The communication objective is what drives the development of the overall communication strategy and the achievement of the goals of each component of the media mix.
The main objective of marketing communication is to seek a cognitive, sensory or behavioral response of the target audience.
That goal could be to increase the percentage of consumers in the target population who would prefer our products over our competitors, or to encourage existing users to use them more often, increase rate of product preference and build a good image of the company with consumers.
But basically, the goal of promotional communication depends on each stage in the customer’s awareness process.
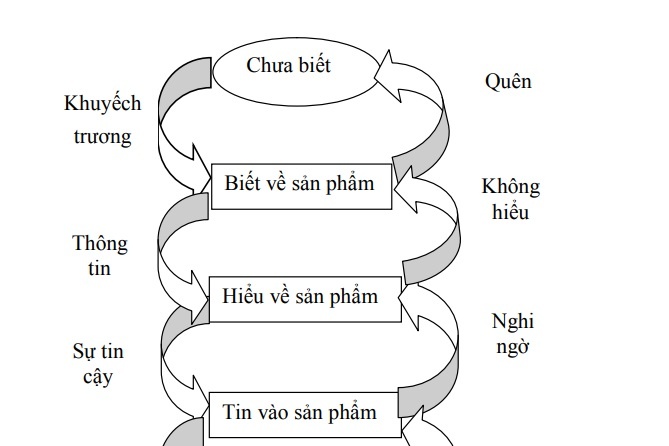
Hình 1.5: Các giai đoạn trong quá trình nhận thức của khách hàng.
For each different stage, there will be a certain communication goal. The model shows that, no matter what attitude consumers have towards our products and services, they can change and improve that attitude for the better, it is important to determine where they are. at what stage of the process and if the change has been effective. Usually communication goals can only focus on one or two specific phases. It is very difficult to influence all stages of a buying process at once.
2.3. Design communication messages.
Communication messages must reflect the company’s communication goals. With the goal of communication at what stage, what is achieved, the message must say what, how to say it logically, expressively and who speaks more persuasively. A communication message is designed to include many content and forms of message expression.
2.3.1. Message content.
o Message content is what the business will say to the target audience to create a desired response. The message should state some benefit, motive, characteristic or reason why the public should think about or research your product.
o The more relevant and attractive the message content is to the interests and preferences of consumers, the more likely it will be to respond to those desires.
o The content of the message can be expressed into topics of reason, feeling, social morality or satisfying the ego of the consumer. Reason is to say the effect and use of the product such as saving, safety, for travel, etc. Emotion is evoking bad or good emotions to promote purchases. Care should be taken when creating a bad emotion because a predictable bad emotion in a message contains so much fear that they will avoid viewing the message.
2.3.2. Message structure
The effectiveness of a message depends not only on its content but also on its structure. A message structure expresses the communicator’s intention to the target audience to stimulate curiosity with messages so that viewers can draw their own conclusions or provide clear information about products or services by means of messages. the message draws a definitive conclusion.
In addition, the message structure can be designed on one side or two sides and each way has its own advantages and disadvantages. The best one-sided message for the public from the outset is biased towards the media’s point of view, while the two-sided argument is suitable for the opposing public with a better education.
2.3.4. Message form
The form of the message has the role of creating attention, interest and persuading the target audience. The form of the message includes decisions about the title, words, color, style of presentation, image, voice, speed, and rhythm. With each media will require an appropriate message form. Print advertising needs to focus on decisions about headlines, text, illustrations, and colors. If the message is broadcast on the radio, it is necessary to carefully choose words, voice and expression, etc.
2.4. Media.
Media is the form that communicators use to reach and communicate a message to a defined target audience.
It is divided into two types: direct channel and indirect channel Direct channel: consists of two or more individuals communicating directly with each other.
This channel is divided into three categories:
o Referral channel: includes sales staff of the business in direct contact with target customers.
o Expert channel: consists of experts speaking to the target public.
o Social channel: is the direct communication between groups of people in society called word of mouth.
Indirect channel: This channel conveys messages without direct contact or communication between the sender and receiver.
Indirect channels include:
o Mass media: such as publications, radio electronic media, display media.
o Atmosphere: a deliberately set setting intended to create or reinforce a tendency to purchase and consume a product.
o Events: are opportunities and occasions organized intentionally to communicate to key audiences such as exhibitions, conferences, etc.
2.5. Determine the media budget.
The process of determining a media budget is about answering three questions: how much does the promotional campaign cost, how is this money distributed, and how is it used to achieve communication goals?
Typically, media budgets are determined by the following four methods:
2.5.1. Based on the ability to budget for promotional communication.
Is a method based on the ability of the business to spend on promotional communication of the year is how much. This method does not allow for a specific budget, making long-term communication planning difficult.
2.5.2. Based on percentage of sales.
The budget is determined as a percentage of sales (for the year or projected) or of the selling price. This approach recognizes the media budget as a variable cost to sales, encouraging management to think of the relationship between promotional costs, selling price, and profit per unit. but the dependence of fluctuating budgets on fluctuations in annual consumption will interfere with long-term planning.
2.5.3. Competitive equilibrium method.
As a method of equalizing competitor costs, this method, while simple, is fraught with risks as businesses vary widely in reputation, resources, opportunities, and marketing objectives. If the opponent is stronger in resources, it will invest more and cause a media war, making both of them lose profits, even if we are weaker, we will lose credibility and collapse.
2.5.4. Methods are based on goals and tasks.
Based on your goals and tasks to achieve, how much will the company have to spend to make that promotional communication budget. This approach has the advantage of requiring management to articulate its assumptions about the relationship between total cost, exposure, trial rate, and frequency of use. However, this method is quite complicated.
2.6. Communication tool.
Communication tools are specific forms of media, including five common communication tools namely advertising, public relations, promotion, direct selling and direct marketing. Each tool has its own advantages and disadvantages, so the analysis of these tools will help businesses evaluate and choose the right tools for their communication strategy.
2.6.1 Advertising.
2.6.1.1. Concept.
Advertising is the use of media to introduce bank products and services to customers.
Nowadays advertising has become a necessary activity of business in general and of banks in particular. Advertising is both a means and a tool to connect commercial activities of commercial banks with the market.
Advertising not only helps the bank to sell more products, but also stimulates customers to form a demand for new products of the bank. In order to improve the effectiveness of advertising, banks need to clearly define advertising objectives, advertising requirements, advertising costs, selection of advertising media, and evaluation of advertising effectiveness.
In advertising activities, traditionally banks as well as businesses, mostly introduce themselves and praise themselves, which does not really create public trust in the bank. This is an issue that needs rethinking in the bank’s advertising strategy. From a modern perspective, if there is a third organization that has enough public trust or has a strong impact on the public to introduce the bank, the effectiveness of advertising will be better promoted.
Advertising features:
o Massiveness: because the message transmission is uniform, many people receive the same message and the buyer knows that everyone will understand their motivation to buy the product.
o Widespread: advertising is received by many people at the same time and is repetitive, so it has a wide impact on the target audience.
o Expressiveness: advertising can create popularity, beautiful images of products and businesses thanks to the effects of images, sounds, colors, ….
o Generality: reflected in whether the public can follow or not follow without any pressure because advertising is monologue and indirect.
Advertising is used to create a lasting image of a product or to stimulate rapid consumption, the advantage of which is to inform many geographically dispersed buyers at a low cost per exposure.
2.6.1.2 Build advertising program.
a. Define advertising goals.
Advertising is a tool of communication, so the goal of advertising is also to achieve the general goals of communication.
Advertising objectives can target the following:
Informational objectives: often used in the product introduction phase to explain information, product uses, describe available services; correct false impressions; make guests less afraid; or build a company image and ultimately gain a certain percentage of the public knowing about the product.
Persuasion Objective: Usually set when the company’s goal is to create selective demand. Persuasive advertising objectives may be to create brand preference; persuade customers to buy immediately; stimulate trial of the brand; change the customer’s view of the product’s use; convince customers to start trading.
Reminder goal: when the product is already well known to the general public and they have already consumed the product, but due to the emergence of new brands of similar products, otherwise remind customers of the existence of the product. products, new brands will appear in their mind, resulting in customers switching to those products, so it is necessary to remind customers that the product will be needed in the future, where the product is sold, help the product take the top position in the customer’s mind.
b. Determine your advertising budget.
Depending on the advertising goals set as well as the reputation of the product brand and the competitive environment to request an appropriate advertising budget. For example, the product launch stage often requires a higher advertising budget than the other stages. Also it depends on the company’s capabilities, can be determined by one of four methods such as determining the media budget but usually it is a percentage of the media budget. Or the total cost of the company’s planned advertising activities.
c. Message design.
An advertising message must express the content and ideas the sender wants to convey. But these content and ideas come from the expectations and benefits of the product that consumers are looking for. An advertising message is often required to be relevant, unique, and truthful, and easy to remember. An advertising message is not merely what to say but also how to be presented effectively, attracting the attention of viewers. Many studies show that usually people really only pay attention for the first 5 seconds. If after that 5 seconds, the ad is not really attractive, they will switch to another TV channel. The format of the message is as follows:
A lifetime sample: shows one or more people using the product under normal conditions.
Lifestyle: shows how well the product fits a lifestyle.
Imagination: creating novelty around the product or its use.
Music: have one or more people or cartoons sing a song about the product.
Personality icon: create a character as a symbol for the product.
Technical expertise: describe the company’s professionalism or product experience.
In addition, attention must be paid to the voice, rhythm, creativity, attraction and title in six types: news, questions, retellings, orders, numbering styles 1,2,3; what, how, why.
d. Deciding on advertising media.
Media selection factors
Quantitative factor:
o Scope of action: describes the vehicle’s ability to contact the object. The number of people using a media during a given period, usually determined by the program’s issue number or frequency.
Program rate = Number of households watching or listening to the program / Number of households with television or radio
Program rate = Number of households watching or listening to the program / Number of households watching TV or radio
o Play frequency: is the number of times that an advertisement appears during a particular period of a media plan.
o Overall rating point (GRP-Gross rating point): is a measure of the overall impact of an advertising medium
GRP = average range x average transmit frequency
When a campaign uses a variety of media, the ad unit calculates an overall rating for each set of media and then adds them together.
However, not every vehicle with a higher overall rating is used, but the overall rating is the basis for deciding which vehicle to invest in. At the same time it depends on the advertising objective. For example, a reminder advertisement would require a medium or program with a wide range rather than a high frequency.
Cost-effective (CPM-Cost per thousand): is a measure of how much an ad unit costs to advertise to reach a thousand people.
CPM = (Cost of Media / Number of Audiences Reached) x 1000
Qualifying factor:
In addition to quantitative measures, it also incorporates subjective assessments based on qualitative factors such as: the fit between the target market and the audience of the medium, the opportunity to expose for advertising, the opportunity to receive advertising….
Specialized media.
| The PTTT | Pros point | Cons point |
| Japan newspaper | Easy use, timely, disseminate wide in the local market, Okay wide acceptance, credibility trust high. | Quickly past, low print quality, little followers. |
| Ti Because | Conclude picture-sound-animation work. Captivating senses, vision enjoy high | Price high, hard to get to the right audience fake targeted, less selective, time time is too short |
| Letters live | Poison Selective mockup, easy to use, are not side by side with other ads pictures in the same letter, to specific individuals. | Price quite tall, has the image of “letter” void”. |
| radio | Grand them, population selectivity and geography High quality, low price. | Only sound, attractive least than television, crowded much advertisement. |
| Magazine lice | Degree population and geographic selection high, reputable and trustworthy. Substance quantity print well, last long, many people listen. | Are not secure posting position advertising fox. Takes time to Okay advertisement. |
| Outside God | Easy used, cheap, less competitive, repeat again many times. | Are not select viewers. |
Maybe you are interested!
-
 Promotional communication solution for Success card of Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development - 1
Promotional communication solution for Success card of Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development - 1 -
 Brief History Of Formation And Development Of Hai Chau Bank For Agriculture And Rural Development .
Brief History Of Formation And Development Of Hai Chau Bank For Agriculture And Rural Development . -
 Functions And Tasks Of Hai Chau Bank For Agriculture And Rural Development.
Functions And Tasks Of Hai Chau Bank For Agriculture And Rural Development. -
 The Position Of Bank For Agriculture And Rural Development Of Vietnam In The Market Compared To Competitors.
The Position Of Bank For Agriculture And Rural Development Of Vietnam In The Market Compared To Competitors. -
 Promotional communication solution for Success card of Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development - 6
Promotional communication solution for Success card of Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development - 6 -
 Promotional communication solution for Success card of Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development - 7
Promotional communication solution for Success card of Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development - 7