223. Kumar, R., A. Kumar, B. Långström, and T. Darreh-Shori (2017), "Discovery of novel choline acetyltransferase inhibitors using structure-based virtual screening", Scientific reports. 7(1), pp. 1-17.
224. Kim, A.-R., R.J. Rylett, and B.H. Shilton (2006), "Substrate binding and catalytic mechanism of human choline acetyltransferase", Biochemistry. 45(49), pp. 14621-14631.
225. Mahoney, E.R., L. Dumitrescu, A.M. Moore, F.E. Cambronero, P.L. De Jager,
M.E.I. Koran, V.A. Petyuk, R.A. Robinson, S. Goyal, and J.A. Schneider (2019), "Brain expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene family in cognitive aging and alzheimer’s disease", Molecular psychiatry, pp. 1-9.
226. Ruiz de Almodovar, C., D. Lambrechts, M. Mazzone, and P. Carmeliet (2009), "Role and therapeutic potential of VEGF in the nervous system", Physiological reviews. 89(2), pp. 607-648.
227. Spuch, C., D. Antequera, A. Portero, G. Orive, R.M. Hernández, J.A. Molina,
F. Bermejo-Pareja, J.L. Pedraz, and E. Carro (2010), "The effect of encapsulated VEGF-secreting cells on brain amyloid load and behavioral impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease", Biomaterials. 31(21), pp. 5608-5618.
228. Caballero, B., S.J. Sherman, and T. Falk (2017), "Insights into the mechanisms involved in protective effects of VEGF-B in dopaminergic neurons", Parkinson’s Disease. 2017.
229. Sugimoto, H., Y. Yamanish, Y. Iimura, and Y. Kawakami (2000), "Donepezil hydrochloride (E2020) and other acetylcholinesterase inhibitors", Current medicinal chemistry. 7(3), pp. 303-339.
230. Ogura, H., T. Kosasa, Y. Kuriya, and Y. Yamanishi (2000), "Comparison of inhibitory activities of donepezil and other cholinesterase inhibitors on acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in vitro", Methods and findings in experimental and clinical pharmacology. 22(8), pp. 609-614.
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
 Nghiên cứu tác dụng cải thiện suy giảm trí nhớ và chống trầm cảm của Hương nhu tía Ocimum sanctum L. trên thực nghiệm - 19
Nghiên cứu tác dụng cải thiện suy giảm trí nhớ và chống trầm cảm của Hương nhu tía Ocimum sanctum L. trên thực nghiệm - 19 -
 Nghiên cứu tác dụng cải thiện suy giảm trí nhớ và chống trầm cảm của Hương nhu tía Ocimum sanctum L. trên thực nghiệm - 20
Nghiên cứu tác dụng cải thiện suy giảm trí nhớ và chống trầm cảm của Hương nhu tía Ocimum sanctum L. trên thực nghiệm - 20 -
 Nghiên cứu tác dụng cải thiện suy giảm trí nhớ và chống trầm cảm của Hương nhu tía Ocimum sanctum L. trên thực nghiệm - 21
Nghiên cứu tác dụng cải thiện suy giảm trí nhớ và chống trầm cảm của Hương nhu tía Ocimum sanctum L. trên thực nghiệm - 21 -
 Nghiên cứu tác dụng cải thiện suy giảm trí nhớ và chống trầm cảm của Hương nhu tía Ocimum sanctum L. trên thực nghiệm - 23
Nghiên cứu tác dụng cải thiện suy giảm trí nhớ và chống trầm cảm của Hương nhu tía Ocimum sanctum L. trên thực nghiệm - 23
Xem toàn bộ 187 trang tài liệu này.
231. Brunton, L.L., B.C. Knollmann, and R. Hilal-Dandan (2018), Goodman & Gilman's: The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 13e. McGraw-Hill Education LLC.
232. Linge, R., A. Pazos, and A. Diaz (2013), "Social isolation differentially affects anxiety and depressive-like responses of bulbectomized mice", Behavioural brain research. 245, pp. 1-6.
233. Mucignat-Caretta, C., M. Bondí, and A. Caretta (2006), "Time course of alterations after olfactory bulbectomy in mice", Physiology & behavior. 89(5), pp. 637-643.
234. Han, F., T. Nakano, Y. Yamamoto, N. Shioda, Y.-M. Lu, and K. Fukunaga (2009), "Improvement of depressive behaviors by nefiracetam is associated with activation of CaM kinases in olfactory bulbectomized mice", Brain research. 1265, pp. 205-214.
235. Takahashi, K., O. Nakagawasai, W. Nemoto, S. Kadota, J. Isono, T. Odaira, W. Sakuma, Y. Arai, T. Tadano, and K. Tan-No (2018), "Memantine ameliorates depressive-like behaviors by regulating hippocampal cell proliferation and neuroprotection in olfactory bulbectomized mice", Neuropharmacology. 137, pp. 141-155.
236. Smaga, I., B. Pomierny, W. Krzyżanowska, L. Pomierny-Chamioło, J. Miszkiel, E. Niedzielska, A. Ogórka, and M. Filip (2012), "N-acetylcysteine possesses antidepressant-like activity through reduction of oxidative stress: behavioral and biochemical analyses in rats", Progress in Neuro- Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry. 39(2), pp. 280-287.
237. Roche, M., D. Kerr, S. Hunt, and J. Kelly (2012), "Neurokinin-1 receptor deletion modulates behavioural and neurochemical alterations in an animal model of depression", Behavioural brain research. 228(1), pp. 91-98.
238. Cryan, J.F., M.E. Page, and I. Lucki (2005), "Differential behavioral effects of the antidepressants reboxetine, fluoxetine, and moclobemide in a modified forced swim test following chronic treatment", Psychopharmacology. 182(3), pp. 335-344.
239. Becker, M., A. Pinhasov, and A. Ornoy (2021), "Animal models of depression: what can they teach us about the human disease?", Diagnostics. 11(1), pp. 123.
240. Sequeira-Cordero, A., A. Salas-Bastos, J. Fornaguera, and J. Brenes (2019), "Behavioural characterisation of chronic unpredictable stress based on ethologically relevant paradigms in rats", Scientific reports. 9(1), pp. 1-21.
241. Der-Avakian, A. and A. Markou (2012), "The neurobiology of anhedonia and other reward-related deficits", Trends in neurosciences. 35(1), pp. 68-77.
242. Di Chiara, G. and G. Tanda (1997), "Blunting of reactivity of dopamine transmission to palatable food: a biochemical marker of anhedonia in the CMS model?".
243. Pruessner, J.C., F. Champagne, M.J. Meaney, and A. Dagher (2004), "Dopamine release in response to a psychological stress in humans and its relationship to early life maternal care: a positron emission tomography study using [11C] raclopride", Journal of Neuroscience. 24(11), pp. 2825-2831.
244. Ebihara, K., H. Fujiwara, S. Awale, D.F. Dibwe, R. Araki, T. Yabe, and K. Matsumoto (2017), "Decrease in endogenous brain allopregnanolone induces
autism spectrum disorder (ASD)-like behavior in mice: A novel animal model of ASD", Behavioural brain research. 334, pp. 6-15.
245. Smolinsky, A.N., C.L. Bergner, J.L. LaPorte, and A.V. Kalueff, Analysis of grooming behavior and its utility in studying animal stress, anxiety, and depression, in Mood and anxiety related phenotypes in mice. 2009, Springer. pp. 21-36.
246. De Montis, M.G., C. Gambarana, and D. Meloni (1993), "α-Methyl-para- tyrosine antagonizes the effect of chronic imipramine on learned helplessness in rats", European journal of pharmacology. 249(2), pp. 179-183.
247. Daubner, S.C., T. Le, and S. Wang (2011), "Tyrosine hydroxylase and regulation of dopamine synthesis", Archives of biochemistry and biophysics. 508(1), pp. 1-12.
248. Miller, H.L., P.L. Delgado, R.M. Salomon, G.R. Heninger, and D.S. Charney (1996), "Effects of α-methyl-para-tyrosine (AMPT) in drug-free depressed patients", Neuropsychopharmacology. 14(3), pp. 151-157.
249. Lam, R.W., E.M. Tam, A. Grewal, and L.N. Yatham (2001), "Effects of alpha- methyl-para-tyrosine-induced catecholamine depletion in patients with seasonal affective disorder in summer remission", Neuropsychopharmacology. 25(1), pp. S97-S101.
250. Thomas, D.M., D.M. Francescutti‐Verbeem, and D.M. Kuhn (2008), "The newly synthesized pool of dopamine determines the severity of methamphetamine‐induced neurotoxicity", Journal of neurochemistry. 105(3), pp. 605-616.
251. Park, D., D. Stone, H. Baker, K. Kim, and T. Joh (1994), "Early induction of rat brain tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) mRNA following parachlorophenylalanine (PCPA) treatment", Molecular brain research. 22(1-4), pp. 20-28.
252. O’Leary, O.F., A.J. Bechtholt, J.J. Crowley, T.E. Hill, M.E. Page, and I. Lucki (2007), "Depletion of serotonin and catecholamines block the acute behavioral response to different classes of antidepressant drugs in the mouse tail suspension test", Psychopharmacology. 192(3), pp. 357-371.
253. Brann, D.W., K. Dhandapani, C. Wakade, V.B. Mahesh, and M.M. Khan (2007), "Neurotrophic and neuroprotective actions of estrogen: basic mechanisms and clinical implications", Steroids. 72(5), pp. 381-405.
254. Gould, E., B.S. McEwen, P. Tanapat, L.A. Galea, and E. Fuchs (1997), "Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult tree shrew is regulated by psychosocial stress and NMDA receptor activation", Journal of Neuroscience. 17(7), pp. 2492-2498.
255. Jacobs, B.L., H. Van Praag, and F. Gage (2000), "Adult brain neurogenesis and psychiatry: a novel theory of depression", Molecular psychiatry. 5(3), pp. 262- 269.
256. Malberg, J.E., A.J. Eisch, E.J. Nestler, and R.S. Duman (2000), "Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus", Journal of Neuroscience. 20(24), pp. 9104-9110.
257. Nakazawa, T., T. Yasuda, J. Ueda, and K. Ohsawa (2003), "Antidepressant-like effects of apigenin and 2, 4, 5-trimethoxycinnamic acid from Perilla frutescens in the forced swimming test", Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 26(4), pp. 474-480.
258. Yi, L.-T., J.-M. Li, Y.-C. Li, Y. Pan, Q. Xu, and L.-D. Kong (2008), "Antidepressant-like behavioral and neurochemical effects of the citrus- associated chemical apigenin", Life sciences. 82(13-14), pp. 741-751.
259. Zhu, S., S. Lei, S. Zhou, L. Jin, S. Zeng, H. Jiang, and H. Zhou (2019), "Luteolin shows antidepressant-like effect by inhibiting and downregulating plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT, Slc29a4)", Journal of Functional Foods. 54, pp. 440-448.
260. Gatchel, J.R., J.S. Rabin, R.F. Buckley, J.J. Locascio, Y.T. Quiroz, H.-S. Yang,
P. Vannini, R.E. Amariglio, D.M. Rentz, and M. Properzi (2019), "Longitudinal association of depression symptoms with cognition and cortical amyloid among community-dwelling older adults", JAMA network open. 2(8), pp. e198964- e198964.
261. Manaharan, T., R. Thirugnanasampandan, R. Jayakumar, G. Ramya, G. Ramnath, and M. Kanthimathi (2014), "Antimetastatic and anti-inflammatory potentials of essential oil from edible Ocimum sanctum leaves", The Scientific World Journal. 2014.
262. Beatović, D., S. Jelačić, Č. Oparnica, D. Krstić-Milošević, J.M. Glamočlija,
M.S. Ristić, and J.D. Šiljegović (2013), "Chemical composition, antioxidative and antimicrobial activity of essential oil of Ocimum sanctum L", Hemijska industrija. 67(3), pp. 427-435.
263. Giridharan, V.V., R.A. Thandavarayan, and T. Konishi, Ocimum sanctum Linn.(Holy Basil) to Improve Cognition, in Diet and Nutrition in Dementia and Cognitive Decline. 2015, Elsevier. pp. 1049-1058.
PHỤ LỤC 1
KẾT QUẢ GIÁM ĐỊNH TÊN KHOA HỌC CỦA CÂY HƯƠNG NHU TÍA
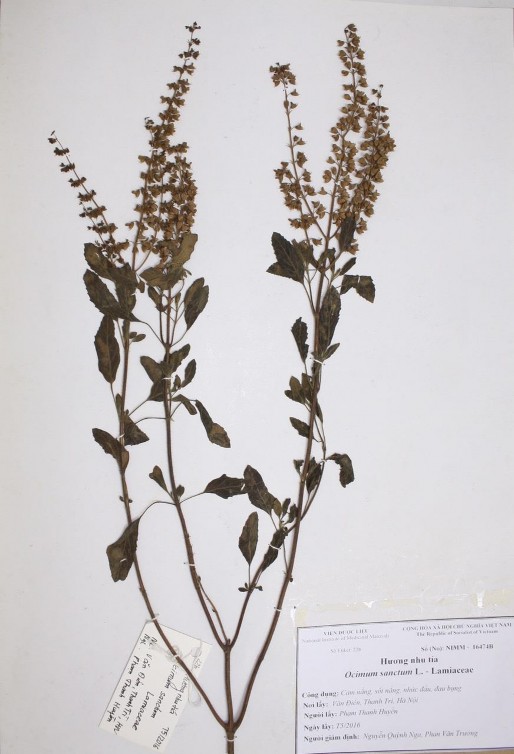

Hình 1. Ảnh chụp tiêu bản cây Hương nhu tía (Ocimum sanctum L.) lưu tại khoa Tài nguyên, Viện Dược liệu
PHỤ LỤC 2
KẾT QUẢ ĐỊNH TÍNH, ĐỊNH LƯỢNG BẰNG HPLC CÁC HỢP CHẤT MARKER TRONG HƯƠNG NHU TÍA
1. Sắc ký đồ các chất phân lập từ cao chiết cồn hương nhu tía
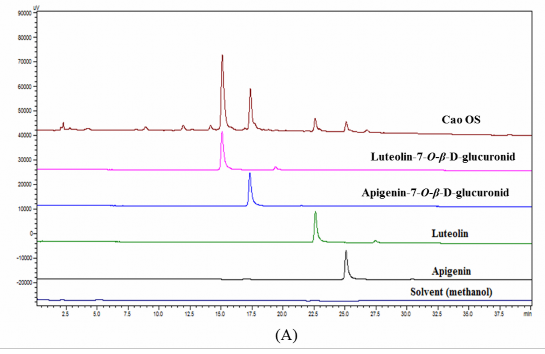
Hình 2A. Sắc ký đồ của cao OS, luteolin, apigenin, luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucoronid và apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucoronid
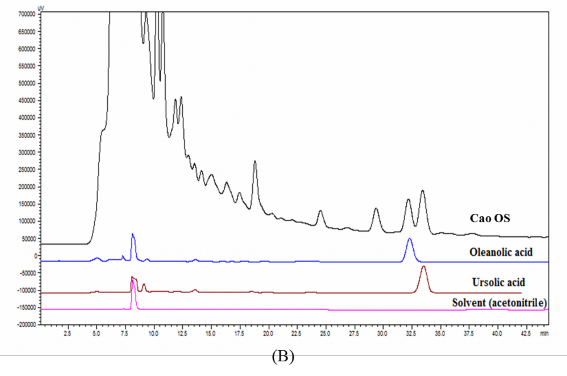
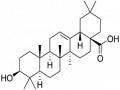
Hình 2B. Sắc ký đồ của cao OS, acid ursolic và acid oleanolic
2. Sắc ký đồ các chất phân lập từ cao ethyl acetat
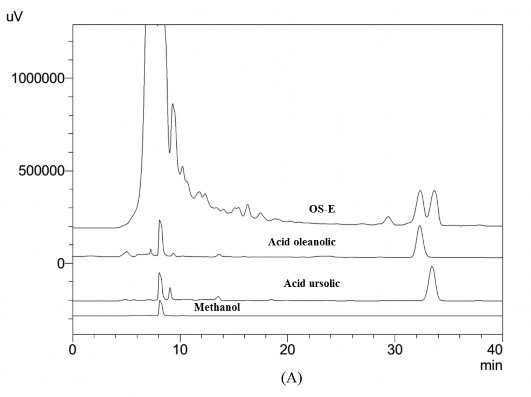
Hình 3A. Sắc ký đồ của cao OS-E, acid ursolic và acid oleanolic
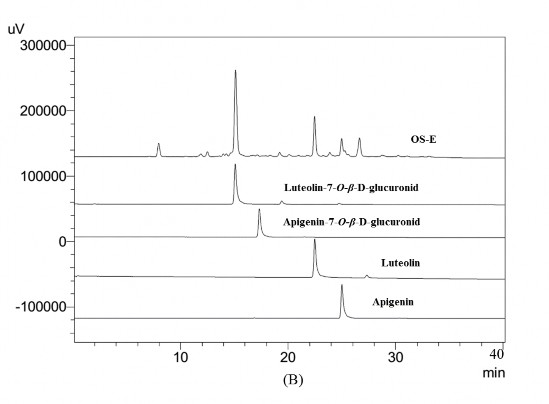
Hình 3B. Sắc ký đồ của cao OS-E, apigenin, luteolin, apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucuronid, luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucuronid
3. Sắc ký đồ các chất phân lập từ cao n-butanol
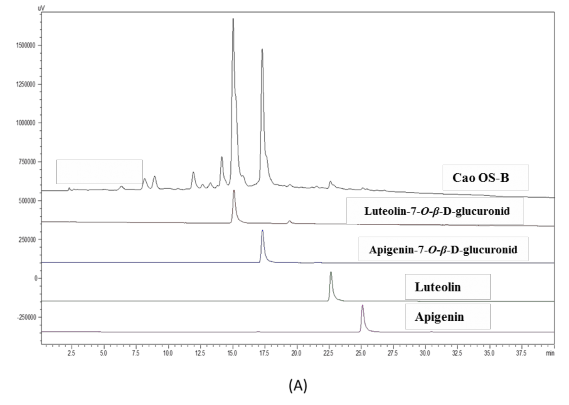
Hình 4A. Sắc ký đồ của cao OS-B, apigenin, luteolin, apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucuronid, luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucuronid
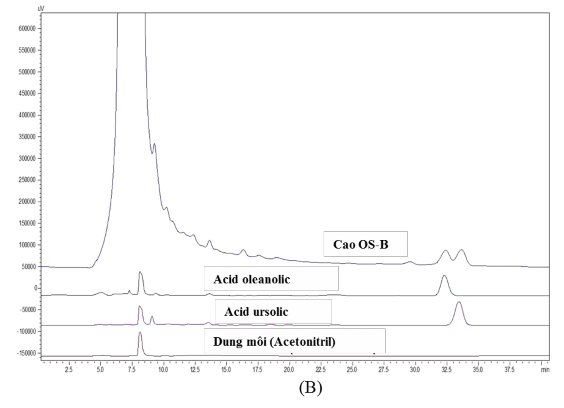
Hình 4B. Sắc ký đồ của cao OS-B, acid ursolic và acid oleanolic