How can a person create an indication, a representation to indicate a reference through a reference expression, and a person can recognize a reference through that reference expression? The first is based on the context, how the reference works in the real context; the second is based on the opposite; the third is based on things in the context of GT; the fourth is based on space, time, people are determined in three-dimensional coordinate system associated with context; the fifth is based on the pragmatic connection between proper names, definite phrases, facts, … which are conventionally associated with within the defined socio-cultural community.
![Export only (dexis) [38; p.183] is one of the methods of object projection, the expression of 1](uploads/2021/08/23/luan-an-tien-si-ngu-van-phat-ngon-chua-hanh-dong-hoi-trong-giao-tiep-mua-ban-bang-tieng-viet-9.jpg)
Export only (dexis) [38; p.183] is one of the methods of object projection, the expression of object projection, is an important element to indicate the object projection of PN because it is an element that means “to show”. The term “pointing” in Vietnamese used to translate the term deictic is derived from the Greek word meaning “pointing”. We can make our interlocutor know the thing we are talking about by using a reference movement to point to that object.
Using the hand to point at the referenced thing has many limitations, because: first, what needs to be projected is infinite, but what can be pointed out is limited. Second, we can only point to specific things, not just abstract things, such as ideas, etc. Thirdly, “NN” pointing is often inappropriate in the politeness principle when GT. Fourth, it can only be done in the present. Fifth, it is human manipulation, not a NN factor.
In NN there is no direct method, only output method. The NN morphemes used to do this “indication” are called deictic expressions, whose imperative condition is that they are used to indicate something with context. Output-only expressions associated with the context in a three-dimensional coordinate: people, space, time.
Only GT people in that context can best understand those three-dimensional coordinates. It is the speaker who determines the coordinates first, and second, the speaker presses on the listener himself, forcing the listener to accept it.
Expressions only appear most clearly in oral, face-to-face, and verbal interactions. Explicit referencing is a form of reference, related to the context, the proximity of the speaker: denoted by proper name, descriptive expression of the object denoted by proximal terms such as hey, here, now…; against the distance from the speaker like that, that, then, then…. They are interpreted symbolically, as forced to depend on positioning towards the speaker center, the deictic center.
The reference is referred to in a three-dimensional coordinate where the speaker is centered: only the persona, only the space, only the time. Corresponding to people in the context we have only personal appearance. Calling is an activity that identifies and refers to objects in the context. Only the address is used to locate the distance according to the proximity axis (solidarity), distance axis. This axis is characterized by two poles: the intimate pole and the alien pole. Social position axis, hierarchical relationship. This axis is characterized by two poles: equal pole and unequal (low – high).
The above distinction also shows the complexity in their use, CTLC according to the coordinate system matching the two-dimensional space of the two axes of closeness and authority. The contemplation in the situation, leading to the decision to choose the form of this or other personal expression, is considered by researchers as a factor of social deixis.
Maybe you are interested!
-
 / The Property Is Not Within The Framework Of The Ht . Structure
/ The Property Is Not Within The Framework Of The Ht . Structure -
 Steps To Follow For The Selection Structure
Steps To Follow For The Selection Structure -
 Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 8
Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 8 -
 Based On The Combination Of Morphological Structure-Purpose Gt-Face-To-Face Nature
Based On The Combination Of Morphological Structure-Purpose Gt-Face-To-Face Nature -
 The Concluding Aspect Of The Question Contains The Act Of Asking Directly
The Concluding Aspect Of The Question Contains The Act Of Asking Directly -
 The Pragmatic Aspect Of Pn Contains Direct Questioning. We Stand On The Pn-Hierarchy Point Of View, Considering The Sentence In The Relationship Between The Pn And The Recipient Of The
The Pragmatic Aspect Of Pn Contains Direct Questioning. We Stand On The Pn-Hierarchy Point Of View, Considering The Sentence In The Relationship Between The Pn And The Recipient Of The
These social export-only factors are always specific. The selection of a certain form and the use of this distinctiveness in the personal appearances of the CTLC. Because the choice of a certain form will inevitably announce something that is distinct from another because they are selected, marked and defined in the coordinate system of the two axes of proximity and authority. We summarize only the pronouns by the following diagram 1.2:
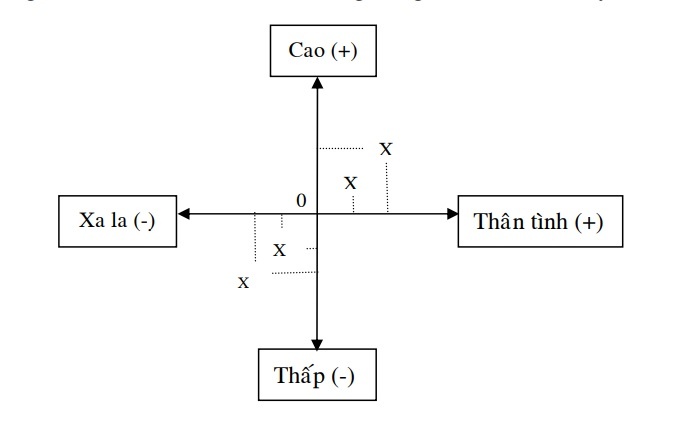
Diagram1.2
Corresponding to the space in the context, we can only output the space used to locate the spatial distance with the speaker, with the situation. The pragmatic meaning usually focuses on the spatial output as the psychological distance in reality. CTLC is also closely related to spatial output because at a close distance the speaker can easily mark something physically and psychologically close to make it easier for the listener to infer.
Corresponding to the time in the context we have only time output. Time output is a method of temporal projection used to locate the psychological time distance of the speaker. CTLC has a strong relationship with temporal output because the speaker can easily mark something about time that is physically and psychologically close to make it easier for the listener to make inferences.
5/ Structure of choice in the relationship between language and culture
According to the common understanding, language is in the cultural category itself, included in the culture itself. [ninety three; 172]. But in reality it is different:
1/ In its practical activities, agriculture has a strong, far-reaching influence and dominates the cultural mechanism in many aspects and at many very complex levels. Language is really a multifaceted premise for the formation of culture.
2/ Culture is wide in scope, there is not a single definition that solves and limits it thoroughly so that we can really take it as a basis for research.
3/ Culture is a broad and complex category. Right from the opening chapter of the General NNH Textbook, Saussure said: “NNH is related to other sciences, but the dividing line is difficult to define” especially the cultural object”, which cannot be seen in the field. How can there be so many strange opinions, so many prejudices, so many illusions, so many fictions as in this field”[67, p 27]
CTLC in the relationship between agriculture and culture:
1. The first point of view that we pay attention to is to see agriculture as a means of communication, expanding cultural understanding among communities in general.
2. The second point of view is that according to Engles’ emphasis, agriculture is an important premise that together with labor forms the “social man”. Therefore, language is the premise to create subjective and objective thinking from which to create cultural objects, specifically: music, painting, sculpture, architecture…[101]
3. The third point of view is that culture is a social institution and state is also a social institution. Based on this point of view, we have the following comments: the perceived value of culture through language and vice versa, language is shaped and regulated by cultural factors and they are always determined by estimation. convention, convention, symbolism of a nation, a social community in the definite coordinate system of space and time. Mental activity must be through material signs.
Agriculture is a spiritual activity, it must be through specific material signs of the culture, such as a way of greeting, a custom of worshiping, a folk dance, an archaeological relic, an architectural line. architecture, a work of painting…. On the contrary, if culture is a spiritual activity, then language plays the role of a physical sign (sound or written) to express that spiritual value. At this time, language is considered as the only means capable of decoding for all types of culture, and vice versa, the types and properties belonging to ethnic culture are shown vividly, associated with language explicitly. or hidden function.
4. The fourth point: the ability to code and decipher automatically what is not said or written must certainly be based on pre-existing knowledge structures. They function as familiar frameworks (schema) from existing experience that are used to account for new experiences.
These familiar frames that are static and relatively fixed are often referred to as frames. A framework that everyone in a social group shares is called a schema or archetype. [194, p.161]. Thus, a group of people of a social community (wide or narrow) capable of coding and decoding explicit or implicit meanings according to language automatically must be based on the schema of the underlying knowledge structure. has the nature of normative, symbolic convention, formed during the long-term use of language in ethnic communities, especially related to culture. That is the cultural schemata (cultural schemata)[183, p. 162].
5. The fifth point of view: when using language according to community habits, according to certain frames to express content, it often puts the speaker in a situation of choosing what frame, such linguistic signal. Which fits the “habit” framework.
The relationship between the structure of choice – language – national culture: Through the structure of choice with language, national culture reveals its own characteristics. On the contrary, the characteristics of national culture help speakers to orient and choose appropriate linguistic signs to reveal both explicit and implicit content.
To study this issue, we need to answer the following questions: How are the characteristics of national culture associated with language? Language through which structure chooses to reveal the meaning of specific culture? How to distribute language choices to express specific cultural identity? All are aimed at serving the problem of “understanding each other” better when communicating with cultures and ethnic languages in a broad field called “intercultural pragmatics” [194, p.165], or research The different ways of speaking determined by the national culture are called “comparative pragmatics” [194, p166], or the study of the speaking actions of non-native speakers, who will communicate in the language. The second language is called “interlinguistic pragmatics” [183, p166].
Due to the limitation of the thesis, we only go into the study of the above issues within the scope of the implicit meanings in the Vietnamese people’s buying and selling communication. The relationship between the structure of choice to create functional meaning and the national cultural characteristics is studied very carefully in Chapter 5.
1.3. CONCLUSION
1/ Researching the act of asking in business communication is actually interested in the process of expressing the most authentic social nature of language in life. Therefore, the precepts on language – speech, principles of communication, principles of dialogue… are indispensable instructions to contribute to the clarification of the theory of language action.
2/ The theory of language action applied to the study of the act of asking in buying and selling communication here is determined with specific psychosocial conditions. The way of creating linguistic meanings through the choice structure is a high expression of that specificity of linguistic actions.
3/ In the process of theorizing, in order to elucidate the specific characteristics of this type of discourse structure in the direction of the above findings, besides the static view, we pay special attention to the dynamical approach. The selected structure is a super-segmental linguistic structure, which does not segment reality according to the paradigm but divides the level of meaning according to the association system, in order to create an allegorical meaning unit, create a goal, establish a pragmatic communicative effect from the dynamic interaction of sociolinguistic thinking with linguistic and non-verbal categories.