The ratio of short-term loans to SMEs on mobilized capital reflects the ability of the Branch to lend short-term loans to SMEs on mobilized capital. From the table, we can see that short-term loans to SMEs account for a very large proportion of the branch’s total mobilized capital. This target is achieved as follows: in 2009 it was 78.86%; in 2010 was 82.34% ; in 2011 was 75.69%. Thus, it can be seen that short-term lending to SMEs is the main lending activity of BIDV Quang Tri. However, this ratio too high is also not good for the Branch.
– Firstly, when investing in a field that is too large, then the diversification of investment will be very low, leading to risks for the Branch when the economy has some disadvantage.
– Second, the large concentration of short-term loans to SMEs will also affect the structure of capital mobilization to match short-term lending activities and ensure interest payment for customers depositing next to them. It also generates profits for the Branch.
2.2.9. Credit cycle analysis
Table 2.14: Credit turnover (2009 – 2011)
Unit: Billion VND
| Items | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 |
| SME debt collection | 1066.02 | 1672.37 | 2225.7 |
| Average outstanding loans SME | 557.96 | 802.92 | 1009.37 |
| SME credit turnover (round) | 1,911 | 2.083 | 2.205 |
Maybe you are interested!
-
 The main solution to improve the quality of short-term loans for small and medium-sized enterprises at Bank for Investment and Development - 1
The main solution to improve the quality of short-term loans for small and medium-sized enterprises at Bank for Investment and Development - 1 -
 The main solution to improve the quality of short-term loans for small and medium-sized enterprises at Bank for Investment and Development - 2
The main solution to improve the quality of short-term loans for small and medium-sized enterprises at Bank for Investment and Development - 2 -
 Chapter 2: Assessment Of Quality Of Short-Term Living Activities For Small And Small Enterprises At Bank For Investment And Development Of Vietnam – Quang Tri Branch
Chapter 2: Assessment Of Quality Of Short-Term Living Activities For Small And Small Enterprises At Bank For Investment And Development Of Vietnam – Quang Tri Branch -
 Labor Situation During The Period 2009 – 2011, The Labor Situation Of Bank For Investment And Development Of Vietnam – Quang Tri Branch Was Constantly Increasing In Quantity And Quality.
Labor Situation During The Period 2009 – 2011, The Labor Situation Of Bank For Investment And Development Of Vietnam – Quang Tri Branch Was Constantly Increasing In Quantity And Quality. -
 Analysis Of Total Loan Profit On Average Total Outstanding Balance
Analysis Of Total Loan Profit On Average Total Outstanding Balance -
 The main solution to improve the quality of short-term loans for small and medium-sized enterprises at Bank for Investment and Development - 7
The main solution to improve the quality of short-term loans for small and medium-sized enterprises at Bank for Investment and Development - 7
This indicator measures the speed of capital turnover of the branch, reflecting how quickly or slowly the loan capital is turned over. The higher the turnover ratio, the better debt collection, the investment capital is not stagnant and improves the efficiency of capital use.
Based on the above data, it can be seen that the credit turnover for SMEs is relatively high at around 2 rounds in the period 2009 – 2011. This is because after the 2008 crisis, the Branch restricted long-term loans. For SMEs, the average loan balance decreases while the debt collection volume increases. Therefore, the credit turnover in 2009 is 1,911 rounds. By 2010, the Branch had started to make long-term loans to SMEs, leading to a rapid increase in average outstanding loans, so the growth rate of SME credit turnover still increased but tended to slow down, reaching 2,083 rounds and 2,205 respectively. rounds in 2010 and 2011.
Table 2.15 : Short-term credit turnover of SMEs (2009 – 2011)
Item 2009 2010 2011
| Revenue from short-term debt collection SMEs | 671.25 | 1134.34 | 1476.52 |
| Average short-term debt balance SMEs | 446.02 | 618.505 | 758.15 |
| SME short-term credit turnover (round) | 1.505 | 1.834 | 1,948 |
In 2009, when the Branch restricted long-term lending to SMEs, it switched to focusing on short-term loans. This caused the average balance of short-term loans to SMEs in 2009 to increase dramatically, so the short-term SME credit turnover at 1,505 rounds was lower than the SME credit turnover.
However, in 2010 this ratio tends to increase gradually and is close to the SME credit turnover, in 2011 because the effect of the growth rate of short-term debt collection SME is much larger than the growth rate. increase in average short-term loans to SMEs. Specifically, the short-term credit turnover of SMEs in 2010 was 1,834 rounds and in 2011 was 1,948 rounds.
Through the above data table and analysis, we can see that the short-term credit turnover of SMEs has been more or less affected by the change of the branch’s lending strategy to SMEs. Although it is increasing over the years from 2009 to 2011 showing an increase in short-term lending efficiency, it is still low compared to SME credit turnover, so measures are needed to improve the turnover rate. more short-term loans.
2.3. Evaluation of the quality of short-term lending activities for small and medium-sized enterprises at Bank for Investment and Development of Vietnam – Quang Tri Branch
Through the analysis and evaluation of each criterion, I give an overview of the quality of short-term loans to small and medium-sized enterprises at Bank for Investment and Development of Vietnam – Quang Tri Branch in the period 2009 – 2011 through SWOT matrix.
3. CHAPTER 3: MAJOR SOLUTIONS TO ENHANCE THE QUALITY OF SHORT-TERM LOANS FOR SMALL AND SME ENTERPRISE AT BANK FOR INVESTMENT AND DEVELOPMENT OF VIETNAM – QUANG TRI BRANCH
3.1. Solutions to promote strengths to seize opportunities
Currently, BIDV’s lending process for corporate customers is very strict. Clearly defining the responsibilities and functions of each department in each step should have well limited overdue debt. With the current competitive economic situation, banks have to seize their own business opportunities. Therefore, branches should simplify loan procedures, reduce loan processing time, and cut costs. reduce unnecessary steps but still have to be on the basis of credit safety.
– Improve the lending process to shorten the loan period and improve the quality of customer service.
The bank should set up a data center on businesses in the area that have registered for operation (linked with the Department of Planning and Investment, the Department of Taxation) to provide a list of businesses, as well as tax codes, operating capital, etc. regulations, … When businesses come to borrow capital, the credit officers only need to submit and process some other documents (economic contracts, invoices…).
The number of documents when doing procedures is too complicated, so simplifying by cutting some unnecessary papers can be reduced.
3.2. Solutions to promote strengths and reduce risks
With loan products and services short-term enterprises are relatively diverse and can serve the borrowing needs of enterprises. Marketing activities are activities that have a great influence on loan expansion. Currently, almost all marketing activities at the Branch do not have a specialized department, only doing general work, so it has not created competitiveness for the Branch.
Establishing and developing a Marketing department
The Branch established and developed a specialized department in the field of marketing in order to capture the market share of deposits as well as loans and promote the branch’s brand in the locality. Actively seek and establish credit relationships with new units, not passively waiting for customers to apply for a loan.
The fact that a bank introduces a new product that creates an advantage for the bank is only temporary in a relatively short time, it is easy for other competitors to imitate and provide similar products. . Therefore, the marketing department must constantly search for customers’ tastes in general and the short-term needs of SMEs in particular to offer products and services that meet customer needs. branch in the province.
In addition, the Branch expressed its interest in SMEs and always sought ways to create comfort for customers every time they came to the bank. By way, the Branch should organize a customer conference every year to receive customers’ opinions on problems in credit, service attitude of the Bank’s officers and employees, etc., so that the Branch can be timely. fix, adjust and perfect.
In addition, it also helps the Branch understand its investment goals and needs, proactively advise customers on production expansion (open more industries to take advantage of existing resources, introduce new technologies, etc.) ) to develop more borrowing needs.
3.3. Solutions to overcome weaknesses to take advantage of opportunities
– Improve credit policy, suitable to the current situation of small and medium enterprises:
Banks diversify forms of credit guarantees to adapt to the characteristics of SMEs. Loan guarantee policy:
Banks can consider projects that are feasible, effective, have the ability to repay, boldly lend without collateral or with only 50% of the loan amount.
And allows businesses to mortgage with assets formed from loans.
In the coming time, when the Credit Guarantee Fund comes into operation, businesses will have more opportunities with loans from banks.
Application of flexible security measures: BIDV needs to flexibly apply various forms of loan security such as pledged assets, mortgages, third-party guarantees, assets formed from loans, inventory of raw materials, etc. warehouse, shipment management, debt collection rights, etc., combined with unsecured lending on the basis of the effectiveness of the investment project/business plan and the business ranking results.
3.4. Solutions to overcome weaknesses to prevent threats
In order to reduce the ratio of short-term loans to SMEs to mobilized capital in order to diversify investment fields, the Branch must take measures to increase mobilized capital. – Branches that need to expand more transaction offices in Lao Bao districts and Quang Tri town:
Lao Bao is a large commercial center that is growing more and more with many supermarkets, and commercial centers of neighboring countries such as Laos, Thailand … domestic and provincial customers often go back and forth. many businesses were born, but there is not a single BIDV office there.
Quang Tri town is the second center of the province after Dong Ha city, developing mainly in agriculture and commerce but still does not have BIDV’s office, many customers in Quang Tri town have relationships with BIDV. have to travel a long distance to get to the branch, thus causing disadvantages to customers.
Branches need to study locations to set up more representative offices in those districts. However, it is necessary to consider the cost of establishment, to ensure that the apparatus must be very streamlined, the service is adequate to ensure the goal of expanding the deposit mobilization network of many subjects.
In addition, the Branch should develop the receipt and payment of savings deposits at home at the request of customers via telephone, Internet. Because these forms will meet the needs of customers who want to avoid the risk of carrying on the road.
– Strengthening measures to prevent risks (especially for Group 5 debt).
Strengthen the ability to prevent and control risks in lending activities. To prevent risks, the Branch annually makes a provision for risks. The amount of provision for risks is deducted at a certain rate for each group of debts and is used to compensate for the occurrence of risks. For group 5 debts, the provision of 100% may still have other losses that have not been provisioned, such as costs of pursuing litigation, handling security assets, etc. Therefore, it is necessary to set a provision greater than 0% for group 1 debts and more than 100% for group 5 debts.
In monitoring loan utilization, loan officers should also be on the lookout for problem loans, such as signs that a problem loan is usually:
– The enterprise is late to repay loans and principals to customers.
– Reduced deposit balance.
There is a change in the management structure of the enterprise.
– Enterprises delay submitting periodic reports. Increase in receivables (because that means the business has not yet collected money).
When detecting the above signs, the branch should notify and coordinate with the enterprise to take timely measures to solve the above situations, overcome difficulties in business operations of the enterprise.
– Strengthening internal control. In order to improve credit quality in general and short-term credit in particular, the Branch is not only interested in expanding credit activities but also must pay due attention to inspection and control to reduce overdue debts and doubtful debts.
The mentioned inspection and control work is not merely to check customers, but more importantly, it is necessary to inspect and supervise the work of credit officers and leaders to help them fully comply. fully in accordance with professional processes and regulations, ensuring safe and effective business in accordance with the law. Therefore, regularly inspecting and evaluating, cultivating ethics for employees: whatever it is, it is necessary to have professional ethics and a high sense of responsibility in an environment that is easy to be tempted by money. coax. For officials who violate ethics, it is necessary to have strict handling measures to avoid the next case.
– Continuously improve the quality of staff. Regularly create conditions for staff to study, improve their professional qualifications and understanding in banking operations and the current economic situation. Organize training courses on credit operations, appraisal… Depending on the objectives, the fields of financing, the credit sectors account for a large proportion of the banking sector (such as the construction industry, commerce, etc.), but organize training for staff specialized in that field. With this solution, it is possible to reduce work pressure for staff, improve analysis skills, and limit subjective risks.
There is a clear reward and discipline policy for employees.
Thereby, improving the sense of responsibility, limiting the negative arising from the staff.
PART III: CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
1. CONCLUSION
1.1. Achievements of the topic
– Synthesize issues on the theoretical basis of SMEs and short-term SME lending activities of commercial banks.
– Analyze data collected from Bank for Investment and Development of Vietnam – Quang Tri Branch using many methods to make assessments on each indicator showing short-term SME lending activities at BIDV Quang Treat. – Overall assessment of short-term SME lending quality of Bank for Investment and Development – Quang Tri Branch through SWOT matrix. From there, some key solutions are proposed to improve the quality of short-term loans for SMEs at BIDV Quang Tri. 1.2. Limitations and directions of topic development – Limitations:
During the research process, the study still encountered some limitations:
– The judgment is subjective in nature, so it may not be highly accurate. Limited knowledge and time, so they have not studied deeply and in detail for each issue to have more accurate assessments.
Theme development direction:
– Due to time and knowledge limitations, the thesis is only conducted based on past secondary data on the situation of short-term SME loans from the Bank for Investment and Development of Vietnam – Quang Tri Branch. In my opinion, it is advisable to carry out surveys, investigate the Branch’s customers and competitors’ customers to get more objective and accurate assessments. From there, practical solutions can be given to improve the quality of short-term loans to SMEs at BIDV Quang Tri Branch. 2. RECOMMENDATIONS
The success of BIDV Quang Tri Branch will contribute to the overall success of BIDV Vietnam. Therefore, in order to improve the quality of short-term SME loans of BIDV Quang Tri Branch, the Bank for Investment and Development should focus on a number of issues:
– The Bank for Investment and Development of Vietnam needs to invest and develop technology in a synchronous and modern manner, creating a foundation for branches and transaction offices to widely develop credit activities, attracting customers. goods to transact with the Bank. Regularly open training courses to improve professional qualifications as well as customer communication skills for bank staff. Additional legal knowledge for employees to help employees recognize scams.
The Head Office must regularly monitor and check the operation of the branches to take timely measures to correct errors in the operation process.
LIST OF REFERENCES
1. Dr. Nguyen Minh Kieu (2009), Commercial banking, Statistical Publishing House.
2. Decision 1138/QD-HĐQT dated November 11, 2011 of BIDV’s Board of Directors on guiding the implementation of credit policy for corporate customers.
3. Decree No. 56/2009/ND-CP of the Government on support for the development of small and medium enterprises. 4. Regulation No. 493/QD-NHNN of the State Bank on debt classification, provisioning, and use of provisions.
5. Law on Credit Institutions 2010
6. Law on State Bank of Vietnam 2010
7. Use of websites:
– www.bidv.com.vn
– www.vneconomy.vn
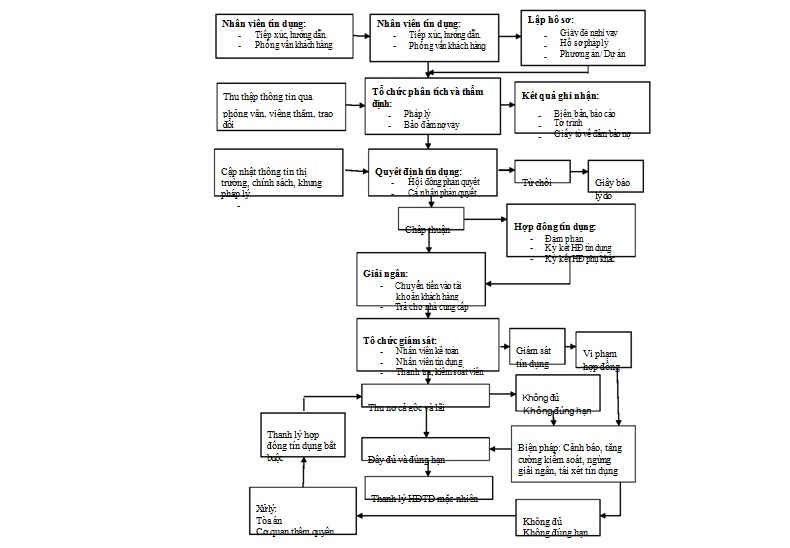
APPENDIX 1: DESCRIPTION OF CREDIT PROCESS
APPENDIX 2: APPLICATIONS, SIZE AND ORIGINAL DEBT AND LOAN OF SHORT-TERM LOANS OF ENTERPRISE
– Loan by item (Lending in installments)
– Subjects of application:
– Enterprises borrow capital on a regular basis. These customers often have unstable income or businesses that use equity and trade credit mainly, only when there is a need to cover temporary financial shortfalls or expand production. bank’s capital only participates in a certain stage of the business cycle.
– Enterprises borrow capital regularly, but are not eligible for a credit line.
– Usually requires the customer to have a guarantee.
Loan amount: Determined based on the customer’s needs, in addition, based on the value of the collateral, the customer’s ability to repay the debt, the customer’s ability to source capital, and the amount of the loan. in accordance with the law and the lending bank.
– Debt repayment rate and repayment term: For the form of loan by item, it can be determined on the basis of each production and business cycle and the revenue source of the enterprise.
– Loan principal and interest: Collected at the same time. When the due date of debt repayment is stated in the credit contract, the customer must actively prepare a debt repayment note to the Bank. The bank will deduct the customer’s deposit to collect debt by.
– Debit to customer’s deposit account – Credit to the Bank’s loan account.
And the interest the Bank will collect after calculating on the stable balance, according to the formula:
Loan interest = Loan amount x Loan interest rate x Loan term
Banks earn interest by:
– Debit to deposit account – Credit to the Bank’s income account.
– In case the customer’s account does not have enough balance for the bank to collect the debt or interest, the bank may consider extending the debt to the customer. If the customer does not extend the debt, the bank will convert the principal or interest to overdue debt and apply the penalty of overdue interest to urge the customer to pay the debt. – Loans according to credit lines (rotating loans) – Subjects of application: Credit line loans are usually applied to businesses that need to borrow capital regularly, have business characteristics, and are The capital transfer is not suitable for the one-time lending method, which has a good reputation with the bank.
– Size of credit line: determined on the basis of an estimate of the largest amount of capital that the business may need at any time during the term of the credit line maintenance.
– The bank can estimate the credit limit from the following data: the accounting report of the previous year, the most recent accounting report along with the production plan for the year, quarter and economic contracts. , construction contract.
– Debt collection: The collection of debt according to the circulating loan account, that is, all sales and service proceeds from customers are used primarily to repay loans, then in terms of bank accounting:
– Credit to revolving loan account and customer’s outstanding balance will decrease.
– If the revolving loan account has zero outstanding balance, it means that the customer has paid off the bank debt at that time. At that time, if there is money from sales, service fees or other receipts, the Bank will transfer to the Credit side of the customer’s deposit account.
– Interest collection: At the end of each month, the bank will calculate interest according to the cumulative method. – If the credit line is still available, the bank will collect interest by debiting the circulating loan account.
– If the credit limit has expired, the bank will deduct money from the customer’s deposit account to collect interest.
APPENDIX 3: BUSINESS LOANS PROCESS AT INVESTMENT AND DEVELOPMENT BANK – QUANG TRI BRANCH
Step 1: Marketing customers and making credit proposal reports:
a. Marketing and Receiving Profiles:
Receive customers’ capital needs, on that basis, guide customers to make credit dossiers according to regulations. When preparing the application, the officer prepares a receipt and requires the customer to submit the application according to the customer’s Credit Profile List as prescribed.
b. Appraisal and preparation of credit proposals:
Based on the credit profile of the customer, the customer relations officer conducts research and appraisal according to the following contents:
– Overall assessment of the customer’s situation.
– Assess the financial situation of the client.
– Score customer credit to apply customer policy. Also refer to the Credit Information Center to evaluate customers.
– Analyze and evaluate the business plan, investment project, loan repayment ability of customers to determine the appropriate form of loan (working capital loan / short-term loan by item or limit.. ) – Assessment of collateral assets according to BIDV’s regulations on secured transactions.
Comprehensive risk assessment and preventive measures, including:
– Objective risk
– Risks stem from customer subjectivity
– Risks arising from BIDV
– Measures to prevent risks of customers
– Prepare credit proposal report
After verifying the credit profile of the customer, the Bank officer shall prepare a Credit Proposal Report together with the Credit Profile and submit it to the Leader of the Customer Relations Department/Leader of the Project Finance Department/Leader of the Delivery Department. Translate.
Leader of Customer Relations Department/Leader of Project Finance Department/Leader of Transaction Department checks the contents of the proposed report and signs it for control.
– Report the credit proposal with the full signature of the Credit Officer and submit it to the Leader of the Customer Relations Department/Leader of the Project Finance Department/Leader of the Transaction Department with all of the Client’s credit records. submitted to the competent authority in the following order:
– In case of customers in group A (which are customers whose credit proposals are not required to be assessed by the Risk Management Department before submitting to the competent authority for credit approval). ) when the credit proposal report is approved by the Deputy Director in charge of customer relations/authority, it will be returned to the customer relations department to handle the steps of this Regulation.
– In case the customer belongs to group B (when the credit proposal report is approved by the Deputy Director in charge of customer relations, the entire credit profile of the customer is forwarded to the Risk Management Department). for risk assessment.
Step 2: Risk assessment a. Receiving records.
The Risk Management Department receives the credit proposal report and Credit Profile from the Customer Relations Department and the Transaction Office under the branch.
The handover of records between departments must be done in writing.
In case the branch transfers the dossier to the Head Office, there must be a document clearly listing specific papers and documents.
b. Risk assessment:
– The risk manager conducts risk assessment of credit proposals and prepares a risk assessment report together with the credit file to submit to the Risk Management Department.
– The leader of the Risk Management Department inspects and reviews the content of the risk assessment report, writes comments and signs for control to submit to the competent authority for risk approval.
Step 3: Credit approval:
– For customers in group B: The credit is considered to be approved for credit extension when the Deputy Director in charge of customer relations/authority signs approval and agrees to grant credit on the Credit Proposal Report. use.
– For customers in group A:
– For a credit under the risk approval authority of the Director/Deputy Director in charge of credit risk management: The credit is considered to be approved for credit extension when there is a full approval signature of the Deputy Director. The independent director in charge of customer relations on the Credit Proposal Report and the Deputy Director/Director in charge of credit risk management on the Risk Appraisal Report.
– For credits under the branch’s credit council’s risk-approving authority:
– The risk management officer is responsible for collecting documents and sending them to the members of the Credit Council.
– A set of copies of dossiers to be sent to members of the Credit Council include:
– The credit proposal report has been signed and approved by the Deputy Director in charge of customer relations.
– The risk assessment report has been approved by the Director/Deputy Director in charge of risk.
– Relevant documents.