KIẾN NGHỊ
1. Tư vấn trước mang thai cho phụ nữ bị động kinh trong độ tuổi sinh đẻ nên được tiến hành thường quy giúp giảm thiểu nguy cơ tai biến cho cả mẹ và thai nhi, đảm bảo quá trình mang thai an toàn.
2. Cần xây dựng một quy trình thống nhất và phù hợp về quản lý, tư vấn giai đoạn trước, trong thai kỳ và hậu sản cho người bệnh động kinh ở độ tuổi sinh đẻ với sự phối hợp chặt chẽ của chuyên ngành Thần kinh, Sản khoa dựa trên các khuyến cáo mới nhất.
DANH MỤC CÔNG TRÌNH NGHIÊN CỨU ĐÃ CÔNG BỐ LIÊN QUAN ĐẾN LUẬN ÁN
1. Nguyễn Thị Thanh Bình, Lê Văn Thính (2019), Women with epilepsy in pregnancy: Clincal, para-clinical characteristics and the role of preconception counseling in controlling seizures, Journal of Clinical Medicine, tập 3 tháng 4: 47-52.
2. Nguyễn Thị Thanh Bình, Lê Văn Thính. (2019), Đặc điểm lâm sàng và một số yếu tố ảnh hưởng đến hoạt động của cơn động kinh trong quá trình mang thai của phụ nữ bị động kinh, Tạp chí Y học Việt Nam, tập 483 số 2 tháng 10: 44-48.
TÀI LIỆU THAM KHẢO
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
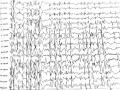
 Điện Não Đồ Trong Cơn Ngưng Hành Vi: Phức Hợp Kịch Phát Nhọn-Sóng Chậm 2-3 Hz Kéo Dài 10 Giây (Bệnh Nhân Nguyễn Mai L. Trong Nghiên Cứu)
Điện Não Đồ Trong Cơn Ngưng Hành Vi: Phức Hợp Kịch Phát Nhọn-Sóng Chậm 2-3 Hz Kéo Dài 10 Giây (Bệnh Nhân Nguyễn Mai L. Trong Nghiên Cứu) -
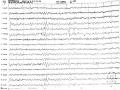
 Điện Não Đồ Ngoài Cơn: Các Kịch Phát Dạng Nhọn-Sóng Chậm Vùng Trán Thái Dương Bên Phải (Bệnh Nhân Phạm Thị Mỹ L. Trong Nghiên Cứu)
Điện Não Đồ Ngoài Cơn: Các Kịch Phát Dạng Nhọn-Sóng Chậm Vùng Trán Thái Dương Bên Phải (Bệnh Nhân Phạm Thị Mỹ L. Trong Nghiên Cứu) -
 Các Yếu Tố Ảnh Hưởng Đến Kết Cục Thai Kỳ Các Yếu Tố Ảnh Hưởng Đến Quyết Định Đẻ Mổ
Các Yếu Tố Ảnh Hưởng Đến Kết Cục Thai Kỳ Các Yếu Tố Ảnh Hưởng Đến Quyết Định Đẻ Mổ -
 Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 19
Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 19 -
 Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 20
Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 20 -
 Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 21
Đặc điểm lâm sàng, cận lâm sàng và một số yếu tố liên quan của động kinh ở phụ nữ có thai - 21
Xem toàn bộ 171 trang tài liệu này.
1. Hirtz D, Thurman DJ, Gwinn-Hardy K, et al. How common are the “common” neurologic disorders? Neurology. 2007;68(5):326–337

2. Tang DH, Malone DC,Warholak TL. Prevalence and incidence of epilepsy in an elderly and low-income population in the United States. J Clin Neurol. 2015;11:252-261.
3. Tomson T, Battino D, Bromley R, et al. Management of epilepsy in pregnancy: a report from the International League Against Epilepsy Task Force on Women and Pregnancy. Epileptic Disord. 2019;21:497.
4. Harden CL, Meador KJ, Pennell PB, et al. Practice parameter update: management issues for women with epilepsy--focus on pregnancy (an evidence-based review): teratogenesis and perinatal outcomes: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee and Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and American Epilepsy Society. Neurology. 2009;73:133.
5. Borthen I, Eide MG, Daltveit AK, Gilhus NE. Obstetric outcome in women with epilepsy: a hospital-based, retrospective study. BJOG. 2011;118:956.
6. Meador KJ, Pennell PB, May RC, et al. Fetal loss and malformations in the MONEAD study of pregnant women with epilepsy. Neurology. 2020; 94:e1502
7. Pennell PB, French JA, Harden CL, et al. Fertility and Birth Outcomes in Women With Epilepsy Seeking Pregnancy. JAMA Neurol. 2018;75:962.
8. Lê Quang Cường và các tác giả. “Động kinh”. Nhà xuất bản Y học. 2005;p:5- 150.
9. Ishijima B. Unitary analysis of epileptic activity in acute and chronic foci and related cortex of cat and monkey. Epilepsia. 1972;13:561–81.
10. Matsumoto H, Ajmone Marsan CA. Cortical cellular phenomena in experimental epilepsy: ictal manifestations. Exp. Neurol. 1964b;25:305–326.
11. Kandel ER, Spencer WA. Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. II. After- potentials and repetitive firing. J Neurophysiol. 1961a;24:243–59.
12. Kandel ER, Spencer WA. The pyramidal cell during hippocampal seizure. Epilepsia. 1961b;2:63–69.
13. De Curtis M, Avanzini G. Interictal spikes in focal epileptogenesis. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001;63:541–567.
14. Cammarota M, Losi G, Chiavegato A, et al. Fast spiking interneuron control of seizure propagation in a cortical slice model of focal epilepsy. J Physiol. 2013; 591(Pt 4):807–22.
15. McCormick D.A, Contreras D. On the cellular and network bases of epileptic seizures. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2001;63:815–846.
16. Prince DA, Wilder BJ. Control mechanisms in cortical epileptogenic foci. “Surround” inhibition. Arch Neurol. 1967;16:194–202.
17. Schevon CA, Weiss SA, McKhann G, et al. Evidence of an inhibitory restraint of seizure activity in humans. Nat Commun. 2012;3:1060.
18. Trevelyan A.J, Sussillo D, Watson B.O, Yuste R.M. Modular propagation of epileptiform activity: evidence for an inhibitory veto in neocortex. J. Neurosci. 2006;26:12447–12455.
19. Trevelyan AJ, Bruns W, Mann EO, et al. The information content of physiological and epileptic brain activity. J Physiol. 2013; 591(Pt 4):799–805.
20. Berg AT, Berkovic SF, Brodie MJ et al. “Revised terminology and concepts for organization of seizures and epilepsies: report of the ILAE Commission on Classification and Terminology, 2005-2009”. Epilepsia. 2010;51(4):676.
21. Fisher RS, Cross JH, French JA et al. Operational classification of seizure types by the International League Against Epilepsy: Position Paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia. 2017; 58(4):522.
22. Stephan US. Evaluation of Seizure Etiology From Routine Testing to Genetic Evaluation. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2019;25(2, Epilepsy):322–342
23. Pillai J, Sperling MR. Interictal EEG and the diagnosis of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2006;47 Suppl 1:14.
24. Chong DJ, Hirsch LJ. Which EEG patterns warrant treatment in the critically ill? Reviewing the evidence for treatment of periodic epileptiform discharges and related patterns. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2005;22:79.
25. Committee Opinion No.723: Guidelines for Diagnostic Imaging During Pregnancy and Lactation. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130(4):e210.
26. Ray JG, Vermeulen MJ, Bharatha A, Montanera WJ, Park AL. Association Between MRI Exposure During Pregnancy and Fetal and Childhood Outcomes. JAMA. 2016;316(9):952.
27. Cannie MM, De Keyzer F, Van Laere S, Leus A, de Mey J, Fourneau C, De Ridder F, Van Cauteren T, Willekens I, Jani JC Potential Heating Effect in the Gravid Uterus by Using 3-T MR Imaging Protocols: Experimental Study in Miniature Pigs. Radiology. 2016;279(3):754
28. Chartier AL, Bouvier MJ, McPherson DR, Stepenosky JE, Taysom DA, Marks RM The Safety of Maternal and Fetal MRI at 3T. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019;213(5):1170.
29. Hiba AH, Lawrence JH. “Neuroimaging in the evaluation of seizures and epilepsy”. Uptodate. 2018; Topic 14040, Version 2.0.
30. Bernasconi A, Cendes F, Theodore WH, et al. Recommendations for the use of structural magnetic resonance imaging in the care of patients with epilepsy: A consensus report from the International League Against Epilepsy Neuroimaging Task Force. Epilepsia. 2019;60(6):1054.
31. Friedman E. Epilepsy imaging in adults: getting it right. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014 Nov;203(5):1093-103.
32. Viale L, Allotey J, Cheong-See F, et al. Epilepsy in pregnancy and reproductive outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2015; 386:1845.
33. MacDonald SC, Bateman BT, McElrath TF, Hernández-Díaz S. Mortality and Morbidity During Delivery Hospitalization Among Pregnant Women With Epilepsy in the United States. JAMA Neurol. 2015;72:981.
34. Kapoor D, Wallace S. Trends in maternal deaths from epilepsy in the United Kingdom: a 30-year retrospective review. Obstet Med. 2014;7:160.
35. Edey S, Moran N, Nashef L. SUDEP and epilepsy-related mortality in pregnancy. Epilepsia. 2014;55:e72.
36. Razaz N, Tomson T, Wikström AK, Cnattingius S. Association Between Pregnancy and Perinatal Outcomes Among Women With Epilepsy. JAMA Neurol. 2017;74:983.
37. Harden CL, Hopp J, Ting TY, et al. Practice parameter update: management issues for women with epilepsy--focus on pregnancy (an evidence-based review): obstetrical complications and change in seizure frequency: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee and Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and American Epilepsy Society. Neurology. 2009;73:126.
38. Bech BH, Kjaersgaard MI, Pedersen HS, et al. Use of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy and risk of spontaneous abortion and stillbirth: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2014;349:g5159.
39. Allotey J, Aroyo-Manzano D, Lopez P, et al. Global variation in pregnancy complications in women with epilepsy: A meta-analysis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2017;215:12.
40. EURAP Study Group. Seizure control and treatment in pregnancy: observations from the EURAP epilepsy pregnancy registry. Neurology. 2006; 66:354
41. Sabers A, aRogvi-Hansen B, Dam M, et al. Pregnancy and epilepsy: a retrospective study of 151 pregnancies. Acta Neurol Scand. 1998;97:164.
42. Reisinger TL, Newman M, Loring DW, et al. Antiepileptic drug clearance and seizure frequency during pregnancy in women with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2013;29:13.
43. Thomas SV, Syam U, Devi JS. Predictors of seizures during pregnancy in women with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2012;53:e85.
44. Pennell PB, French JA, May RC, et al. Changes in Seizure Frequency and Antiepileptic Therapy during Pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2547.
45. Cagnetti C, Lattanzi S, Foschi N, et al. Seizure course during pregnancy in catamenial epilepsy. Neurology. 2014;83:339.
46. Bjørk MH, Veiby G, Reiter SC, et al. Depression and anxiety in women with epilepsy during pregnancy and after delivery: a prospective population-based cohort study on frequency, risk factors, medication, and prognosis. Epilepsia. 2015;56:28.
47. Galanti M, Newport DJ, Pennell PB, et al. Postpartum depression in women with epilepsy: influence of antiepileptic drugs in a prospective study. Epilepsy Behav. 2009;16:426.
48. Meador KJ, Pennell PB, Harden CL, et al. Pregnancy registries in epilepsy: a consensus statement on health outcomes. Neurology. 2008;71:1109.
49. Hernández-Díaz S, Werler MM, Walker AM, Mitchell AA. Folic acid antagonists during pregnancy and the risk of birth defects. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:1608.
50. Tomson T, Battino D, Bonizzoni E, et al. Dose-dependent risk of malformations with antiepileptic drugs: an analysis of data from the EURAP epilepsy and pregnancy registry. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:609.
51. Koch S, Lösche G, Jager-Romän E, et al. Major and minor birth malformations and antiepileptic drugs. Neurology. 1992;42:83.
52. Tomson T, Battino D, Bonizzoni E, et al. Comparative risk of major congenital malformations with eight different antiepileptic drugs: a prospective cohort study of the EURAP registry. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:530-538.
53. Holmes LB, Harvey EA, Coull BA, et al. The teratogenicity of anticonvulsant drugs. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1132.
54. Morrow J, Russell A, Guthrie E, et al. Malformation risks of antiepileptic drugs in pregnancy: a prospective study from the UK Epilepsy and Pregnancy Register. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006;77:193.
55. Holmes LB, Mittendorf R, Shen A, et al. Fetal effects of anticonvulsant polytherapies: different risks from different drug combinations. Arch Neurol. 2011;68:1275.
56. Meador KJ, Baker GA, Finnell RH, et al. In utero antiepileptic drug exposure: fetal death and malformations. Neurology. 2006;67:407.
57. Meador KJ, Pennell PB, May RC, et al. Changes in antiepileptic drug- prescribing patterns in pregnant women with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2018; 84:10.
58. Artama M, Auvinen A, Raudaskoski T, et al. Antiepileptic drug use of women with epilepsy and congenital malformations in offspring. Neurology. 2005; 64:1874.
59. Vajda FJ, Eadie MJ. Maternal valproate dosage and foetal malformations. Acta Neurol Scand. 2005;112:137.
60. Vajda FJ, O'Brien TJ, Lander CM, et al. Teratogenesis in repeated pregnancies in antiepileptic drug-treated women. Epilepsia. 2013;54:181.
61. Campbell E, Devenney E, Morrow J, et al. Recurrence risk of congenital malformations in infants exposed to antiepileptic drugs in utero. Epilepsia. 2013;54:165.
62. Finnell RH, Buehler BA, Kerr BM, et al. Clinical and experimental studies linking oxidative metabolism to phenytoin-induced teratogenesis. Neurology. 1992;42:25.
63. Parman T, Chen G, Wells PG. Free radical intermediates of phenytoin and related teratogens. Prostaglandin H synthase-catalyzed bioactivation, electron paramagnetic resonance spectrometry, and photochemical product analysis. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:25079.
64. Tomson T, Battino D. Teratogenic effects of antiepileptic drugs. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11:803.
65. Koch S, Lösche G, Jager-Romän E, et al. Major and minor birth malformations and antiepileptic drugs. Neurology. 1992;42:83.
66. Veiby G, Daltveit AK, Engelsen BA, Gilhus NE. Pregnancy, delivery, and outcome for the child in maternal epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2009;50:2130
67. Bromfield EB, Dworetzky BA, Wyszynski DF, et al. Valproate teratogenicity and epilepsy syndrome. Epilepsia. 2008;49:2122.
68. Hernández-Díaz S, Smith CR, Shen A, et al. Comparative safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. Neurology. 2012;78:1692.