Social society is strictly regulated by the principle of selection, the principle of habit, the rule of society, the rule of using the language, the ritual of the cultural identity of the nation’s psychological and cultural characteristics prescribed to create YNH NH. example (76, p 131), chapter 4) the same mechanism, can create many different YNH.
The listener, depending on the accompanying conditions, can fully or completely recognize the speaker’s intention (the intention is less but the inference is more or vice versa). More or less mutual understanding makes the opening/closing mechanism from both sides interact. The encoding-decoding process overlaps, expands, or shrinks. The open YNH NH mechanism is often in the aesthetic sense in poetry. The YNHANH mechanism is normally closed in GT conversation. The opening/closing mechanism that generates YNHNH must be based on CTLC. The process of creating YNH NH makes CTLC more complete, more standard, more familiar, more effective, more diverse in style.
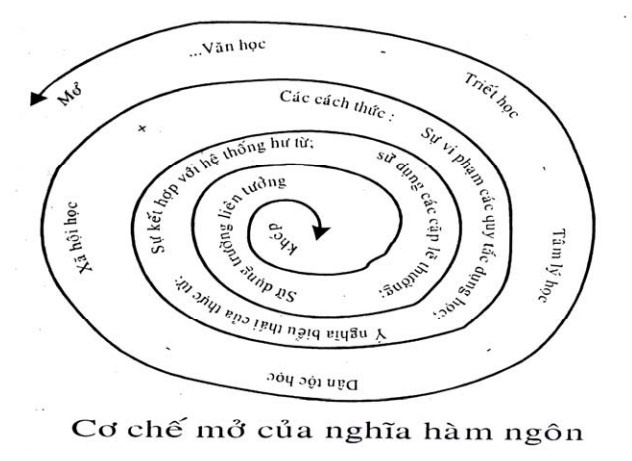
3.3. CONCLUSION
1. When studying the act of asking, we especially explain the structure of choice to create implied meaning, which is an inevitable product of linguistic activities in the transactional transaction. 2. This implicit meaning-making mechanism is the choice of linguistic material belonging to the linguistic element at different levels and aspects in the dynamic direction of CTLC to create implicit meaning with the maximum use of weak Non-linguistic factor, combined with linguistic reprocessing in the minds of coders and decoders is the third factor, turning CTLC into a meta-segmentative linguistic structure, into a meta-linguistic variant (metaphor). complex) to create a system of holistic units of meaning.
3. The problem of perceiving information associated with state action, through YNH NH of CTLC in GTMB is not simply a matter of identifying the existing conceptual meanings of words, but rather identifying new meanings in dynamic and oriented directions. pragmatic and effective GT, through a specific environment with defined socio-psychological conditions. 4. The process of implementing the principle of cooperation (to ensure close interests) in GTMB has made the partners implement the principle of politeness, establishing relationships and affection in an open manner on many fronts through communication. via CTLC.
This has dominated the feature of high pragmatic function in GT practice. 153 CHAPTER 4: PHOTOGRAPHY AND PHOTOGRAPHY OF PHOTOGRAPHY CONTAINS ASKING ACTION IN COMMUNICATION OF PURCHASES 4.1.GENERAL OF PHOTOGRAPHY AND POINTS 4.1.1. The role of pronouns and research tasks Vocabulary is an activity and an activity that plays an important and indispensable role in the process of reasoning, creating women to carry out GT activities in general and GTMB in particular. Socialism is considered as a means to reveal social interaction, to perform the communication function and is subject to the principle of choice, the principle of habit of social rules, of GT etiquette, of rules using language, of psychological characteristics, national culture prescribed. Social society is a dynamic, flexible, and varied structure in state function.
It always adjusts to suit the speaking context in order to achieve the highest GT efficiency in order to “close the gap” with the GT audience. Vocational language arts must be accepted by the community, have conventions suitable to the context of culture, personal relationships, cultural traditions… Therefore, society has a way of choosing relatively separate linguistic elements. Distinctive properties are emphasized in this thesis by their use and frequency in trading. When studying this issue, we will in turn answer the questions with “who”: Who has relationship with whom?;”what”:Who claims what to whom? Who says what to whom?;”how”: how to address effectively?; “when”?When to use this TXH?…;”where”? Where to use this TXH?; “why”? Why use one social network but not another?;”how?” What is appropriate to address?…
4.1.2. Research status of pronouns and ways of addressing 154 So far, there have been many research works on socialism and socialism, but the study of them within MB has not yet been fully mentioned. and systems. The problem of Vietnamese sociology has 2 stages:
4.1.2.1. It is the very early work of Alexandre de Rhodes, from 1651 in the “Portuguese-Latin Dictionary” devoted several pages to describe Vietnamese society. Next, Truong Vinh Ki provided a table of personal pronouns in 1884. Then there was the way of calling “pronoun” by Tran Trong Kim in the book “Vietnamese grammar”, Hanoi, 1940. In 1951, M. B. Emeneau in his work “Studies in Vietnamese grammar” has spent more than thirty pages on pronouns. In 1965, author Thompson L. C also paid attention to the expressive levels of social behavior. Vietnamese linguists have also worked on socialism. It is possible to mention Nguyen Tai Can, Dinh Van Duc, although not a monograph on sociology, but also refer to Vietnamese sociology relatively systematically in studies of general vocabulary.
Luong Van Hy in the book “Practice of speech and semantic meaning – reference system of people in Vietnamese” (1990) studies the word kin, professional word, personal pronoun. Nguyen Phu Phong (1960) “Vietnamese personal pronouns”, examining social relations from a grammatical point of view. 4.1.2.2. Vocabulary in pragmatics of communicative language Until the works of Nguyen Van Chien, Nhu Y, Bui Minh Yen, Nguyen Minh Thuyet, Hoang Thi Chau, Bui Khanh The, Bui Manh Hung, Mai Xuan Huy, Pham Ngoc Thuong, Nguyen Van Quang, Pham Ngoc Ham, Truong Thi Diem, Hoang Anh Thi, Le Thanh Kim, etc., the social studies research has really approached in the direction of GT executive activities, with expressive nuances of address and structure. address, address strategy, address situation, address scope…
The results of 155 studies on sociology of previous authors have laid an important foundation and premise to help us study this issue. 4.1.3. Overview of the relationship between the vocative words and the social choice structure is one of the important factors in the CTLC of women with OS in the MB speech event. It is a state element created, selected to suit the context of GT, strategy of GT, purpose of GT, so it is forced to rely on CTLC.
On the contrary, when CTLC is used, TXH/CXH makes the CTLC even more perfect, becoming a better, more refined, more familiar model. Socialism/Social society has a close relationship with LC in the following factors: first, the selection of GT role in personal and social relations. Because people are the sum total of social relationships, each individual can have many different GT roles. We temporarily call a set of roles, including different roles. For example: father, head, buyer… Second, the selection of GT role is appropriate according to the relationship with the interlocutor. Third, the selection of GT role is suitable for GT context.
Those are the socio-cultural factors associated with the traditional curriculum, which have a direct influence on the selection and use of agricultural means such as qualifications, experience, scope, topics, communication systems, etc. Fourthly, choose the role of GT so that it is suitable with a series of other factors associated with the context, which are factors: hierarchy, age, status, motivation, personality, lifestyle, occupation, personality, and personality. substance, function, … Fifth, selected according to the hierarchical relationship in the family, based on blood relations: yes/no; previous/next generation class; sex; on lower; big and small; exterior…
Sixth, choosing according to the relationship of authority or position creates a gap in social behavior relations, based on the factors of social status, gender, age… Seventh, choosing and defining roles according to the point of view. linkage system or combination of many relations according to a coordinate specifying two dimensions due to the position axis and the proximity axis. Example (93): B:Uncle, please buy something for me!; 156 M:Are you very old?; B: Well…, what do you choose to buy?… In (93), sellers use social media with a kind of close interpersonal relationship, which is of course a temporary, unstable relationship. Address the family relationship “brother”, respectfully to the buyer for the purpose of selling the goods. But the buyer did not agree with TXH “Anh”, expressed another YNH NH with a redundant OS, intentionally violating the motto of quantity. 4.2. CLASSIFICATION OF SUBSTANCES
4.2.1. Classification of two general groups of the system of pronouns in Vietnamese We know that in many foreign languages, such as English, there are only a few TXHs, and in Vietnamese, the number of TXHs, including pronouns. personal and non-personal pronouns, many times more. Although the sociological system in Vietnamese is very rich and diverse, in general they only include two large groups: – Personal pronouns, this is a group of specialized personal pronouns of Vietnamese: I, tao, me , me, that person, you, bay, mi, me, it, he, he, she, she, them, them, we, us, them, you, he, I… -Personal pronouns, most of the social groups of the non-personal pronouns are derived from nouns, including the following groups: firstly, nouns indicating kinship relations: grandfather, mother, …; the second is the nouns indicating social positions: president, boss…;the third is professional nouns: teachers, officials…; the fourth is the nouns indicating proper names: Hong, Lan…; the fifth is the nouns indicating how to call in place of the role: three small stacks… Criteria to distinguish the two main groups
1/ These main criteria are: specificity; provisional nature; use or non-use in a definite person; true role-playing; long history, more obvious origin; narrowness of the scope of use.
2/Besides, they are also distinguished by three other criteria: 157 – Criterion of meaning: personal pronouns are words that often carry the meaning of object, while the group of non-personal pronouns carry the meaning of nouns. only things. -Criteria of function-role used: personal pronouns are usually only used in a definite person, used to “profess” or “ho” while the group of non-personal pronouns are often used to “confess” to each other. to “ho” – Criteria for the ability to combine: personal pronouns are often not able to directly combine with demonstrative or predicate pronouns after it, while non-personal pronouns have the ability combined as of a noun. The foregoing is presented briefly in the following table:
| STT | CRITERIA distinguish two large groups | PRONOUNS personal | NON-PROJECT pronouns | STT | CRITERIA distinguish two large groups | PRONOUNS personal | NON-PROJECT pronouns | STT | CRITERIA distinguish two large groups | PRONOUN personal |
| first | -specificity | (+) many | (-) little | first | -specificity | (+) many | (-) little | first | -specificity | (+) many |
| 2 | – provisionalness | (-) little | (+) many | 2 | – provisionalness | (-) little | (+) many | 2 | – provisionalness | (-) little |
| 3 | – the nature of using or not using in a definite person | (+) many | (-) little | 3 | – the nature of using or not using in a definite person | (+) many | (-) little | 3 | – the nature of using or not using in a definite person | (+) many |
Maybe you are interested!
-
 Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 18
Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 18 -
 Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 19
Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 19 -
 Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 20
Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 20 -
 Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 22
Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 22 -
 Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 23
Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 23 -
 Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 24
Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 24
Diagram 4.1
4.2.2. The criteria for classifying social status are both general and specific
| STT | BASIS-Criteria | SOCIAL CLASSIFICATIONS | SOCIAL TOOLS |
| first | Judging by the criteria of using a fixed or temporary social network in the context | -The social status is really fixed: has the characteristic of having the meaning of objectivity and having special words to refer to the the 1st, 2nd, 3rd person. | -I, me, me, we … -you, you, -it, he, she, y, she, thi… |
| – Temporary social status: temporarily used in context with equivalent functions as pronouns and distributed in all 3 persons: DT indicates kinship relations, DT position , occupation, place, and social relations. , first name… | -Mr, grandmother, brother, sister, aunt, uncle … gross President, ministers, … -this, there, there, behind that … -you, comrades … -Nguyễn Van A | ||
| 2 | Considering the position of the speaker/ listener in the conversation conversation | – Direct, direct social – Non-direct socialization, indirect relations | -me, you, brother, uncle, me, … -it, he, she, her, she, he… |
| 3 | Judging by the etiquette criteria of the conversation | -Ritual Society -Riteless Society | -Name, title… -I, you… |
| 4 | In terms of the level of intimacy, the emotional level of the speaker/listener in the conversation | Social media is intimate | -you, me, me, you, you, aunt, uncle, uncle, dad, aunt… |
| Socialism has the nature of hating each other. | -he, she, she, her, you, me… | ||
| -Social is of normal social nature | – Me, brother, aunt, uncle, uncle, aunt… | ||
| – Social media is objective in nature | – I, comrade, director… | ||
| 5 | Judging by the criteria for hierarchical levels | -Superior Social | – Grandpa, Grandma, Uncle, Aunt, Uncle… |
| – Social level shoulder-to-shoulder, same age | – me, me, me, you, me, you… | ||
| -Low level social status | – children, grandchildren, you, you… | ||
| 6 | According to the criteria of marital relationship | -TXH belongs to the paternal family | – uncle, aunt, uncle… |
| -TXH belongs to the foreign family | – aunt, uncle, aunt. . | ||
| 7 | Considering the criteria for age effects | – Social status for people who are about 2 generations away from themselves (older) | -grandparents… |
| -Social is for people who are about 1 generation away from me (older) | – Aunt, Uncle, Uncle, … | ||
| -TXH is for people of the same generation, the same age as me, or younger than me (young or teenager) | – brother, sister, me, friend… | ||
| 8 | By gender criteria calculation | -TXH for men | – uncle, uncle, aunt, uncle… |
| -TXH for women | – sister, aunt, aunt, aunt… | ||
| – Social media is common for both sexes | – uncle, friend, comrade, mate… | ||
| 9 | Considering the criteria of blood relation | -Social kinship has a direct relationship… | – Aunt, uncle, aunt, brother, sister… |
| -Social kinship has a different lineage relationship | -uncle, aunt, aunt… | ||
| ten | In terms of dialect, locality | -TXH belongs to the c Bo dialect | -ba, dad… |
| -TXH belongs to Chinese dialect | – Mom, plating… | ||
| -TXH belongs to the Southern dialect | – purple, mom… | ||
| -Social for all 3 regions | – Grandpa, Grandma, Aunt… | ||
| 11 | Criteria for listening to karma | -Depending on occupation | – teachers, doctors, doctors … |
| twelfth | Subject criteria | -Depending on the subject (normal , sensitive …) | – aunt, uncle, you, me… |
| 13 | Job Criteria | -Depending on position | – Professor, President… |
| 14 | Criteria for naming identifiers | Attache under its own name, secret identity | -Nguyen Thi B… |
| 15 | Criteria of habits, styles, cultures, qualifications, and behavior | -Depending on the habits and styles of each region, family, and individual | – purple, u, bruise, o, cancer… |
The Vietnamese sociology system is not a static and immutable system, but an open and dynamic system. From a few original, authentic personal pronouns, the Vietnamese social system has gradually added a large number of other social groups. Users of social networks are based on these criteria, and at the same time select and combine these criteria together to suit the GT situation, attitude, affection, interpersonal relationship, GT purpose. , cultural traditions, personal behavior, age, gender, occupation, qualifications, physical state, psychological state, temperament.
4.3. SAMPLES OF CHARACTERISTICS IN NORMAL COMMUNICATION AND BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
Vocabulary in Vietnamese is also very rich and diverse. The stereotype of the address is based on the following criteria: ritual/non-ritual; subjective/objective; manifest/implicit; normative/non-regulatory; standard/non-standard; … 4.3.1. Addressing with personal pronouns
This is a specialized social class, which has existed for a long time, different from the class of non-personal pronouns that are transformed purely to be used for temporary address. Those are the words: me, me, me, me, me, other, you, he, he, she, he, it, y, old, she.
4.3.2. Address by first and last name
This is also a very expressive socialism and also has a relatively wide range of uses. How to use this method of address depends on the relationship between the characters. That relationship can be of different degrees, intimate or not intimate, authoritative or not powerful, different degrees of high and low status, different age levels… But there is one condition that stands out. of this method of addressing is the mutual acquaintance of both GT parties or at least one party. Addressing by first and last name, including the following methods:
Address by name: for example, Tam, Huong…; (2) Addressing by name combined with a noun of kin is converted into a noun indicating the unit: for example, Uncle Lam, Uncle Hoai… (3) Addressing by middle name plus first name: for example, Van Dung…; (4) Address by surname: for example: Tran, Nguyen…; (5) Addressing by surname combined with the word kin: for example, Uncle Tran, Uncle Nguyen…; (6) Address by full name: for example, Bui Thi An…; (7) Addressing by full name and surname combined with the word kin: for example, Mr. Pham Ba; (8) Addressing by a combination of a kinship noun and a position noun: for example, Uncle Director Chi, …; (10) Full name in combination with nouns of relatives and nouns of position: for example, Uncle General Director Nguyen Nam; (11) Addressing with nouns, positions and names: for example, director Binh…; (12) Addressing by surname plus title from position: for example, principal Tran, …;(13) Addressing with title word combined with full name: for example, Secretary Tran Thi B… 4.3.3. Addressing with nouns indicating kinship – position – occupation – number of words – converted predicate
(1) Nouns of relatives, for example: aunt, uncle, uncle, brother, sister, … (94): “Auntie, what did you buy?”; (2) Address by ordinal numbers, for example: Two, Three, Four, Five… (95) “Hai, buy something for her?”; (3) Addressing by title, for example: Director, Chairman, … (96): “What would the director like to choose?”; (4) Addressing with words indicating places; for example: this, that, here, there… (97): “If you don’t sell, then go somewhere else!”; (5) Addressing with words indicating social relations, for example: friend, comrade, friend… (98): “Do you have good rice? Weigh for a few kilos!”; (6) Addressing with professional words, for example: rickshaw, cyclo, . . (99) “Fish seller, come here!”; (7) Addressing with a transformation predicate, for example: darling, baby, Út… 4.3.4. Addressing by changing the role or name of a loved one
(1) Addressing by the names of relatives such as husband, wife and children, etc. Example (100): “What are you buying, Ms. Quy?” (Qui is her husband’s name); (2) Address by replacing the role of relatives such as husband, wife and children…Example (101): “Why is the noodle soup so sour, Ti’s cheek?” 4.3.5. Vocabulary by combination:
1) The kinship is combined with the occupational occupation; (2) The kinship is combined with the position designation; (3) Job title combined with occupation designation; (4) The kinship is combined with the noun indicating the family name with the noun indicating the occupation (5) The kinship is combined with the DT indicating the family name and the DT indicating the title.
| Ways to use with acquaintances GTMB | Ways to use with strangers GTMB | The CHs in the regular GT | Specific classification of social networks | ||
| (+) | (little) | (0) | (+) | (little) | (0) |
| Address by first and last name | -Address by name | ||||
| -Address by middle name plus first name | |||||
| -Address by surname | |||||
| – Full name and surname. etc | |||||
| Address with TXH | -Pronouns | ||||
| – Social reputation of relatives | |||||
| -Address by ordinal number | |||||
| Addressing with nouns | -Address with nouns indicating titles | ||||
| -Address with nouns of place | |||||
| -Address with nouns indicating social relations | |||||
| Coral noun pulse by profession now | |||||
| Addressing by replacing the roles of loved ones | -Replace the role or name of: husband, wife, children | ||||
| Vocabulary by combination | -The word kin combined with the word listening to karma | ||||
| – The word kin combined with the resignation of the title | |||||
| -From kinship combined with the fourth number in family, relatives. | |||||
| -From kinship combined with name |
4.4. FROM FAMILY IN COMMUNICATION BUY AND SELL
4.4.1. Overview of kinship words
In addition to the really fixed social class classes such as: me, me, ta, you, bay, he…, we pay special attention to the temporary social class: nouns indicating kinship relations; position only; indicate occupation, place, social relationship … in which, we found that the frequency of using nouns indicating kinship relations accounts for the highest percentage, especially in the households of the GTMB. The tendency of Vietnamese people to address themselves with nouns indicating kinship relations, “familyization” of the Vietnamese people is very popular, that is, using TXH to refer to kinship relations with people who are not related. This can be explained, because the Vietnamese kinship social system is capable of performing many functions simultaneously with other foreign activities. Those are the functions: The function of referencing GT characters for the purpose of answering the “who said” PNHs; ” talk to”; “to whom”; The social positioning function of GT participants: about social status, age positioning,position, occupation, capacity, qualifications, status of luxury, residential area in urban or rural areas, dialects from place to place…; Function to create GT relationship, determine the level of body – profile…. All of the above functions are governed by the following basic principles: (1) the principle of traditional respect; (2) the principle of politeness; (3) the principle of rights; (4) the principle of ensuring the modesty “professing humility – exalting”; (5) principles of relationship building; (6) the self-centered principle to refer to addressing relationships; or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).occupation, capacity, qualifications, status, urban or rural residence, dialects from one place to another…; Function to create GT relationship, determine the level of body – profile…. All of the above functions are governed by the following basic principles: (1) the principle of traditional respect; (2) the principle of politeness; (3) the principle of rights; (4) the principle of ensuring modesty “professing humility – honoring”; (5) principles of relationship building; (6) the self-centered principle to refer to addressing relationships; or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).occupation, capacity, qualifications, status, urban or rural residence, dialects from one place to another…; Function to create GT relationship, determine the level of body – profile…. All of the above functions are governed by the following basic principles: (1) the principle of traditional respect; (2) the principle of politeness; (3) the principle of rights; (4) the principle of ensuring the modesty “professing humility – exalting”; (5) principles of relationship building; (6) self-centred principles to refer to addressing relationships; or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).level, status, status of residence in urban or rural areas, dialects from place to place, etc.; Function to create GT relationship, determine the level of body – profile…. All of the above functions are governed by the following basic principles: (1) the principle of traditional respect; (2) the principle of politeness; (3) the principle of rights; (4) the principle of ensuring the modesty “professing humility – exalting”; (5) principles of relationship building; (6) self-centred principles to refer to addressing relationships; or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).education level, status, status of residence in urban or rural areas, dialects from place to place, etc.; Function to create GT relationship, determine the level of body – profile…. All of the above functions are governed by the following basic principles: (1) the principle of traditional respect; (2) the principle of politeness; (3) the principle of rights; (4) the principle of ensuring the modesty “professing humility – exalting”; (5) principles of relationship building; (6) the self-centered principle to refer to addressing relationships; or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).urban or rural residence, dialects from one place to another…; Function to create GT relationship, determine the level of body – profile…. All of the above functions are governed by the following basic principles: (1) the principle of traditional respect; (2) the principle of politeness; (3) the principle of rights; (4) the principle of ensuring the modesty “professing humility – exalting”; (5) principles of relationship building; (6) self-centred principles to refer to addressing relationships; or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).urban or rural residence, dialects from one place to another…; Function to create GT relationship, determine the level of body – profile…. All of the above functions are governed by the following basic principles: (1) the principle of traditional respect; (2) the principle of politeness; (3) the principle of rights; (4) the principle of ensuring the modesty “professing humility – exalting”; (5) principles of relationship building; (6) self-centred principles to refer to addressing relationships; or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).Function to create GT relationship, determine the level of body – profile…. All of the above functions are governed by the following basic principles: (1) the principle of traditional respect; (2) the principle of politeness; (3) the principle of rights; (4) the principle of ensuring the modesty “professing humility – honoring”; (5) principles of relationship building; (6) self-centred principles to refer to addressing relationships; or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).Function to create GT relationship, determine the level of body – profile…. All of the above functions are governed by the following basic principles: (1) the principle of traditional respect; (2) the principle of politeness; (3) the principle of rights; (4) the principle of ensuring the modesty “professing humility – exalting”; (5) principles of relationship building; (6) self-centred principles to refer to addressing relationships; or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).(1) the principle of traditional respect; (2) the principle of politeness; (3) the principle of rights; (4) the principle of ensuring the modesty “professing humility – exalting”; (5) principles of relationship building; (6) self-centred principles to refer to addressing relationships; or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).(1) the principle of traditional respect; (2) the principle of politeness; (3) the principle of rights; (4) the principle of ensuring the modesty “professing humility – exalting”; (5) principles of relationship building; (6) self-centred principles to refer to addressing relationships; or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).or take other people as the center to refer to the surrounding relationships; (7) the principle of “familyization”; (8) the emotional principle “regulate intimacy, not regulate intimacy”; the principle of kinship is based on personal relationships; (9) the principle of upper and lower hierarchy (respecting position); (10) principle of identity (emotional, slight difference).
Components of expressive meaning in sociology include: emotional-emotional component indicating the relationship between the meaning of a word and the range of affective-emotional perception, which is related to the inherent output of the word and the normal element. -reasonable evaluation indicates the relationship between the meaning of the word with the perceptual range of “true-false” assessment; agree-disagree” in relation to the inherent indicative of the word. Components of the meaning of use, in sociology include: the element indicating the relationship between the user and the scope of use of the word relative to the inherent output of the word; and the element indicating the relationship of users with usage habits is considered by everyone in society as standard, correct and exemplary, ensuring the unity and stability of the national culture. For real personal pronouns of Vietnamese in general,Elements in their indicative meanings are often expressive or neutral or negative- impolite.
The group of non-personal pronouns, which are mainly nouns indicating kinship relations, can completely meet the requirement to show different expressive levels of the elements in the indicative meaning. There are usually four typical levels of expression:
formal – neutral – intimate – contemptuous. At the same time, the group of nouns indicating kinship relations also shows clear opposites (presented in diagrams 4.2; diagram 4.3; diagram 4.4), when addressing in both GT roles that the pronoun group personal identity cannot fully meet, clearly show the principles of GT of the Vietnamese people.
4.4.2. Analytical data source
In order to have a more objective view of the social media used in shopping carts, we reviewed 1000 recorded conversations in Hanoi, Nha Trang, and Ho Chi Minh City in the range of retail locations. We have listed and classified the PNs containing the OS in those conversations. The survey results show that 80% of PNHMBs use nouns indicating kinship relationships as their address.
4.4.3. Analysis of results from kinship names in sales communication
In fact, the statistical results on the use of social networks only relative to kinship are only relative. Because in a MB conversation, TXH is used many times, even in a conversation the buyer and seller also change the TXH many times depending on the GT strategy. However, we try to give a relative ratio as follows: Mr (20/500, rate of 4%); foreign, domestic (10/500, rate of 2%), three (50/500, rate of 10%); brother, uncle, uncle (36/500, rate 7.2%); sister, aunt, o, aunt (202/500, rate 40, 4%); children, grandchildren, grandchildren in the pronunciation is (70/500, rate 14%); in contrast, children, children and grandchildren in the way of pronouncing, the ratio is very high (430/500, rate of 86%); father, father, father, teacher, purple, bug (12/500, rate 2.4%) ; mother, bu, cheek, tumor, bruise, plating, mother, aunt (20/500, rate 4%); you (15/500, 3% rate); uncle (3/500, rate 0.06%); uncle (aunt and uncle, 30/500, rate 6%); aunt (23/500, rate 4, 6%); Aunt (9/500, rate 1.8%).
4.4.4. Survey of kinship words in business communication
4.4.4.1.Consider the words “uncle”-“aunt”
The words “uncle” and “aunt” share the same great meaning of “no blood relation” and are opposite in the meaning of “gender”.
a/ Distinguishing: “uncle1”: is her husband or aunt’s aunt “step-2”: is the brother or brother-in-law of the husband or wife “uncle 3”: is the mother’s second husband (step-stepfather)






