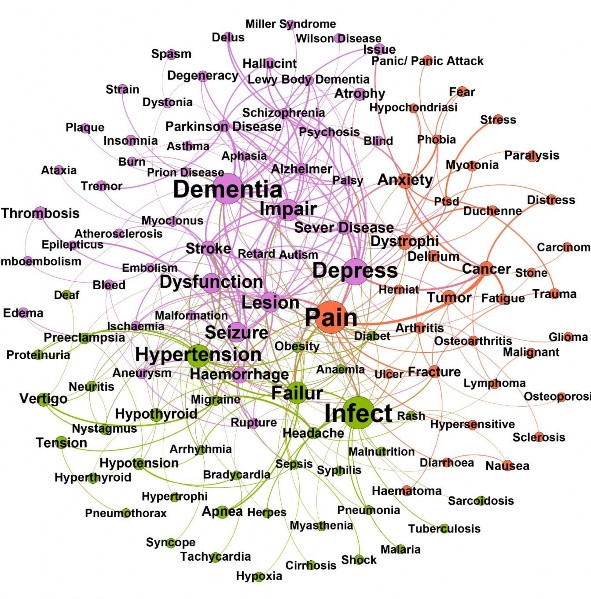
Hình 3. 12. Mạng tương tác Bệnh và Triệu chứng của tập dữ liệu Thần kinh
Mạng tương tác Bệnh và Triệu chứng của tập dữ liệu Thần kinh có 131 thực thể và 360 kết nối. Chúng được chia làm 3 nhóm. Nhiễm khuẩn (Infect), đau (Pain), mất trí (Dementia) thuộc 3 nhóm có kích thước lớn nhất.
Dựa vào Bảng 3.16., đối với tập dữ liệu Thần kinh, tăng huyết áp (Hypertension)- đột quỵ (Stroke), nhiễm khuẩn (Infect)- đột quỵ, ác tính (Malignant)- gãy xương (Fracture), chấn thương (Trauma)- gãy xương, cơn sốt (Fever)- phát ban (Rash) là những cặp liên quan có trọng số lớn nhất.
Bảng 3.16. Bảng thống kê giá trị tương tác giữa Bệnh và Triệu chứng của tập dữ liệu Thần kinh
Stroke | Arthritis | Carcinoma | Fracture | Rash | |
Hypertension | 7.74 | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.54 | 0.38 |
Infect | 3.31 | 1.28 | 0.53 | 2.69 | 0.86 |
Malignant | 0.45 | 0.39 | 0.46 | 0.98 | 0.15 |
Trauma | 1.08 | 0.33 | 0.25 | 2.34 | 0.13 |
Fever | 0.62 | 015 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 1.51 |
Có thể bạn quan tâm!
-
 Mạng Tương Tác Y Học Dưới Góc Nhìn Toàn Cảnh Của Tập Dữ Liệu Gốc
Mạng Tương Tác Y Học Dưới Góc Nhìn Toàn Cảnh Của Tập Dữ Liệu Gốc -
 Mạng Tương Tác Y Học Dưới Góc Nhìn Toàn Cảnh Của Tập Dữ Liệu Thần Kinh
Mạng Tương Tác Y Học Dưới Góc Nhìn Toàn Cảnh Của Tập Dữ Liệu Thần Kinh -
 Mạng Tương Tác Triệu Chứng Và Cơ Quan Của Tập Dữ Liệu Thần Kinh
Mạng Tương Tác Triệu Chứng Và Cơ Quan Của Tập Dữ Liệu Thần Kinh -
 Bước đầu xây dựng mạng tương tác y học áp dụng trí tuệ nhân tạo lên dữ liệu sách y khoa của Đại học Oxford - 8
Bước đầu xây dựng mạng tương tác y học áp dụng trí tuệ nhân tạo lên dữ liệu sách y khoa của Đại học Oxford - 8
Xem toàn bộ 73 trang tài liệu này.
CHƯƠNG 4: KẾT LUẬN
Nghiên cứu đã đề xuất một phương pháp xây dựng mạng tương tác Y học trên các tập dữ liệu là các sách giáo khoa Y học của Đại học Oxford với sự hỗ trợ của các phương pháp học máy của trí tuệ nhân tạo. Cụ thể, với các thuật toán như kiểm định thống kê t-test, PageRank, chúng tôi đã xây dựng được các mạng tương tác tương thích với tri thức Y học.
Nghiên cứu này được thực hiện bằng việc thu thập được 97 đầu sách và chúng cũng được xếp vào 3 nhóm nhỏ hơn: Tim mạch, Thần kinh, Nội tiết. Vậy với 4 tập dữ liệu và 3 loại mạng: mạng tổng thể, Triệu chứng- Cơ Quan, Bệnh- Triệu chứng, chúng tôi thu thập được 12 mạng. Chúng phản ánh được sự liên quan giữa các thực thể và tính chất của chúng thông qua kích thước và màu sắc giữa các thực thể.
Và nghiên cứu cũng đã đánh giá định tính được hiệu quả của mạng tương tác nhờ giá trị tương tác giữa các thực thể trong mỗi tập dữ liệu. Tuy nhiên, sự liên quan giữa các thực thể trong từng mạng lại có trọng số khác nhau cho thấy được đặc trưng trong từng lĩnh vực.
Thông qua nghiên cứu này, chúng tôi kỳ vọng đóng góp một phương pháp xây dựng các mạng tương tác biểu diễn tri thức Y học một cách toàn diện và hiệu quả, hỗ trợ cho các bác sĩ trong chẩn đoán và bệnh nhân trong việc tiếp cận các thông tin Y khoa. Bên cạnh đó, ứng dụng của nghiên cứu này còn mở ra nhiều triển vọng trong liên ngành Y sinh- tin học.
TÀI LIỆU THAM KHẢO
1. Ai, Qingyao, et al. (2018), "Learning heterogeneous knowledge base embeddings for explainable recommendation", Algorithms. 11(9), p. 137.
2. Anand, Gyanesh (2020), "Knowledge Graphs in Medical Domain".
3. Barnett, G. O., et al. (1987), "DXplain. An evolving diagnostic decision- support system", JAMA. 258(1), pp. 67-74.
4. Bhbosale, S, Pujari, V, and Multani, Z (2020), "Advantages And Disadvantages Of Artificial Intellegence", Aayushi International Interdisciplinary Research Journal, pp. 227-230.
5. Bisson, L. J., et al. (2014), "Accuracy of a computer-based diagnostic program for ambulatory patients with knee pain", Am J Sports Med. 42(10), pp. 2371- 6.
6. Cheng, Binjie, et al. (2021), "Research on medical knowledge graph for stroke", Journal of Healthcare Engineering. 2021.
7. Ernst, Patrick, et al. (2014), Knowlife: a knowledge graph for health and life sciences, 2014 IEEE 30th International Conference on Data Engineering, IEEE, pp. 1254-1257.
8. Gann, B (2012), "Giving patients choice and control: health informatics on the patient journey", Yearbook of medical informatics. 21(01), pp. 70-73.
9. Gunn, AA (1976), "The diagnosis of acute abdominal pain with computer analysis", Journal of the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh. 21(3), pp. 170-172.
10. Ji, Bin, et al. (2019), "A hybrid approach for named entity recognition in Chinese electronic medical record", BMC medical informatics and decision making. 19(2), pp. 149-158.
11. Jupyter Notebook, accessed 19-4-2022, from http://localhost:8888/tree.
12. Kovacevic, A., et al. (2013), "Combining rules and machine learning for extraction of temporal expressions and events from clinical narratives", J Am Med Inform Assoc. 20(5), pp. 859-66.
13. Ledley, Robert S and Lusted, Lee B (1959), "Reasoning foundations of medical diagnosis", Science. 130(3366), pp. 9-21.
14. Li, Fei, et al. (2019), "Fine-tuning bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT)–based models on large-scale electronic health record notes: an empirical study", JMIR medical informatics. 7(3), p. e14830.
15. Li, Haodi, et al. (2017), "CNN-based ranking for biomedical entity normalization", BMC bioinformatics. 18(11), pp. 79-86.
16. Li, Linfeng, et al. (2019), "PrTransH: embedding probabilistic medical knowledge from real world EMR data".
17. Li, Linfeng, et al. (2020), "Real-world data medical knowledge graph: construction and applications", Artificial intelligence in medicine. 103, p. 101817.
18. Lou, Yinxia, et al. (2017), "A transition-based joint model for disease named entity recognition and normalization", Bioinformatics. 33(15), pp. 2363-2371.
19. Luo, Ling, et al. (2018), "An attention-based BiLSTM-CRF approach to document-level chemical named entity recognition", Bioinformatics. 34(8), pp. 1381-1388.
20. Lusted, L. B. (1955), "Medical electronics", N Engl J Med. 252(14), pp. 580- 5.
21. Middleton, B., et al. (1991), "Probabilistic diagnosis using a reformulation of the INTERNIST-1/QMR knowledge base. II. Evaluation of diagnostic performance", Methods Inf Med. 30(4), pp. 256-67.
22. Miller, R. A. (1994), "Medical diagnostic decision support systems--past, present, and future: a threaded bibliography and brief commentary", J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1(1), pp. 8-27.
23. Ramesh, AN, et al. (2004), "Artificial intelligence in medicine", Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England. 86(5), p. 334.
24. Ramos, Eduardo (2017), The Open Graph Viz Platform, accessed 1-4-2022, from https://gephi.org/.
25. Rotmensch, Maya, et al. (2017), "Learning a health knowledge graph from electronic medical records", Scientific reports. 7(1), pp. 1-11.
26. Shapiro, Stuart C (1992), Encyclopedia of artificial intelligence second edition, John.
27. Shi, Longxiang, et al. (2017), "Semantic health knowledge graph: semantic integration of heterogeneous medical knowledge and services", BioMed research international. 2017.
28. Shwe, M. A., et al. (1991), "Probabilistic diagnosis using a reformulation of the INTERNIST-1/QMR knowledge base. I. The probabilistic model and inference algorithms", Methods Inf Med. 30(4), pp. 241-55.
29. Tang, Buzhou, et al. (2013), Recognizing clinical entities in hospital discharge summaries using Structural Support Vector Machines with word representation features, BMC medical informatics and decision making, BioMed Central, pp. 1-10.
30. Tang, Hangwi and Ng, Jennifer Hwee Kwoon (2006), "Googling for a diagnosis—use of Google as a diagnostic aid: internet based study", Bmj. 333(7579), pp. 1143-1145.
31. Vinay K. Chaudhri, Naren Chittar, Michael Genesereth (2021), An Introduction to Knowledge Graphs, Editor^Editors.
32. Wang, Meng, et al. (2017), "Safe medicine recommendation via medical knowledge graph embedding", ArXiv e-prints, p. arXiv: 1710.05980.
33. Wang, Rui, et al. (2019), "Knowledge graph embedding via graph attenuated attention networks", IEEE Access. 8, pp. 5212-5224.
34. Winter, First AI and Amendment, Mansfield (2003), "Lighthill report* Crevier 1993", Russell & Norvig, p. 22.
35. Zhang, Yu, et al. (2018), "Clinical named entity recognition from Chinese electronic health records via machine learning methods", JMIR medical informatics. 6(4), p. e9965.
36. Zhukovsky, KV (2015), "A method of inverse differential operators using ortogonal polynomials and special functions for solving some types of differential equations and physical problems", Moscow University Physics Bulletin. 70(2), pp. 93-100.
37. Zou, Xiaohan (2020), A survey on application of knowledge graph, Journal of Physics: Conference Series, IOP Publishing, p. 012016.
PHỤ LỤC
Phụ lục 1: Thông tin các đầu sách giáo trình của Oxfords Tập dữ liệu gốc
Tên Sách | Số trang | Số từ | Số trang sau tiền xử lý | Tổng số từ sau tiền xử lý | |
1 | Oxford American Handbook of Cardiology | 658 | 164,638 | 355 | 22,326 |
2 | Oxford American handbook of clinical pharmacy | 752 | 173,881 | 359 | 22,563 |
3 | Oxford American Handbook of Disaster Medicine | 801 | 183,485 | 365 | 27,131 |
4 | Oxford American handbook of endocrinology and diabetes | 697 | 167,800 | 510 | 32,103 |
5 | Oxford American Handbook of Hospice and Palliative Medicine and Supportive Care | 469 | 136,881 | 268 | 20,764 |
6 | Oxford American Handbook of Neurology | 431 | 87,408 | 143 | 4,518 |
7 | Oxford American Handbook of Oncology | 799 | 168,712 | 310 | 19,883 |
8 | Oxford American Handbook of Rheumatology | 576 | 153,416 | 385 | 30,466 |
9 | Oxford Handbook for the Foundation Programme | 597 | 204,661 | 418 | 26,048 |
10 | Oxford Handbook of Anaesthesia | 1,280 | 322,447 | 902 | 73,061 |
11 | Oxford handbook of cardiac nursing | 381 | 93,096 | 253 | 15,222 |
12 | Oxford handbook of cardiology | 829 | 196,899 | 537 | 39,629 |
13 | Oxford Handbook of Children's and Young People's Nursing | 994 | 202,015 | 458 | 33,513 |
14 | Oxford Handbook of Clinical and Healthcare Research | 570 | 169,369 | 336 | 29,205 |
15 | Oxford Handbook of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation | 956 | 201,320 | 327 | 17,393 |
16 | Oxford Handbook of Clinical Dentistry | 768 | 209,109 | 444 | 29,763 |
17 | Oxford Handbook of Clinical Diagnosis | 641 | 148,355 | 287 | 16,741 |
18 | Oxford Handbook of Clinical Examination and Practical Skills | 733 | 159,134 | 282 | 12,828 |
19 | Oxford Handbook of Clinical Haematology | 794 | 185,896 | 342 | 21,485 |
20 | Oxford Handbook of Clinical Immunology and Allergy | 614 | 164,980 | 374 | 18,382 |
21 | Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine | 852 | 362,488 | 678 | 70,255 |
22 | Oxford handbook of clinical pathology | 350 | 77,381 | 274 | 15,918 |
23 | OXFORD HANDBOOK OF CLINICAL PHARMACY | 678 | 202,440 | 424 | 26,700 |
24 | Oxford handbook of clinical skills for children's and young people's nursing | 585 | 170,572 | 481 | 39,951 |
25 | Oxford Handbook of Clinical Specialties | 817 | 407,303 | 709 | 76,151 |
26 | Oxford Handbook of Clinical Surgery | 776 | 183,799 | 436 | 23,054 |
27 | Oxford handbook of critical care | 656 | 119,917 | 224 | 14,379 |
28 | Oxford handbook of critical care nursing | 516 | 105,677 | 180 | 10,069 |
29 | Oxford Handbook of Dental Nursing | 387 | 88,287 | 245 | 15,449 |
30 | Oxford Handbook of Dental Patient Care | 680 | 147,268 | 304 | 20,151 |
31 | Oxford handbook of dialysis | 657 | 142,923 | 268 | 17,202 |
Oxford handbook of emergency medicine | 735 | 234,903 | 604 | 52,610 | |
33 | Oxford Handbook of Emergency Nursing | 793 | 179,506 | 356 | 18,234 |
34 | Oxford handbook of endocrinology and diabetes | 880 | 152,468 | 244 | 10,700 |
35 | Oxford handbook of epidemiology for clinicians | 283 | 80,451 | 217 | 16,111 |
36 | Oxford Handbook of Expedition and Wilderness Medicine | 811 | 208,048 | 443 | 29,727 |
37 | Oxford handbook of forensic medicine | 555 | 166,171 | 429 | 32,231 |
38 | Oxford Handbook of Gastrointestinal Nursing | 711 | 144,937 | 332 | 25,468 |
39 | Oxford handbook of geriatric medicine | 683 | 192,085 | 541 | 36,469 |
40 | Oxford handbook of infectious diseases and microbiology | 849 | 295,357 | 723 | 57,766 |
41 | Oxford handbook of key clinical evidence | 923 | 237,247 | 514 | 29,026 |
42 | Oxford handbook of medical dermatology | 671 | 180,604 | 394 | 24,597 |
43 | Oxford Handbook of Medical Imaging | 429 | 71,952 | 218 | 13,117 |
44 | Oxford Handbook of Medical Sciences | 940 | 218,702 | 439 | 25,934 |
45 | Oxford Handbook of Medical Statistics | 483 | 112,193 | 207 | 12,574 |
46 | Oxford handbook of mental health nursing | 400 | 89,796 | 183 | 11,293 |
47 | Oxford Handbook of Midwifery | 728 | 201,073 | 517 | 42,701 |
48 | Oxford Handbook of Neonatology | 542 | 102,508 | 154 | 5,804 |
49 | Oxford Handbook of Nephrology and Hypertension | 956 | 269,471 | 783 | 62,834 |
50 | Oxford handbook of neurology | 503 | 69,313 | 98 | 4,897 |
51 | Oxford handbook of nutrition and dietetics | 745 | 191,258 | 522 | 42,358 |
52 | Oxford Handbook of Obstetrics and Gynaecology | 798 | 166,005 | 516 | 32,964 |
53 | Oxford handbook of occupational health | 833 | 185,082 | 550 | 39,116 |
54 | Oxford Handbook of Operative Surgery | 1,010 | 210,842 | 385 | 19,232 |
55 | Oxford Handbook of Ophthalmology | 1,157 | 255,814 | 485 | 26,447 |
56 | Oxford handbook of paediatrics | 1,045 | 223,235 | 437 | 22,124 |
57 | Oxford handbook of pain management | 358 | 96,921 | 275 | 19,431 |
58 | Oxford handbook of palliative care | 1,016 | 269,283 | 535 | 36,068 |
59 | Oxford handbook of pre-hospital care | 706 | 111,927 | 169 | 10,369 |
60 | -Oxford handbook of primary care and community nursing | 801 | 219,191 | 525 | 43,361 |
61 | Oxford Handbook of Psychiatry | 1,042 | 302,525 | 700 | 55,032 |
62 | Oxford handbook of public health practice | 582 | 195,793 | 461 | 41,070 |
63 | Oxford Handbook of Renal Nursing | 574 | 136,297 | 392 | 26,586 |
64 | Oxford Handbook of Reproductive Medicine and Family Planning | 375 | 85,533 | 208 | 12,154 |
65 | Oxford Handbook of Respiratory Medicine | 822 | 192,504 | 427 | 29,566 |
66 | Oxford Handbook of Respiratory Nursing | 643 | 135,801 | 239 | 12,294 |
67 | Oxford handbook of sport and exercise medicine | 740 | 184,166 | 515 | 41,326 |
68 | Oxford handbook of surgical nursing | 746 | 195,844 | 394 | 22,369 |
69 | Oxford Handbook of Urology | 819 | 206,573 | 463 | 33,963 |
70 | Oxford Textbook of Anaesthesia for the Elderly Patient | 304 | 276,253 | 291 | 60,872 |
71 | Oxford Textbook of Cardiothoracic Anaesthesia | 475 | 327,561 | 424 | 73,603 |
72 | Oxford textbook of children’s sport and exercise medicine | 669 | 602,643 | 616 | 158,373 |
73 | Oxford Textbook of Clinical Nephrology | 2,921 | 2,280,647 | 2,736 | 644,293 |
74 | Oxford textbook of clinical neurophysiology | 448 | 299,366 | 365 | 69,682 |
32
Oxford textbook of cognitive neurology and dementia | 470 | 369,194 | 427 | 90,143 | |
76 | Oxford textbook of communication in oncology and palliative care | 420 | 342,045 | 388 | 82,676 |
77 | Oxford Textbook of Critical Care | 1,877 | 1,186,821 | 1,614 | 307,293 |
78 | Oxford Textbook of Epilepsy and Epileptic Seizures | 377 | 346,459 | 354 | 74,841 |
79 | Oxford Textbook of Global Public Health | 1,615 | 1,460,769 | 1,553 | 401,967 |
80 | Oxford Textbook of Neuromuscular Disorders | 366 | 262,578 | 330 | 58,271 |
81 | Oxford Textbook of Neurorehabilitation | 439 | 356,234 | 408 | 91,047 |
82 | Oxford textbook of obstetric anaesthesia | 895 | 693,891 | 831 | 168,953 |
83 | Oxford Textbook of Old Age Psychiatry | 821 | 810,964 | 782 | 201,600 |
84 | Oxford Textbook of Oncology | 973 | 809,119 | 912 | 209,991 |
85 | Oxford Textbook of Osteoarthritis and Crystal Arthropathy | 497 | 367,310 | 422 | 94,592 |
86 | Oxford Textbook of Palliative Care for Children | 853 | 446,636 | 779 | 101,090 |
87 | Oxford Textbook of Palliative Medicine | 1,228 | 1,008,084 | 1,135 | 255,163 |
88 | Oxford Textbook of Palliative Nursing | 1,351 | 964,682 | 1,211 | 248,429 |
89 | Oxford Textbook of Palliative Social Work | 781 | 578,928 | 714 | 155,390 |
90 | Oxford Textbook of Psychiatry | 2,019 | 1,855,737 | 1,961 | 471,315 |
91 | Oxford textbook of public health | 3,890 | 1,615,588 | 3,535 | 439,593 |
92 | Oxford Textbook of Rheumatology | 1,475 | 1,158,986 | 1,396 | 293,182 |
93 | Oxford textbook of sleep disorders | 527 | 402,235 | 462 | 101,092 |
94 | Oxford textbook of stroke and cerebrovascular disease | 278 | 242,165 | 270 | 53,769 |
95 | Oxford Textbook of Vasculitis | 655 | 512,015 | 597 | 139,470 |
96 | Oxford Textbook of Vertigo and Imbalance | 345 | 256,532 | 317 | 56,895 |
97 | Oxford textbook of violence prevention _ epidemiology, evidence, and policy | 327 | 228,120 | 269 | 57,039 |




