1.2. THEORY OF Structural Selection to CREATE MEANING
1.2.1. Pragmatic information
G. Miller (1978) talked about the diversity of pragmatics expressed through the morphological structure of the language, containing pragmatic information, which is the supplementary information through the most basic semantic content information. determined, associated with a specific speech context.

Pragmatic information is made up of a choice structure that creates implicit meaning. Stable and static knowledge and skills in relation to application and selection (linguistic factors), interaction with events and communication situations (non-verbal), on the basis of maximizing The profound social nature of language through thinking, capacity, and creativity of individuals represents sociolinguistics, in order to achieve the highest communication efficiency.
All the structural elements and targets of the above selected structure will help the language become lively and flexible, creating the ability to create, understand and transmit semantic information with perfect volume and color. completely new in the linguistic direction.
Pragmatic information is complementary to the basic semantics provided by language activities. Thus, the structure of choice to create implicit meaning has brought about new semantic and pragmatic information of speech acts in language function.
1.2.2. Structure of choice (CTLC)
1.2.2. 1. The concept of choice structure
The selected structure is the meta-segmentation structure of the process of creating new meanings, establishing effective communication and identifying meanings in the allegorical direction, that is, creating comprehensive implicit meaning units for pragmatic information. complementary and can only divide the level of meaning according to the associative system (explicit, implication level), but cannot segment reality according to the paradigm, not divide the meaning according to the semantic axis according to the type of paragraph structure. , associated with the process of coding and decoding from the dynamic perspective of communication activities in a specific context, choosing the explicit structure as the form of the discourse structure.
1.2.2.2. Basic properties of the choice structure
a/ Going from the specific characteristics of the act of asking in buying and selling, the thesis establishes a comprehensive, structured, structured selection structure model with operating rules, to understand and explain the mechanism of meaning creation. language function.
b/ The effective communication in the allegorical direction of CTLC is formed from a polite strategy to ensure rights, based on mutual understanding of the psychology of communication between the buying and selling roles of the environment, namely communication. purchase.
c/ The structure of choice to create functional meaning is a meta-linguistic convention, because, although not separate from the linguistic signal, established from the language code, but in the process of operation, through the mechanism of the language code. By itself, through the dynamic and subjective processing line of thinking, promoting the social nature through the individual, the inherent real meaning of language has been destroyed, and the original real meaning no longer exists. but only take advantage of the material shell of the signal, contact, and interact with two linguistic and non-linguistic elements to reprocess, nullify the inherent real meaning of the language, and at the same time be replaced with a new meaning. It is the process of coding language in a non-linguistic direction and linguisticizing non-linguistic elements.
d/ The language of the choice structure in its wholeness has turned into a reference expression in the thinking manipulation of coders and decoders.
e/ We cannot formally identify the choice structure from a static perspective, interpreting it separately from the language communication activity associated with the user’s coding and decoding process, but it must be formed in dynamic position.
1.2.2.3. Causes of formation, establishment of choice structure model
We would like to propose the name, concept of CTLC, from the following reasons:
1/ Subjective causes: Going from the very specific characteristics of the operating system in GTMB, LA determines the purpose is how to find and establish a comprehensive model, full of factors with rules. , how to be able to explain the semantic meaning mechanism.
2/ Cause from the language side The first cause is the problem of meaning. The most difficult thing of current language research and also the most difficult problem that the thesis poses is the problem of MEANING. What does it mean? This question is now and will be difficult to answer for many years to come. When analyzing and synthesizing meaning, if we only rely on the relationship between the signifier and the signified, we cannot understand it thoroughly.
Because the signal is not fixed in its appearance. It determines the meaning mechanism, identifies the communication effect formed from the semantic mechanism of pragmatics, based on the theory of semiotics, sociolinguistics, psychology, and culture. … The next cause is linguistic signals, including: non-verbal factors: context; gesture…; linguistic factors: there are 3 relationships: signal-signal (Learning), signal-reality (semantics), signal-user (pragmatics).
So, when it comes to pragmatics, we have only mentioned one side of the signal. At the same time, when it comes to semantics, the relationship between meaning and language users or Grice, also known as unnatural meaning, is not fully resolved. When solving the problem of meaning, the choice structure has always taken into account both linguistic factors (natural meaning – unnatural meaning) and non-linguistic factors, .
Another reason is that the speaker often performs the act of speaking with purpose and conviction. To achieve good results, the implementer must develop an action plan. So the communicator executes the plan using CTLC.
A two-way signal created and interpreted by two different individuals, besides ensuring that the linguistic signal must have a common background, the two communication roles also differ in many aspects, such as: age, knowledge , experience, position, own purpose…. Therefore, to ensure the ability to maintain the dialogue, the communicators must have a choice of content and linguistic signals, in order to ensure the appropriateness with the role, communication strategy, with the current utterance context. present, with the ability to receive and decode information that the speaker can predict in the listener…
The selection of content and linguistic signals of CTLC also serves to perform three other functions of speaking action, expressive function, announcement, and evaluation in communication. Another cause is the creative process of selecting and arranging linguistic signals to express thoughts well, to create “new” meanings according to the intention in the best possible way. CTLC has an important role in creating meaning.
All pragmatic information, especially implicit information, although not clearly shown on the surface of the PN, and not fully expressed through the form but reflected in the semantic content, is the result of using the structure. selection architecture.
The final cause is that F. Armengaud argued that “Practical? A young subject is the convergence of many social sciences with vague boundaries” [63]. And David Crystal [203, pp.240] also said, we cannot define a clear boundary between meanings (semantics); with sociolinguistics; with extralinguistic contexts. The choice structure demonstrated through the thesis helps us to clearly see the boundary line and relationship between the issues of meaning, sociolinguistics and extra-linguistic context and serves “directly how to use language”. This reason is directly related to the problem proposed by the thesis, which is CTLC.
1.2.2 4. Origin and process of selection structure
In fact, the roots of the language used the choice construct. That is the science of “rhetorique”, called “rhetoric”, dating back to Greco-Roman antiquity. In modern times, it is used by philosophers and logicians such as L. Wittgenstein (1926), CW Morris (1938), K. Carnap (1942), J. Austin (1962), R. Montague (1968), J. Searle (1969)… built a theoretical system around the first half of the twentieth century. Starting in the 60s, the problem of choosing words to achieve effective communication has been studied by linguists in many different aspects.
Among the three aspects of learning, semantics, and pragmatics, the aspect of learning has been interested in surveying for a long time by researchers and has obtained many remarkable results. Recently, world linguistics in general and Vietnamese linguistics in particular are interested in semantics, pragmatics and propose some new types of structures such as: predicate – reference (semantic) structure; thematic structure; message structure.
CTLC differs from the message structure in that: the message structure is only interested in the information of the utterance, mainly the old news and especially the new news. That is, the utterance is only valuable to the receiver when it gives him information that he did not know before. Because in practice, people pay little attention to whether the received utterance is a simple or complex sentence, a main or a minor part, etc., but only pay attention to the meaning of the utterance, to new, necessary and complementary information. useful. But the structure of the message also cannot stand, without relying on the conclusion, on the syntactic rules of the sentence. The syntactic structure is well studied for a long time.
The relationship between them is a relationship that is both unified, inconsistent, and as close as two sides of a piece of paper that are inseparable. That relationship vividly shows the duality of the pragmatic plane: this structure is the container that represents the formal side of the meaning, the content of the other’s contained content and vice versa. The choice structure will have a strong impact on the implementation of the main intent purpose and strongly affect the communication strategy of the utterance. It presents various nuances of subtle refraction and discursive modes on many related but unequal linguistic levels, such as vocative words, cultural schemas, etc.
1.2.2.5. Structural elements of the selection structure
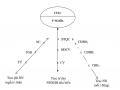
The choice structure is a meta-segmentation structure, which cannot segment reality according to the paradigm, but can only divide the level of meaning according to the association system. In terms of structure from the signaling mechanism, CTLC has the following main elements:
a/ Non-NN elements (underground circuit, static axis, which is an important premise and support for creating meaning) Formation of a formal overlapping mechanism (objective and non-physical) for the expression of The structure of choice to create the above-mentioned connotative meaning, from its depth, it cannot be separated from the impact pressure of non-linguistic factors Non-linguistic factors include two main forms: non-linguistic (linguistic) factors. scenes, gestures, gestures, attitudes, etc.) and extra-linguistic pressure factors (which is the pressure from the unnatural meaning of the language, the meaning pressure caused by presuppositions and presuppositions).
For a long time now, we often talk about the issue of presumption and presupposition, but when we take the act of asking in transactional communication as the main research object, we realize that they are governed and created strong pressure outside the language to create meaning, stemming from the psychology of buying and selling, from the very own world of the trading environment, of the partners (both sides clearly understand the intentions, beliefs, etc.) , each other’s manner). Non-verbal factors have the function of influencing and exerting great pressure from the outside on the choice structure to create implicit meanings. In contrast, a choice structure that utilizes and selects these specific non-verbal elements to create new meanings is very effective. In fact, they are not separate, but crisscross, overlap.
b/ Linguistic factor is a key and indispensable factor in the selection of linguistic signals to create implied meanings, including: form of the signifier; the meaningful content of the signified (ND meaning inherent which Grice calls natural meaning and ND extended meaning or unnatural meaning). The linguistic element is made up of the basis of the explicit message structure based on the signifier and the signified at level 1 (both tangible and intangible). That explicit message structure turns into a second-order formal signifier, to express the content meaning extended in the allegorical direction of the second-order signified…
LANGUAGE MEANING STRUCTURE JUMP LANGUAGE MEANING STRUCTURE
| CBĐ (HT) b. 1 =>NN object | CBĐ level 2 (HT 2) (object + non-physical language) | CBĐ level 3 (HT3) |
| CĐBĐ (ND)b. 1 => explicit meaning (structure of explicit message) | CBĐ level 2 (HT 2) (object + non-physical language) | CBĐ level 3 (HT3) |
| CĐBĐ level 2 (ND 2)=> (Meaning of level 1 language) | CĐBĐ level 3 (ND3) => (figurative meaning |
Maybe you are interested!
-
 Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 2
Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 2 -
 The Problem Of The Relationship Between Language And Speech
The Problem Of The Relationship Between Language And Speech -
 Principle Of “Local Hypothesis” And “Similar Reasoning”
Principle Of “Local Hypothesis” And “Similar Reasoning” -
 / The Property Is Not Within The Framework Of The Ht . Structure
/ The Property Is Not Within The Framework Of The Ht . Structure -
 Steps To Follow For The Selection Structure
Steps To Follow For The Selection Structure -
 Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 8
Statements containing the act of asking questions in business communication in Vietnamese - 8
Diagram 1.1 Contents of the extended implicit meaning