Deploying money transfer services up to 140 foreign currencies, transferring money by bank drafts, consulting on setting up export documents, etc. to meet the diverse needs of customers.
Officially becoming the first level agent of Western Union Remittance Company, marking an important development in remittance activities at SCB. Western Union’s sales and remittances increased steadily throughout the year, providing a stable source of income and reducing cash management costs for the bank.
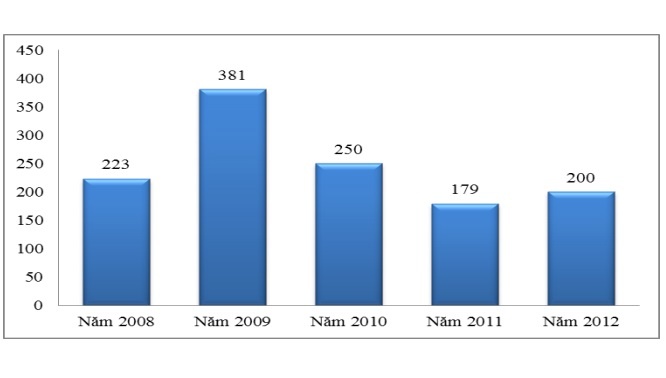
Figure 2.6: Sales of international payments (Unit: million USD)
(Source: SCB Annual Report 2008, 2009, 2010, 2012)
2.7.3.7. Other service activities
Forex trading
SCB’s foreign exchange business grew strongly in 2009 with a turnover of USD 3,099 million. However, from 2010 to 2011, sales decreased sharply. At the end of 2011, international payment revenue reached 1,070 million USD. 2011 was a volatile year for the domestic and international gold and foreign currency markets. Many individuals and economic organizations still have the mentality of hoarding gold and foreign currencies. This poses many risks not only to the bank but also to the customer. Aware of that, SCB on the one hand always ensures a sufficient quantity of gold – foreign currency to fully meet the needs of customers with an appropriate and competitive exchange rate from time to time. On the other hand, SCB also focuses on promoting the marketing of derivative products such as futures, swaps, etc., in order to help customers have more tools in hedging against exchange rate risk, helping customers to take the initiative in trading. business plans.
In addition, SCB also has a daily money market newsletter to provide customers with timely information related to foreign currencies in the most general and objective manner.
Maybe you are interested!
-
 The Effectiveness Of Banking Service Quality
The Effectiveness Of Banking Service Quality -
 The Role Of Customer Satisfaction In The Development Of The Bank
The Role Of Customer Satisfaction In The Development Of The Bank -
 Overview Of Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank After The Consolidation
Overview Of Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank After The Consolidation -
 Correction Of Research Models And Hypotheses
Correction Of Research Models And Hypotheses -
 Evaluation Of Customer Satisfaction With Service Quality At Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank After Consolidation
Evaluation Of Customer Satisfaction With Service Quality At Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank After Consolidation -
 Solution Group To Improve Customer Satisfaction
Solution Group To Improve Customer Satisfaction
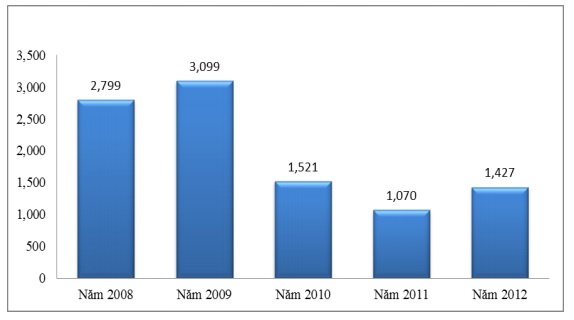
Figure 2.7: Foreign exchange trading volume (Unit: million USD)
(Source: SCB Annual Report 2008, 2009, 2010, 2012)
Treasury Services
In addition to services such as counting, currency exchange, money verification, cash collection/disbursement, etc., SCB also provides collection and payment services for customers at home or other locations at the request of customers. Treasury service revenue in 2012 was VND 10 billion, an increase of 66.66% compared to 2011. Treasury services also contribute to diversifying products and services at SCB to meet the needs of customers.
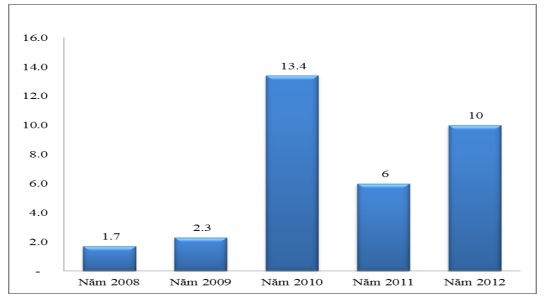
Figure 2.8: Revenue from treasury services (Unit: billion VND)
(Source: SCB Annual Report 2008, 2009, 2010, 2012)
Investment activities
In order to diversify business activities, SCB’s investment activities have received more and more attention and have made remarkable progress. Investment activities of SCB increased from 700 billion VND (in 2008) to 736 billion VND (2009). However, this activity decreased in 2010 (519 billion VND) and increased again in 2011 (542 billion VND). 2012 was a very difficult year, so SCB limited investment, so investment revenue was only 72 billion dong, down 490 billion dong compared to 2011.
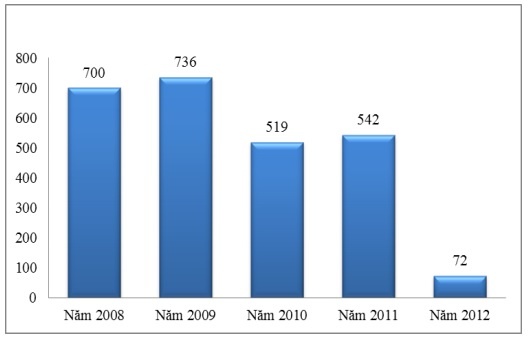
Figure 2.9: Investment revenue (Unit: Billion VND)
(Source: SCB Annual Report 2008, 2009, 2010, 2012)
Investment activities have brought SCB many benefits such as dividends, increased value of investments, expansion of SCB brand promotion. In particular, capital contribution has contributed to increasing the use of SCB’s products, services and utilities in businesses/investors such as payment activities, salary payments via card…
2.8. Assess the current status of customer satisfaction about products and services of Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank
2.8.1. Result
In recent years, although the domestic and international economic situation has had many fluctuations, greatly affecting the socio-economic situation, but SCB has achieved the following results:
– SCB’s mobilized capital continued to grow from 2008 to 2012 as a result of applying many measures to increase mobilized capital such as deploying deposit products, deposit programs with competitive interest rates, etc. competition, attractive promotions, preferential policies for middle-aged and VIP customers, diversifying forms of mobilization such as issuing valuable papers.
– In addition, SCB also focuses on developing foreign currency deposit products to attract deposits to compensate for the shortage of VND capital due to increasingly intense competition in the market.
– Support services are also improved better such as domestic payment services, international payments, card services, e-banking program upgrade with new utilities to better serve the needs of customers. transactions and account management via the internet of customers.
– The customer care policies implemented and well implemented by SCB in the past time show the interest and desire to build a long-term cooperative relationship with customers. Through programs such as giving birthday gifts to customers; giving gifts on March 8, October 20; practical gifts such as raincoats, helmets, umbrellas, etc. Although the gift value is not great, it has helped customers feel SCB’s care for each customer.
– In addition, receiving customer comments on SCB’s services is also very important in building a customer care department and completing the process of handling customer comments. . SCB’s efforts in taking better care of customers have attracted customers’ interest in SCB’s services.
– Currently, SCB has a transaction network with more than 230 points across 26 provinces and cities across the country, which has also contributed to improving SCB’s competitive advantage, market share and operating scale compared to other banks.
– In addition to improving the quality of infrastructure and expanding the network, SCB’s service quality has also improved significantly, especially the staff directly serving customers. With the goal of improving the quality of human resources, SCB has paid great attention to the recruitment of new employees as well as internal training to improve and perfect the skills and professionalism of the staff and leaders. religion.
2.8.2. Limit
Besides the achieved results, SCB’s service quality also has certain limitations:
– Although internet banking service has been improved and offers many incentives for customers, it has not yet integrated all the deposit products being deployed, so customers still have to come and make transactions at transaction points.
– ATM machine malfunction makes it difficult for customers to withdraw money.
– The quality of operations at transaction points has improved, but it is mainly in contact with customers directly at the counter, so it is still relatively passive, not fully promoting the ability of employees and available resources.
– Although the transaction process and procedures have been uniformly issued, it is still cumbersome, not convenient, and the transaction time is still slow.
– The State Bank’s regulation of the ceiling deposit interest rate as well as the interest rate on early settlement has led to some products and customer care programs of SCB having to be discontinued or less attractive to customers. family.
– Employees’ uniforms cause difficulties in brand recognition and are not consistent throughout the entire SCB system after the consolidation.
– SCB’s brand is not outstanding, making it easy for customers to confuse with Sacombank and Saigonbank.
– The transaction point is small, the decoration is monotonous and not eye-catching. Some transaction points are old and degraded.
– Customer care policies such as giving birthday gifts are less valuable than other banks.
2.9. Research on customer satisfaction with service quality at Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank after consolidation
2.9.1. Research models
The study uses SERVPERF model to build a research model of the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction.
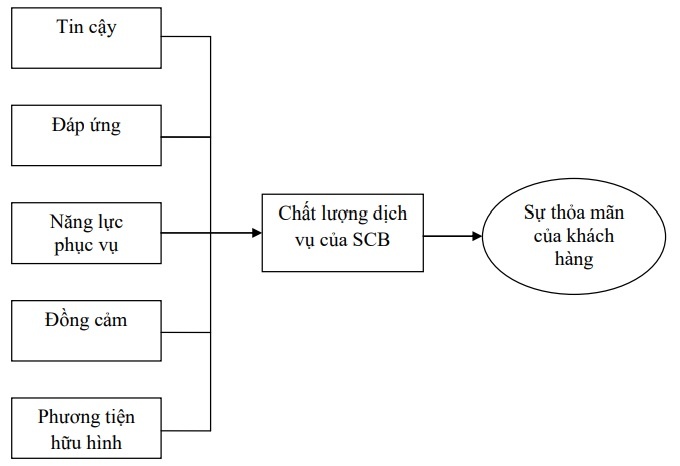
Figure 2.1: Research model
2.9.2. Research hypothesis
From the research model (see Figure 2.1), the following hypotheses are stated:
H1: The Trust component is positively correlated with service quality and customer satisfaction.
H2: Satisfaction component is positively correlated with service quality and customer satisfaction.
H3: The service capacity component is positively correlated with service quality and customer satisfaction.
H4: The Empathy component is positively correlated with service quality and customer satisfaction.
H5: Tangible media component is positively correlated with service quality and customer satisfaction.
2.9.3. research process
The process is carried out in two main research steps: preliminary research and formal research (see Figure 2.2).
Preliminary research: conducted with qualitative method through two main parts:
First, discuss the opinion of experts in the banking sector. From there, establish the initial scale, adjust and add variables and components to get the official scale based on the SERVPERF model and refer to the scale according to the study “Measurement of service quality in the field of service quality”. banking sector” (Le Van Huy and Pham Thanh Thao, 2008) (see Appendix 1).
Then, conduct interviews with ten (10) customers to find out if the respondents understand the variables in the scale correctly, the components in the scale are appropriate and if there are any other components arising. From there, a formal questionnaire for formal research was developed. The results of the qualitative research show that most of the questions are relatively clearly understood and most of the questions are answered.
Formal study: Data is collected from an expected sample of 300 survey questionnaires by convenience sampling method. After being coded and cleaned, the data undergoes steps of factor analysis to explore EFA, test Cronbach alpha reliability coefficient, correlation analysis, multiple regression analysis to determine the influencing components. on customer satisfaction and the influence of those components. In addition, the study also carried out T-test, ANOVA analysis in assessing the satisfaction of different customer groups by customer type (individuals, businesses, age, gender) with the support of software SPSS version 16.
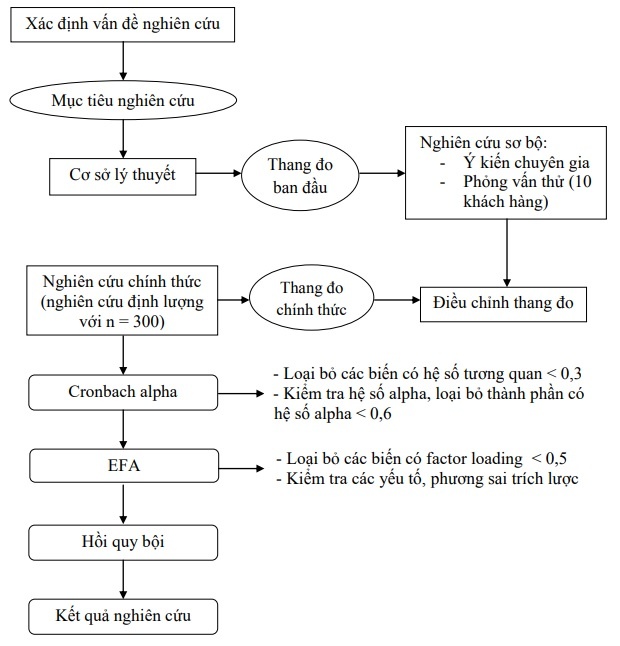
Figure 2.2: Research process
2.9.4. Survey process
2.9.4.1. Questionnaire design
The study uses the SERVPERF model with five components Reliability, Responsiveness, Service Capability, Empathy and Tangible Means. The study used a 5-point Likert scale, from (1) Not good to (5) Very good. The questionnaire consists of the following five parts:
Part I: Some personal information of customers such as age, gender, income …
Part II: Overall assessment of customers about SCB’s services that customers have or are using.
Part III: Customer’s assessment of SCB’s service quality before and after consolidation.
Part IV: Level of customer satisfaction.
Part V: Customer opinions to improve service quality of SCB. The official questionnaire was designed with 34 observed variables (see Appendix 3).
2.9.4.2. Determine the required number of samples
This study uses convenience sampling method. In the data analysis method, the larger the sample size, the better because it is based on the theory of large sample distribution. How much sample size is appropriate is usually determined empirically (Nguyen Dinh Tho and Nguyen Thi Mai Trang, 2011). Normally, the representativeness of the selected sample will be appropriate in proportion to one (1) observed variable requiring at least five (5) samples.
The survey model in this study includes 5 independent factors with 34 observed variables, so the required number of samples is 34×5=170 samples. To obtain highly reliable information, the author expected the study sample size to be 300.
To achieve the set sample size, 300 questionnaires were conducted to survey customers directly at the counter and emailed to customers with the support of colleagues at transaction offices in the city. Ho Chi Minh.
The result was 251 votes with a guaranteed response rate of 83.67% (251/300), of which 17 were rejected as invalid. Therefore, the number of samples left to include in the analysis is 234 samples.
2.9.4.3. Building a scale
The scale to measure customer satisfaction with service quality at SCB includes 34 observed variables with 5 components. In which, the Trust component includes 6 observed variables; Response component consists of 9 observed variables; The service capacity component consists of 6 observed variables; component Empathy includes 6 observed variables; component Tangible means includes 7 observed variables. Observable variables are coded for the convenience of using SPSS 16.0 software (see Appendix 4).
2.9.5. Analyze research results
2.9.5.1. Description of survey form
- Gender, 55.1% of customers are female and 44.9% of customers are male. It shows quite evenly, there is no big difference between male and female customers (see chart 2.10).
- Age, customers over 25 to 40 years old account for the highest proportion (42.3%) and customers over 55 years old account for the lowest rate (14.1%), the remaining customers account for the percentage. relative (from 17.5% to 26.1%). The age of the survey sample is quite uniform, not focusing on any age group (see chart 2.11).
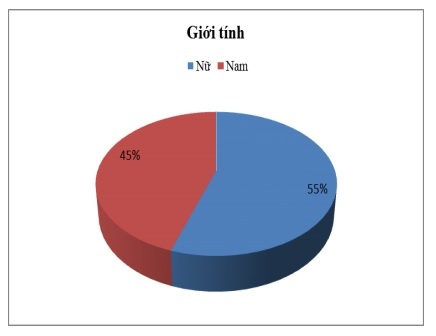
Figure 2.10: Gender
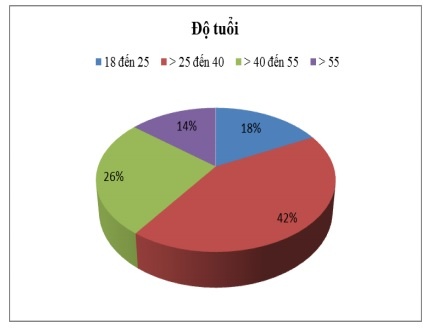
Figure 2.11: Age
(Source: Appendix 5)
- Regarding transaction customers, individual customers account for 76.5% and corporate customers are 23.5%, showing a large difference, but this difference is appropriate because individual customers accounts for 95% of customers in the entire SCB system (see chart 2.12).
- In terms of transaction time, customers trading over 24 months accounted for the highest percentage (32.5%), followed by customers trading from 6 months to 12 months (23.1%), and trading customers. over 12 months to 18 months (23.5%). The rest are customers trading under 6 months and over 18 months to 24 months (see chart 2.13).
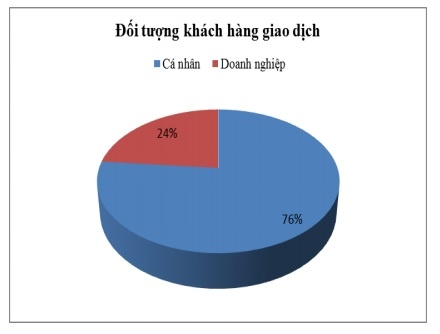
Figure 2.12: Target customers
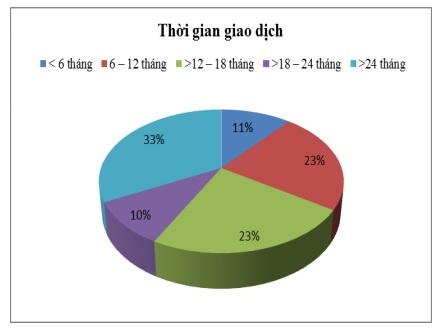
Figure 2.13: Trading time
(Source: Appendix 5)
In terms of income, customers with incomes from VND 9 million to VND 24 million accounted for the highest proportion (35%), followed by customers with income over VND 24 million (30%), customers with income from 6 million to 9 million dong (24%) and finally customers with income below 6 million dong.
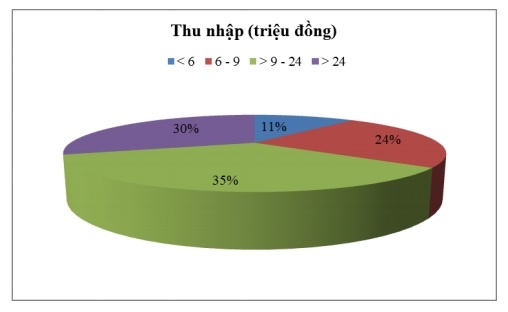
Figure 2.14: Income of customers
(Source: Appendix 5)






