MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING
UNIVERSITY OF ECONOMY HO CHI MINH CITY
NGUYEN THI Rieng
INFLUENCE FACTOR
TO LIQUIDITY RISK OF VIETNAM COMMERCIAL BANKS
SPECIALITY: FINANCE-BANKING CODE: 60340201
MASTER THESIS OF ECONOMY
SCIENTIFIC GUIDE Assoc. Dr. PHAM VAN NGAN
City. Ho Chi Minh - Year 2015
GUARANTEE
I hereby declare that this is my own research work.
The data and results stated in the thesis are honest and have never been published in any other works.
Author
Nguyen Thi Rieng
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ACCESSORY COVER DISCLAIMER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
LIST OF Acronyms1 LIST OF TABLES2
INTRODUCTION 1
1. The urgency of the topic 1
2. Research objective 2
3. Research object and scope 2
4. Research Methods 2
5. Overview of the situation of domestic and foreign studies related to the topic 3
6. The contributions of the topic 5
7. Structure of the topic 6
CHAPTER I. OVERVIEW OF FACTORS A
1.1. Liquidity of commercial banks 7
1.1.1. Commercial bank liquidity concept 7
1.1.2. Liquidity supply and demand for commercial banks 8
1.2. Commercial bank liquidity risk 9
1.2.1. The concept of commercial bank liquidity risk 9
1.2.2. Causes of liquidity risk of commercial banks 11
1.3. Liquidity risk management 13
1.4. The role of liquidity risk management 14
1.5. Measure liquidity risk 15
1.5.1. Liquidity Source Approach and Liquidity Usage 16
1.5.2. Measure liquidity risk through 16 . liquidity indicators
1.5.3. Funding Gap Method 18
1.6. Research model of factors affecting liquidity risk of commercial banks 19
CONCLUSION CHAPTER I 22
CHAPTER II. SITUATION OF FACTORS AFFECTING LIQUIDITY RISK OF VIETNAM COMMERCIAL BANKS 23
2.1. Overview of the liquidity situation of Vietnam's commercial banking system in recent years 23
2.1.1 Overview of the operation of Vietnam's commercial banking system 23
2.1.2. Current status of liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks in the period 2007-2013 26
2.2. Analysis of factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnam's commercial banking system 31
2.2.1. Model of factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnam's commercial banking system
2.2.2. Research results 33
2.2.3. Discussing research results 43
CONCLUSION OF CHAPTER II 49
CHAPTER 3: SOLUTIONS IMPACT FACTORS POSITIVE AFFECTING FACILITIES OF VIETNAM COMMERCIAL BANKERS 50
3.1. For Vietnamese commercial banks 50
3.1.1. Regarding the policy of increasing capital, increasing assets, and managing assets - bank capital in recent years. 50
3.1.2. Good implementation of futures risk management 51
3.1.3. Ensure a balance ratio between Assets and Liabilities 51
3.1.4. Strengthening forecasting of macroeconomic conditions 52
3.1.5. Accelerating capital mobilization and diversifying mobilized capital sources 52
3.1.6. Strengthening customer due diligence and audit work 53
3.1.7. Building a team of qualified, capable and ethical employees 53
3.1.8. Improving the promotion of the bank's image and brand 54
3.1.9. Building a reasonable internal capital transfer mechanism 54
3.1.10. Implement 55 . system linkage
3.2. Some recommendations for State management agencies 56
3.2.1. Completing the legal system to ensure efficiency in work 56
3.2.2. Restructuring the commercial banking system 56
3.2.3. Strengthen and improve remote monitoring of commercial banks 57
3.2.4. Zoning for commercial banks with weak liquidity 58
3.2.5. Speeding up the equitization of state-owned commercial banks 58
CONCLUSION OF CHAPTER III 60
CONCLUSION 61
REFERENCES APPENDIX
LIST OF ACRONYMS
Acronyms | Explain |
CAR | Minimum capital adequacy ratio |
ETA | The ratio of own capital to total capital |
FGAP | Liquidity gap on total assets |
GDP | gross domestic product |
IMF | International Monetary Fund |
INF | Inflation rate |
SBV | State bank |
NH | Commercial Bank |
Central Bank | Central bank |
ROE | Return on equity |
SIZE | Size of total assets |
Credit institutions | Credit institutions |
TLA | Loan-to-total assets ratio |
TSC | Property has |
TSN | Debt assets |
Maybe you are interested!
-
 Factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks - 2
Factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks - 2 -
 Factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks - 3
Factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks - 3 -
 Factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks - 4
Factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks - 4 -
 Factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks - 5
Factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks - 5

LIST OF TABLES
Table List
Table 2.1. Descriptive statistics results 33
Table 2.2. Estimation results with Pooled model when there are no factors outside the banking system 36
Table 2.3. Estimation results with Pooled model when there are factors outside the banking system 37
Table 2.4. Estimation results with 38 . FEM model
Table 2.5. Estimation results with 39 . REM model
![]() ................................................. ............41
................................................. ............41
![]() estimated with REM model after removing excess variable 42
estimated with REM model after removing excess variable 42
Table 2.8. Scale of total assets of commercial banks in the period 2007-2013 46
List of charts
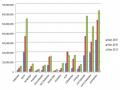
Chart 2.1. Total assets of some Vietnamese commercial banks over the years 30
Chart 2.2. Loan situation of some Vietnamese commercial banks over the years 35
Chart 2.3. Equity capital of some Vietnamese commercial banks over the years 36
PREAMBLE
1. Urgency of the topic
Liquidity and liquidity risk management are decisive factors for the safety of any commercial bank. A bank's liquidity is reflected in its willingness to pay customers and its ability to cover losses when risks occur. Once the liquidity risk occurs, depending on the level and spread, it can stop the operation of commercial banks. Therefore, one of the main tasks of a bank is to ensure liquidity. In today's world, many banks are facing liquidity stress, as fierce competition for attracting deposits forces banks to look for other sources of funding. Unreasonable liquidity is the first sign of financial instability. Along with the development of financial markets, Opportunities and risks in liquidity management of commercial banks also increase accordingly. This shows the importance of planning for liquidity needs with stable and low-cost methods to finance the operations of commercial banks in an increasingly competitive world.
With a relatively high growth rate and an increasingly affirmed position in the international arena, Vietnam is becoming a destination for foreign investment flows. Contributing to that success, it is impossible not to mention the banking industry, which is considered the lifeblood of the economy. In the past time, due to the negative impacts of the instability of the macro economy and other economic mechanisms. State policies, liquidity of the commercial banking system were seriously affected. This affects not only the business of the bank itself, but also the money market and the economy as a whole.
Being aware of the important role of liquidity risk management in banking activities as well as seeing the urgency of determining factors affecting liquidity risk of commercial banks, I have chosen the topic. research:
“ FACTORS AFFECTING THE CLUBILITY RISK OF VIETNAM COMMERCIAL BANKS ”
make your thesis topic.
2. Research objective
- Find out the factors affecting the liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks.
- Measure the impact of each factor variable on liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks in order to identify important factors in order to propose solutions to positively affect the risk factors. liquidity of Vietnamese commercial banks.
3. Object and scope of research
- Research object: factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks.
- Scope of the study: The data used to conduct the research are collected from the financial statements of 14 Vietnamese commercial banks in the period from 2007 to 2013. Macro-economic data is collected. from IMF data.
4. Research Methodology
To carry out my research I use the following research methods:
- Methods of statistics, comparison and analysis of data on business performance and liquidity situation of Vietnamese commercial banks from 2007 to 2013.
- Quantitative research method to test and identify factors through values, reliability, test research models and research hypotheses, determine the degree of influence of factors on liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks.
5. Overview of the situation of domestic and foreign studies related to the topic
The issue of liquidity and liquidity risk is one of the top concerns of many banks in the world. There have been many research studies on the factors affecting the liquidity risk of commercial banks. valuable conclusions.
In the study " Micro and macro factors affecting the liquidity of commercial banks in the UK " 1 by Valla and Saes-Escorbiac (2006), the authors said that bank liquidity depends on the following factors: following: Bank profitability (-), Probability of getting support from the last lender (-), Credit growth. (-), Bank size(-), Gross domestic product growth (-), Short-term interest rates, show the effectiveness of monetary policy (-)
Research paper on “ Determining factors of liquidity risk of banks from emerging economies ” 2 with panel data regression analysis by Bunda and Desquilbet (2008) argues that liquidity risk of banks banks are assumed
1Valla and Saes-Escorbiac, (2006),Bank-specific and macroeconomic determinants of liquidity of English banks
2 Bunda and Desquilbet, (2008), Determinants of liquidity risk of banks from emerging economies,
working paper
depends on the behavior of banks, the market, the macroeconomic environment and the exchange rate regime, in particular on the following factors:
- Total assets measure the size of the bank (-)
- Asset equity ratio measures capital adequacy (+)
- Interest rates (-)
- Ratio of public expenditure to gross domestic product (+)
- Inflation rate (+)
- Financial crisis.(-)
- Exchange rate mode
The study "Relationship between capital, liquidity and risk in commercial banks" 3 by two authors Tamara Kochubey and Dorota Kowalczyk (2014) shows that US commercial banks simultaneously coordinate short-term adjustments in financial capital, risk and liquidity in two stages before and during the crisis. Accordingly, in the pre-crisis period, short-term adjustments in capital have a negative effect on short-term risk adjustments, and vice versa, an increase in risk tolerance reduces the risk ratio. capital of the bank and increase the index
Liquidity. During the crisis period, banks cut possible risks, reduce the risk of asset portfolios, loan portfolios when the risk of capital ratios declines. The study also concludes that an increase in risk causes a decrease in the capital ratio, as well as bank liquidity and capital adjustments are negatively related.
In the study "Factors affecting the liquidity of Slovak commercial banks" 4 by Pavla Vodova (2011) also had many results.
3 Tamara Kochubey and Dorota Kowalczyk, (2014), The relationship between Capital, Liquidity and risk in Commercial Banks, working paper.
4 Pavla Vodova, (2011) Determinants of Commercial Bank' Liquidity in the Czech Republic, working
paper
valuable argument. By reviewing the data of Slovak commercial banks together with the macroeconomic data for the period 2001-2010 and the panel data regression analysis, the author has concluded that the decrease in bank liquidity is mainly due to as a result of the financial crisis. Commercial banks tend to hold less liquid assets when bank profits increase, capital adequacy ratio is high and bank size is large, thereby increasing the bank's liquidity risk. Accordingly, the variables on interest rates (lending interest rates, interbank transaction rates and monetary policy interest rates), interest rates, bad debt rates and inflation rates do not have a significant impact. on the liquidity of Slovak commercial banks.
![]()
In the study "Factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnam's commercial banking system" 5![]() author Truong Quang Thong (2013) concluded that
author Truong Quang Thong (2013) concluded that ![]() the
the
![]()
, ![]()
![]() noise rate
noise rate ![]() _
_ ![]() _
_
scale, i.e. special factors ![]() expressed through the effects of policy lag.
expressed through the effects of policy lag.
6. Contributions of the topic
- Systematize general theoretical issues on liquidity and liquidity risk as well as factors affecting liquidity risk in Vietnamese commercial banks. Therefore, the results of the study will have certain contributions to the completion of the theoretical framework of liquidity risk.
- Through the results obtained from running the panel data regression model, the author draws the conclusion that liquidity risk is negatively affected by the size of the bank's total assets and the loan-to-loan ratio. total assets has a positive effect on risk
5 Truong Quang Thong, 2013. Factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnam's commercial banking systems. Economic Development Magazine, No. 276, pp. 50-62
Liquidity. This conclusion allows the author to make some useful recommendations in managing liquidity risk of commercial banks in practice. However, contrary to initial expectation, other factors such as equity to total capital ratio, return on equity ratio, economic growth rate, inflation rate are not significant. statistical significance in analyzing the effect on liquidity risk.
Besides the positive contributions, the study also has some limitations. Due to time constraints, the author has not been able to collect data to include in the model the policy impact variables, other macro variables such as unemployment rate, exchange rate regime, interest rate, etc. interbank rate…
- In the future with data sources and deeper knowledge, the author wishes to perfect the measurement model with higher reliability. From there, we can offer more specific and effective solutions to increase liquidity and manage liquidity risk more effectively.
7. Structure of the topic
In addition to the introduction, conclusion, table of contents, list of abbreviations, list of figures and tables, list of references; The thesis is organized into three chapters as follows:
Chapter I. Overview of factors affecting liquidity risk of commercial banks
Chapter II. Actual situation of factors affecting liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks
Chapter III. Solutions to positively affect the liquidity risk of Vietnamese commercial banks
CHAPTER I. OVERVIEW OF FACTORS AFFECTING LIQUIDITY RISK OF COMMERCIAL BANKS
1.1. Liquidity of commercial banks
1.1.1. Commercial bank liquidity concept
As we all know, in many studies, the term "liquidity" has been used by many authors, but it is not easy to define it. The definition of liquidity is abstract and requires high thinking. Historically, liquidity has paralleled the evolution of the concept of money and has changed with the expansion of finance, to a broader extent, with improvements in structure and function. capacity of the financial system.
Financial theory holds that, given capital market imperfections, moving capital between economic sectors over a period of time requires an appropriate amount of risk-free financial assets in the economy: as a store of value and as a medium of exchange accepted by a wide range of market participants. That is the definition of paper money or fiat money, money that functions both as an accounting unit and as an intermediary for exchange. This refers to a traditional and simplest form of liquidity, which is asset liquidity. Financial theory also explains the role of commercial banks as liquidity providers: by their function of subsidizing loans or holding primary debt securities issued by business entities. economy in need of additional capital, by the function of pooling capital from investors by issuing indirect debt securities. Due to the large growth and especially the contractual characteristics of these debt securities, they have been accepted as an alternative to the legal monetary base. This has led to the definition of the concept of bank liquidity.
Liquidity is the ability to access assets or capital that can be repaid at a reasonable cost as soon as capital needs arise 6 . An asset is considered liquid when it meets the following criteria: available quantity to buy or sell, available market to trade, available time to trade, reasonable price.
A source of capital is said to be highly liquid when the cost of mobilization is low and the time to mobilize is fast. An asset is said to be highly liquid when its cost to cash is low and its ability to convert to cash quickly. In fact, assets with high liquidity include valuable papers such as Treasury bills, certificates of deposit, promissory notes, bills of exchange, etc., low liquid assets such as real estate, chains. production, machinery and equipment…
1.1.2. Liquidity supply and demand for commercial banks
Liquidity supply is the source of liquidity for a bank, including funds that increase the bank's ability to pay. Liquidity supply includes: cash, deposits at the State Bank, deposits at other credit institutions, deposit collection from customers, credit customers repaying principal and interest, selling TSCs of commercial banks, borrowing from the market interbank market, collected from other receivables.
Liquidity demand: is the capital that reduces the bank's treasury, is the capital requirements for different activities of the bank. Liquidity demand includes: refunding deposits to customers, repaying loans, transferring money to pay at customer's request, paying operating expenses, paying payments to the state budget, pay dividends, pay other debts…
The bank's net liquidity position in a given period, with details on the source and use of liquidity sources, can be established by administrators to serve liquidity management needs. Accordingly, the net liquidity position is determined as follows:
6 Assoc.Prof.Dr. Tran Huy Hoang, Textbook of Commercial Banking Administration, Labor and Social Publishing House, 2011