy in girls and women of childbearing potential. Epilepsia. 2015 Jul;56(7):1006-19.
136. Hauser WA, et al. Incidence of epilepsy and unprovoked seizures in Rochester, Minnesota: 1935-1984. Epilepsia. 1993 May-Jun;34(3):453-68.
137. Kotsopoulos IA, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of incidence studies of epilepsy and unprovoked seizures. Epilepsia. 2002 Nov;43(11):1402-9.
138. Nei M, Daly S, Liporace J. A maternal complex partial seizure in labor can affect fetal heart rate. Neurology. 1998;51:904.
139. Sahoo S, et al. Maternal complex partial seizure associated with fetal distress. Arch Neurol. 2005 Aug;62(8):1304-5
140. Hiilesmaa V, Teramo K. Fetal and Maternal Risks with Seizures. Epilepsy in women. First published: 24 January 2013; Chapter 10.
141. Gaily E, Kantola-Sorsa E, Granström ML. Intelligence of children of epileptic mothers. J Pediatr. 1988;113:677-684.
142. Gaily E, Kantola-Sorsa E, Granström ML. Specific cognitive dysfunction in children with epileptic mothers. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1990;32:403.
143. Sabers A. Influences on seizure activity in pregnant women with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2009;15(2):230.
144. Vajda FJ, Hitchcock A, et al. Seizure control in antiepileptic drug-treated pregnancy. Epilepsia. 2008 Jan;49(1):172-6.
145. Wallace H, Shorvon S, Tallis R. Age-specific incidence and prevalence rates of treated epilepsy in an unselected population of 2,052,922 and age-specific fertility rates of women with epilepsy. Lancet. 1998;352(9145):1970.
146. Duncan S, Read CL, Brodie MJ. How common is catamenial epilepsy? Epilepsia.1993 Sep-Oct;34(5):827-31.
147. Bazán AC et al. Menstrual cycle worsening of epileptic seizures in women with symptomatic focal epilepsy. Arq.Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2005 Sept;63(3b):751–756.
148. Tomson T, Landmark CJ, Battino D. Antiepileptic drug treatment in pregnancy: changes in drug disposition and their clinical implications. Epilepsia. 2013;54(3):405.
149. Voinescu PE, Park S, Chen LQ, et al. Antiepileptic drug clearances during pregnancy and clinical implications for women with epilepsy. Neurology. 2018;91(13): 1228-36.
150. Herzog AG et al. Predictors of unintended pregnancy in women with epilepsy. Neurology. 2017; Feb 21;88(8):728-733.
151. Pillai J, Sperling MR. Interictal EEG and the diagnosis of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2006;47 Suppl 1:14.
152. Betts T, Fox C. Proactive pre-conception counselling for women with epilepsy- is it effective? Seizure.1999 Sep;8(6):322-7
153. Pennell PB. Pregnancy in women who have epilepsy.Review Neurol Clin. 2004 Nov;22(4):799-820.
154. Crawford P, Hudson S. Understanding the information needs of women with epilepsy at different lifestages: results of the 'Ideal World' survey. Seizure. 2003 Oct;12(7):502-7
155. Kinney MO, Morrow J. Epilepsy in pregnancy. BMJ. 2016 Jun 2;353:i2880