Thus, customer satisfaction is the customer’s perception of the quality of banking services. If customers perceive service quality at a good, very good level, customers will feel satisfied. On the contrary, if the customer’s perception of service quality is not good, on average, customers feel unsatisfied.
1.8.2. The role of customer satisfaction in the development of the bank
Customer satisfaction plays an important role in the existence and development of the bank:
First, customer return: a satisfied customer often returns to use the service or product. Most of the bank’s revenue comes from old customers. Long-term customer satisfaction also creates long-term attachment and attachment of customers to the bank.

Second, costs: unsatisfied customers with products and services can increase business costs. If the customer is not satisfied with the product or service, then support may be required which will increase the operating costs. Or the customer can return the product which will affect the cost of the warranty. More importantly, the cost of acquiring new customers is much higher than the cost of maintaining existing customers.
Third, free marketing: when customers are satisfied, it is likely that they will buy again and customers will share information with friends and relatives. This is an extremely effective form of word of mouth marketing that helps the bank not spend any advertising costs and still increase revenue.
Fourth, cross-sell products: when customers feel satisfied, they will intend to use more other products and services. Just like that, the bank can sell more products based on the trust, loyalty, and long-term attachment of customers to the bank. Conversely, if the customer is not satisfied, of course the bank will not be able to cross-sell products and services.
1.8.3. The relationship between banking service quality and customer satisfaction
Maybe you are interested!
-
 Evaluation of customer satisfaction for service quality at Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank after consolidation - 1
Evaluation of customer satisfaction for service quality at Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank after consolidation - 1 -
 Evaluation of customer satisfaction for service quality at Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank after consolidation - 2
Evaluation of customer satisfaction for service quality at Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank after consolidation - 2 -
 The Effectiveness Of Banking Service Quality
The Effectiveness Of Banking Service Quality -
 Overview Of Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank After The Consolidation
Overview Of Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank After The Consolidation -
 Assess The Current Status Of Customer Satisfaction About Products And Services Of Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank
Assess The Current Status Of Customer Satisfaction About Products And Services Of Saigon Commercial Joint Stock Bank -
 Correction Of Research Models And Hypotheses
Correction Of Research Models And Hypotheses
There is a relationship between service quality and satisfaction (Cronin and Taylor, 1992). Satisfaction is the consumer’s response when the desired is met (Oliver, 1980), which is the customer’s response to the difference between the desired and the perceived level after using the product/service. Thus, satisfaction is a function of the difference between received results and expectations (Kotler, 2007). Parasuraman et al. (1993).
S.Sivesan (2012) concluded that service quality has an impact on customer satisfaction. Bank leaders or regulators need to identify the key quality determinants, clearly manage customer expectations, and improve their knowledge and skills to serve customers.
Abdul (2012) points out that customer perceptions change depending on the nature of the service. Measuring customer satisfaction with surveys or focus groups will make a useful contribution for banks to improve. Banks need to look at areas of weakness in order to respond to customer requests.
According to Ahasanul et al. (2009), customer perception and satisfaction can be considered as the key for banks to improve service quality. Manage the delivery of high quality service to increase customer satisfaction.
Commercial banks should pay more attention to service quality and staff capacity development. There was no significant difference between perceived emotional value and employee competency: both values were assessed by customers. Employee competencies (dedication to work, knowledge and expertise) and moral values (good mentality; comfort and security guaranteed; reliability and satisfaction; positive emotions) and experience) is most important to customers’ perceptions of the emotional value and competence of retail bankers. This encourages retail banking managers to always give their full attention to developing employees’ competencies and creating emotional value. Furthermore, during an economic downturn, retail banking managers should invest in employee training and think about empowering those on the front lines. In addition, service quality is also identified by customers as having an important influence on customer satisfaction (Neringa et al., 2012).
In summary, service quality and customer satisfaction have a close relationship. Service quality is an important factor affecting customer satisfaction. If the service quality is better than expected, the customer will be satisfied and the bank will achieve the goal of satisfying the customer’s requirements. The higher the satisfaction, the higher the customer’s attachment and loyalty to the bank’s brand.
1.9. Some models of satisfaction measurement
1.9.1. SERVQUAL model (Parasuraman et al., 1988)
Service quality components: SERVQUAL measures service perception through the following five service quality components:
1. Reliability: demonstrates the ability to perform the service appropriately and on time the first time.
2. Responsiveness: showing service staff’s willingness to provide timely service to customers.
3. Service capacity: showing professional qualifications and polite and welcoming service to customers.
4. Empathy: showing care for each individual customer.
5. Tangible means: shown through appearance, dress of service staff, equipment to perform the service.
According to SERVQUAL model, service quality is determined as follows:
Service quality = Perceived level – Expected value
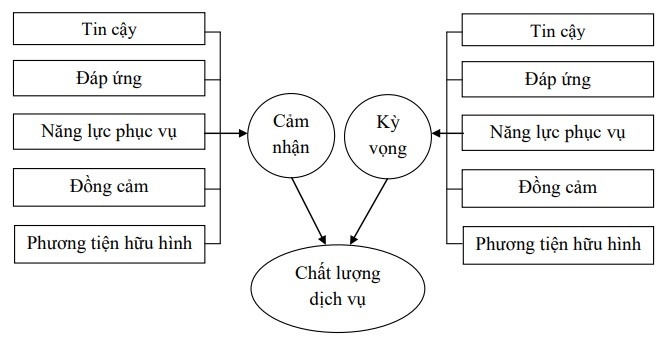
Figure 1.1: SERVQUAL . model
The scale set consists of two parts, each part has 22 observed variables. The first part aims to determine the customer’s expectations for the service in general. That is, not interested in a particular business. The second part aims to determine the customer’s perception of the service performance of the surveyed enterprise. That is, based on the specific service of the surveyed business to evaluate. From the research results, the aim is to recognize the gap between customers’ perception of service quality provided by enterprises and customers’ expectations for that service quality.
Application of the model: helps businesses assess customer expectations and perceptions of service quality. This model also helps businesses determine exactly which areas need management attention and service quality improvement.
Limitations of the model:
-Due to the desire to find a model that can represent all types of service quality, these researchers keep only those components that are common and suitable for all types of services. Therefore, some elements are necessary and suitable for some types of services, but because they are not suitable for the majority, they have been removed.
– Do not consider external factors as well as marketing activities, but only focus on internal factors.
– The concept of expectation is also quite vague for respondents. Therefore, using SERVQUAL scale may affect the quality of collected data, leading to reduced reliability and instability of observed variables (Nguyen Huy Phong and Pham Ngoc Thuy, 2007).
The customer expectations part of the SERVQUAL model does not add any additional information to the customer perception (Babakus and Boller, 1992).
1.9.2. SERVPERF model (Cronin and Taylor, 1992)
Service quality components: SERVPERF model is built based on SERVQUAL model. Cronin and Taylor (1992) argue that the level of customer perception towards the service performance of the enterprise best reflects the service quality. This model eliminates the evaluation of expectations, but only the evaluation of customer feelings. According to the SERVPERF model, service quality is determined as follows: Service quality = Perceived level.
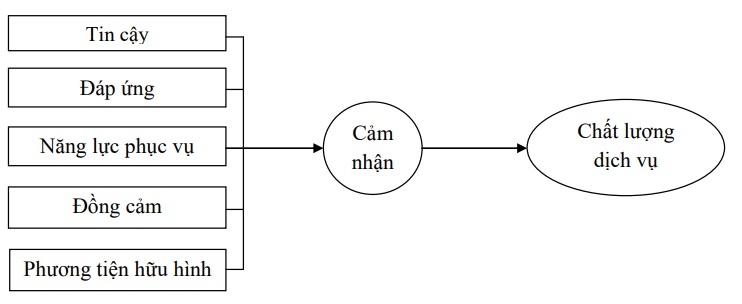
Figure 1.2: SERVPERF . model
Application of the model: Quality of service should be conceptualized and measured by customer attitudes. The performance-only SERVPERF model is more efficient than SERVQUAL because it reduces the number of variables by 50% and the results show better results. Quality of service is an antecedent of customer satisfaction and can influence customer purchase intention.
Limitations of the model: it has not been generalized to all types of services and the quantitative relationship between customer satisfaction and service quality has not been established.
1.9.3. Models of Quality and Engineering (FSQ and TSQ) (Grönross, 1984)
Service Quality Components: The FSQ and TSQ models focus on two main aspects of service quality, functional quality (FSQ: Functional Service Quality: how the business performs the service) and technical quality. Technical Service Quality (TSQ: Technical Service Quality: what service does the business provide) and service quality are strongly influenced by corporate image.
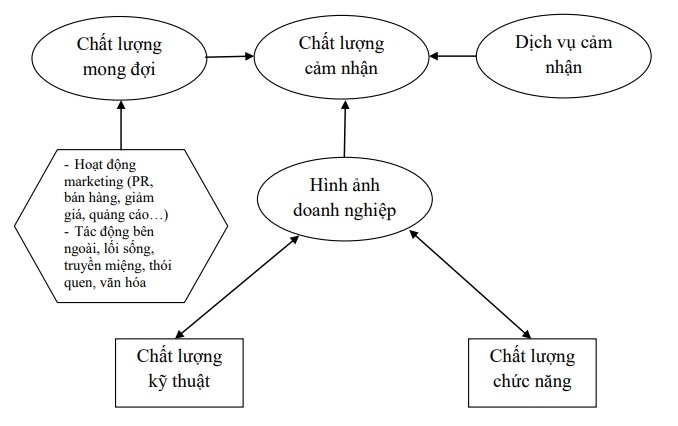
Figure 1.3: FSQ and TSQ . model
According to this model, perceived service quality is not only influenced by the customer’s experience of judging whether the quality is perceived as good, average, or bad. It is also influenced by the perceived service quality as well as the outcome of the evaluation process.
- Technical quality: is the result of the interaction process between the enterprise and the customer in which the enterprise provides the service and the customer receives the service.
- Functional quality: shows the service performance of the business, reflecting how the service is provided. In the correlation between the two aspects mentioned above, functional quality plays a more important role.
- Corporate image: understood as the general perception/impression of customers about the business. If businesses create a good image in the hearts of customers, they easily overlook the shortcomings that occur in the process of using the service. Corporate image is an invaluable asset and has a positive impact on customers’ evaluation of service quality, product value and their satisfaction.
Application of the model: according to this model, quality service depends on technical quality, functional quality and corporate image. Functional quality is more important than technical quality.
Limitations of the model: The model does not explain how the measurement of technical quality and skill quality is made.
1.9.4. Expectations-Feeling Model (Oliver, 1980)
According to Oliver (1980), the theory of “expectations-perceptions” includes two sub-processes that have an independent impact on customer satisfaction: pre-purchase product/service expectations and customer satisfaction. customer’s perception of the product/service after experiencing it. After using the product/service, the customer compares their perception of the actual experience with their expectations.
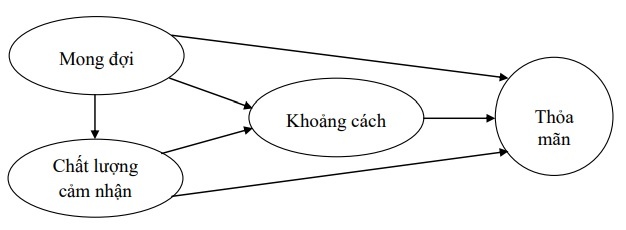
Hình 1.4: Mô hình Kỳ vọng – Cảm nhận
Figure 1.4: Model Expectations – Perceptions
This study uses the SERVPERF model for the following four reasons:
Firstly, SERVPERF model inherits SERVQUAL model and focuses on service quality.
Second, evidence from the experience of Cronin and Taylor doing comparative studies in the four areas of banking, pest control, drying and fast food; and Parasuraman’s studies also show that SERVPERF is better than SERVQUAL.
Third, using the SERVPERF model will give better results than the SERVQUAL model, and the SERVPERF questionnaire is more than half shorter than SERVQUAL, not boring and time consuming for the respondents. In addition, the SERVPERF scale is simple, but gives better results because when asked about the customer perception level, they tend to compare between the desire and the feeling in their head to answer the question (Nguyen Huy Phong et al. Pham Ngoc Thuy, 2007).






