43. J. W. Betts , M. Hornsey, P. G. Higgins, K. Lucassen, et al., Restoring the activity of the antibiotic aztreonam using the polyphenol epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) against multidrug-resistant clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Journal of Medical Microbiology, 2019, 68(10), 1552-1559.
44. J. Landau, Z. Wang, G. Yang, W. Ding and C. Yang, Inhibition of spontaneous formation of lung tumors and rhabdomyosarcomas in A/J mice by black and green tea, Carcinogenesis, 1998, 19:501–507.
45. L. Jian, L.P. Xie, A. H. Lee, C. W. Binns, Protective effect of green tea against prostate cancer: a casecontrol study in southeast China, International Journal of Cancer, 2004, 108(1), 130-135.
46. M. Mendilaharsu, E. De Stefani, H. Deneo-Pellegrini, J. C. Carzoglio, A. Ronco, Consumption of tea and coffee and the risk of lung cancer in cigarette-smoking men: a case-control study in Uruguay, Lung Cancer, 1998, 19(2), 101–107.
47. L. Zhong, M. S. Goldberg, Y. T. Gao, J. A. Hanley, M. E. Parent, F. Jin, A population-based case-control study of lung cancer and green tea consumption among women living in Shanghai, China, Epidemiology, 2001, 12(6), 695–700.
48. J. Wang, W. Zhang, L. Sun, et al., Green tea drinking and risk of pancreatic cancer: A large-scale, population-based case-control study in urban Shanghai, Cancer Epidemiol, 2012, 36(6), e354-358.
49. Q. M. Wang, Q.Y. Gong, J. J. Yan, et al., Association between green tea intake and coronary artery disease in a Chinese population, Circulation Journal, 74(2), 294-300.
50. L. Arab, W. Liu, D. Elashoff, Green and black tea consumption and risk of stroke: a meta-analysis, Stroke, 2009; 40(5), 1786-1792.
51. Y. Song, J. E. Manson, J. E. Buring, H. D. Sesso, S. Liu, Associations of dietary flavonoids with risk of type 2 diabetes, and markers of insulin resistance and systemic inflammation in women: a prospective study and cross-sectional analysis, Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 2005, 24(5), 376-384.
52. H. Iso, C. Date, K. Wakai, M. Fukui, A. Tamakoshi, The relationship between green tea and total caffeine intake and risk for self-reported type 2 diabetes among Japanese adults, Annals of Internal Medicine, 2006, 144(8), 554-562
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
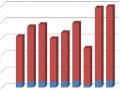
 Hàm Lượng Cr Trung Bình Trong Các Mẫu Chè Mộc Châu
Hàm Lượng Cr Trung Bình Trong Các Mẫu Chè Mộc Châu -
 A) Biểu Đồ Sự Phân Bố Dạng Mn Trong Các Mẫu Chè Cđ-Nt, S89-Nt, Bm-Plvà Sk-Pl
A) Biểu Đồ Sự Phân Bố Dạng Mn Trong Các Mẫu Chè Cđ-Nt, S89-Nt, Bm-Plvà Sk-Pl -
 Đã Nghiên Cứu Một Cách Có Hệ Thống Các Cơ Sở Lý Thuyết Và Thực Nghiệm Nhằm Hoàn Thiện Quy Trình Phân Tích Hàm Lượng Dạng Mn, Cr Lá Chè Sử Dụng Kỹ
Đã Nghiên Cứu Một Cách Có Hệ Thống Các Cơ Sở Lý Thuyết Và Thực Nghiệm Nhằm Hoàn Thiện Quy Trình Phân Tích Hàm Lượng Dạng Mn, Cr Lá Chè Sử Dụng Kỹ -
 Phân tích hàm lượng một số dạng crom, mangan trong lá chè trên địa bàn huyện Mộc Châu và huyện bắc yên tỉnh Sơn La - 21
Phân tích hàm lượng một số dạng crom, mangan trong lá chè trên địa bàn huyện Mộc Châu và huyện bắc yên tỉnh Sơn La - 21
Xem toàn bộ 175 trang tài liệu này.
53. Đỗ Tất Lợi, Những cây thuốc và vị thuốc Việt Nam, NXB Y học, 2015.
54. P. K. Tarafder, R. K. Mondal, L. Kunkal, P. Murugan and D. P. S. Rathore, Liquid - Liquid Extraction and Spectrophotometric Determination of Mn(II) in Geochemical Samples, Chemia analityczna, 2004, 49(2), 251-260.

55. A. I. C. Ehirim, C. O. Ibe, I. O. Achinihu and M. O. C. Ogwuegbu, Liquid-liquid Extraction Separation of Manganese (II) and Tungsten (VI) by 4-butanoyl-3- methyl-1-phenylpyrazol-5-one in Chloroform, Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2014, 7(10), 22-26.
56. A. Ouejhani, M. Dachraoui, G. lalleve, and J. F. Fauvarque, Hexavalent Chromium Recovery By Liquid – Liquid Extraction With Tributylphosphate from Acidic Chloride Media, Analytical Science, 2003, 19(11), 1499-1504.
57. C.P. Mane, S.V. Mahamuni, S.S. Kolekar, S.H. Han, M.A. Anuse, Hexavalent chromium recovery by liquid–liquid extraction with 2-octylaminopyridine from acidic chloride media and its sequential separation from other heavy toxic metal ions, Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2016, 9(2), S1420-S1427.
58. B. Michalke, Manganese speciation using capillary electrophoresis - ICP - mass spectrometry, Journal of Chromatography A, 2004, 1050 (1), 69-76.
59. A. Mallah, S. Q. Memon, A. R. Solangi, A. Khan, Separation and Determination of Chromium (III) Chromium (VI), Gold (III) and Arsenic (V) by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Using 2-Acetylpyridine-4- phenylthiosemicarbazone as Complexing Reagent, Journal of the Chemical Society of Pakistan, 2014, 36(2), 255-262.
60. R. G. Wuilloud, S. S. Kannamkumarath, J. A. Caruso, Speciation of nickel, copper, zinc, and manganese in different edible nuts: a comparative study of molecular size distribution by SEC–UV–ICP–MS, Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2004, 379(3), 495-503.
61. A. Tobiasz, M. Sołtys, E. Kurys, K. Domagała, D. D. Adamska, S. Walas, Multicomutation flow system for manganese speciation by solid phase extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry, Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2017, 134 (1), 11-16.
62. B. Leśniewska, A. Jeglikowska and B. G. Żyłkiewicz, Chromium Speciation in Wastewater and Sewage by Solid-Phase Extraction Using a New Diphenylcarbazone-Incorporated Resin, Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2016,
227: 291.
63. Đặng Ngọc Định, Trương Thị Hương, Phạm Thị Ngọc Mai, Nguyễn Xuân Trung, Nghiên cứu sử dụng vật liệu vỏ trấu biến tính làm vật liệu chiết pha rắn kết hợp với phương pháp F-AAS để xác định lượng vết crôm, Tạp chí phân tích Hóa, Lý và Sinh học, 2015, 20(3), 49-57.
64. E. G. Szymanko, A. Tobiasz, N. Miliszkiewicz, D. D. Adamska and S. Walas, Evaluation of Manganese(II) and Manganese(VII) Speciation in Water Samples by Ion Pair Highperformance Liquid Chromatography-inductively, Analytical Letters, 2017, 50(13), 2147-2160.
65. B. Lesniewska and B. G. Zylkiewicz, Speciation of Chromium in Alkaline Soil Extracts by an Ion-Pair Reversed Phase HPLC-ICP MS Method, Molecules, 2019, 24(6): 1172.
66. H. Watanabe, T. Kamidate, S. Kawamorita, K. Haraguchi, and M. Miyajima, Distribution of nickel(II), cadmium(II) and copper (II) chelates of 2-(2- Pyridylazo)-5-methylphenol in two phases separated from micellar solution of nonionic surfactant, Analytical Sciences, 1987, 3, 433-436.
67. T. Saitoh, Y. Kimura, T. Kamidate, H. Watanabe, K. Haraguchi, Distribution Equilibria of Metal Chelates with Thiazolylazo Dyes between Two Phases Formed from an Aqueous Micellar Solution of a Nonionic Surfactant, Analytical Sciences, 1989, 5, 577-581.
68. S. Kori, Cloud point extraction coupled with back extraction: a green methodology in analytical chemistry, Forensic Sciences Research, 2019, 1-16.
69. K. Pytlakowska, V. Kozik, M. Dabioch, Complex-forming organic ligands in cloud-point extraction of metal ions: A review, Talanta, 15 June 2013, 110, 202- 228.
70. W. L. Hinze, Cloud point extraction and preconcentration procedures for organic and related pollutants of state concern, North Carolina, 1992, 3-4.
71. E. K. Paleologos, D. L. Giokas, M. I. Karayannis, Micelle - mediated separation and cloud-point extraction, Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2005, 24(5), 426-436.
72. M. F. Silva, E. S. Cerutti, L. D. Martinez, Coupling cloud point extraction to instrumental detection systems for metal analysis, Microchimica Acta, 2006,
155(3), 349-364.
73. R. Rahnama, S. Eram and M. R. Jamali, Ligand-less Rapidly Synergistic Cloud Point Extraction as an Efficient Method for the Separation and Preconcentration of Trace Amounts of Lead from Food and Water Samples, Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 2014, Vol. 25(4), 658-664.
74. X. Yang, G. Li, X. Yang, Z. Jia and N. Luo, Determination of Manganese in Environmental Samples by UV-Vis after Cloud Point Extraction, 2nd International Conference on Green Materials and Environmental Engineering, 2015, 91-94.
75. S. Nekouei and F. Nekouei, Application of Cloud Point Extraction for the Determination of Manganese(II) in Water Samples, Chiang Mai J. Sci., 2015, 42(2), 417-428.
76. M. Masrournia, A. Nezhadali, B. T. Darban, Z. Ahmadabaddi, H. Mollaei, Speciation of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) in Water Sample by Spectrophotometry with Cloud Point Extraction, The 1st International Applied Geological Congress, Department of Geology, Islamic Azad University - Mashad Branch, Iran, 2010, 26-28.
77. J. B. Burnecka, A. S. Madeja, W. Zyrnicki, Determination of toxic and other trace elements in calcium-rich materials using cloud point extraction and inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry, Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 182, P. 477-483.
78. J. Li, P. Liang, T. Q. Shi, and H. B. Lu, Cloud point extraction preconcentration and ICP-OES determination of trace chromium and copper in water samples, Atomic Spectroscopy, 2003, 24(5), 169-172.
79. G. Peng, Q. He, G. Zhou, Y. Li, X. Su, M. Liua and L. Fan, Determination of heavy metals in water samples using dual-cloud point extraction coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, Analytical Methods, 2015, 7, 6732-6739.
80. Y. Yamini, M. Faraji, S. Shariati, R. Hassani, M. Ghambarian, On-line metals preconcentration and simultaneous determination using cloud point extraction and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry in water samples, Analytica chimica acta, 2008, 612(2), 144-151.
81. D. Harvey, Modern analytical chemistry, McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2000, New York.
82. A. Walsh, The application of atomic absorption spectra to chemical analysis, Spectrochimica Acta, 1955, 7, 108-117.
83. M. S. Arain, T. G. Kazi, H. I. Afridi, S. A. Arain, J. Ali, Naeemullah, et al., Preconcentration and determination of manganese in biological samples by dual-cloud point extraction coupled with flame atomic absorption spectrometry, Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2014, 29(12), 2349-2355.
84. A. R. Rod, S. Borhani and F. Shemirani, Cloud point preconcentration and flame atomic absorption spectrometry: application to the determination of manganese in milk and water samples, European Food Research and Technology, 2006, 223(5), 649-653.
85. M. A. Bezerra, A. L. B. Conceição, and S. L. C. Ferreira, A Pre-Concentration Procedure Using Cloud Point Extraction for the Determination of Manganese in Saline Effluents of a Petroleum Refinery by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Microchim Acta, 2006, 154, 149-152.
86. V. A. Lemos and G. T. David, An On-Line Cloud Point Extraction System for Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Determination of Trace Manganese in Food Samples, Microchemical Journal, 2010, 94 (1), 42-47.
87. M. A. Farajzadeh and M. R. Fallahi, Simultaneous Cloud-Point Extraction of Nine Cations from Water Samples and Their Determination by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Analytical Sciences, 2006, 22, 635-638.
88. S. Yalçin, H. Filik, and R. Apak, Speciation Analysis of Manganese in Tea Samples Using Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry after Cloud Point Extraction, Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 67(1), 47-55.
89. Nguyễn Thị Hiên, Lưu Thị Nguyệt Minh, Vũ Đức Lợi, Dương Tuấn Hưng, Lê Sỹ Bình, Nghiên cứu xác định dạng mangan trong lá chè bằng phương pháp chiết điểm mù và phổ hấp thụ nguyên tử, Tạp chí Hóa học, 2014, 52(6A), 88-92.
90. Z. Yildiz, G. Arslan, A. Tor, Preconcentrative separation of chromium(III) species from chromium(VI) by cloud point extraction and determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry, Microchim Acta, 2011, 174(3), 399-405.
91. H. I. Ulusoy, R. Gürkan, O. Yilmaz, and M. Akçay, Development of a Cloud
Point Extraction and Preconcentration Method for Chromium(III) and Total Chromium Prior to Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 67(2), 131-139.
92. F. Shemirani, S.D. Abkenar, R.R. Kozani, M.S. Niasari and A. A. Mirroshandel, The Application of Cloud Point Extraction for the Preconcentration and Speciation of Chromium by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Canadian Journal of Analytical Sciences and Spectroscopy, 2004, 49(1), 31-36.
93. N. N. Meeravali, M. A. Reddy and S. J. Kumar, Cloud Point Extraction of Trace Metals from Seawater and Determination by Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry with Iridium Permanent Modifier, Analytical Sciences, 2007, 23, 351-356.
94. M. Ezoddin, F. Shemirani, R. Khani, Application of mixed-micelle cloud point extraction for speciation analysis of chromium in water samples by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry, Desalination, 2010, 262 (1-3), 183-187.
95. M. Sun, Q. Wu, Cloud point extraction combined with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for speciation of Cr(III) in human serum samples, Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2012, 60, 14-18.
96. Nguyễn Xuân Trung, Lê Thị Hạnh, Nghiên cứu kỹ thuật chiết điểm mù (cloud point extraction) và phương pháp quang phổ hấp thụ nguyên tử (AAS) xác định lượng vết ion kim loại, Tạp chí phân tích Hóa, Lý và Sinh học, 2016, 21(1), 14- 22.
97. Trần Thị Hoài Linh, Lê Thị Thanh Trân, Nguyễn Thị Tố Uyên, Sử dụng kỹ thuật chiết điểm mù kết hợp với phương pháp quang phổ hấp thụ phân tử để xác định hàm lượng kẽm trong một số mẫu rau thương phẩm tại Đà Lạt, Tạp chí Khoa học Công nghệ và Thực phẩm, 2020, 20(1), 117-126.
98. Bộ Nông nghiệp và Phát triển nông thôn, Quy chuẩn kỹ thuật Quốc gia QCVN 01–28:2010/BNNPTNT về chè – quy trình lấy mẫu phân tích chất lượng - an toàn vệ sinh thực phẩm, 2010, Hà Nội, Việt Nam.
99. Md. H. Rashid, Ze. Fardous, M. A. Zaman Chowdhury, Md. Khorshed Alam, Md. Latiful Bari, M. Moniruzzaman and S. H. Gan, Determination of heavy
metals in the soils of tea plantations and in fresh and processed tea leaves: an evaluation of six digestion methods, Chemistry Central Journal (2016), 10 : 7.
100. ABM Helal Uddin, Reem Saadi Khalid, Mohamed Alaama, Abdualrahman M. Abdualkader, Abdulrazak Kasmuri and S. A. Abbas, Comparative study of three digestion methods for elemental analysis in traditional medicine products using atomic absorption spectrometry, Journal of Analytical Science and Technology (2016) 7 : 6.
101. Trần Cao Sơn (2010), Thẩm định phương pháp trong phân tích hóa học và vi sinh vật, NXB khoa học và kỹ thuật Hà Nội.
102. R. D. W. Kemmitt and R. D. Peacock, The Chemistry of Manganese, Technetium and Rhenium, Pergamon Text in Inorganic Chemistry, 1973, 22, Pergamon Press. 871-872.
103. Phạm Thị Kim Giang, Khảo sát, nghiên cứu xác định một số nguyên tố trong nước Lâm Thao - Phú Thọ bằng phương pháp đo quang để đánh giá, xử lí ô nhiễm, Luận án Tiến sĩ Hoá học, Trường Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội, 2013.
104. A. R. Freitas, M. Silva, M. L. Ramos, L. L. G. Justino et al., Synthesis, structure, and spectral and electrochemical properties of chromium(iii) tris-(8- hydroxyquinolinate), Dalton Transactions, 2015,44(25), 11491-11503.
105. S. A. Hutapea, A. Saefumillah, and E. W. Asijati, Development of Cr(III) analytical method in dairy products by cloud point extraction using graphite furnace atomic absorption spectroscopy, AIP Conference Proceedings 2242, 040013 (2020); https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0010652.
106. F. Tadayon, F. R. H. Abadi, Speciation of Chromium in Organicfruit Samples with Cloud Point Extraction Separation and Preconcentration and Determination by UV-VIS Spectrophotomety, 2014, Academic Research International Vol. 5(2), 140-147.
107. E. Mohajeri and G. D. Noudeh, Effect of Temperature on the Critical Micelle Concentration and Micellization Thermodynamic of Nonionic Surfactants: Polyoxyethylene Sorbitan Fatty Acid Esters, E-Journal of Chemistry, 2012, 9(4), 2268-2274.
108. Z. Sun, P. Liang, Determination of Cr(III) and total chromium in water samples by cloud point extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry, Microchim Acta, 2008, 162: 121–125.
109. AOAC International, Guidance for Standard Method Performance Requirements, 2016, P. 9.
110. S. Antakli, N. Sarkis, A. Mahmod, A. Check, Determination of Copper, Iron, Manganese, Nickel and Zinc in Tea Leaf Consumed in Syria by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry after Microwave Digestion, Asian Journal of Chemistry, 2011, 23 (7), 3268-3272.
111. A. Prkić, A. Jurić, J. Giljanović, N. Politeo, et al., Monitoring content of cadmium, calcium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium and manganese in tea leaves by electrothermal and flame atomizer atomic absorption spectrometry, Open Chemistry, 2017, 15 (1), 200 - 207.
112. J. Zhang, R. Yang, R. Chen, Y. Peng, X. Wen and L. Gao, Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Tea Leaves and Potential Health Risk Assessment: A Case Study from Puan County, Guizhou Province, China, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2018, 15, 133.
113. Nguyễn Đăng Đức, Lê Thị Vân, Nguyễn Tô Giang, Đỗ Thị Nga, Xác định hàm lượng đồng và crom trong chè xanh ở Thái Nguyên bằng phương pháp phổ hấp thụ nguyên tử, Tạp chí Khoa học và Công nghệ Đại học Thái Nguyên, 2013, 104 (04), 101 – 107.
114. J. B. Cirocka, M. Grembecka, P. Szefer, Monitoring of essential and heavy metals in green tea from different geographical origins, Environ Monit Assess, 2016, 188: 183.
115. T. Barman, A. K. Barooah, B. C. Goswami, N. Sharma, S. Panja, P. Khare,
T. Karak, Contents of Chromium and Arsenic in Tea (Camellia sinensis L.): Extent of Transfer into Tea Infusion and Health Consequence, Biological Trace Element Research, 2020, 196 (1), 318–329.
116. R. Street, J. Száková, O. Drábek, L. Mládková, The status of micronutrients (Cu, Fe, Mn, Zn) in tea and tea infusions in selected samples imported to the Czech Republic, Czech J. Food Sci., 2006, 24 (2), 62–71.