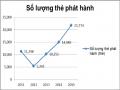
2.1.4.3 Cardholder
A person who is issued a card by the issuing bank to use. Cardholder is the only person authorized to use his/her card. Each cardholder is assigned a PIN by the issuing bank. Cardholders can use their cards to pay for goods and services at CSCNTs and withdraw cash at ATMs or cash advance points. Cardholder is responsible for:
Preserve the card so that others cannot steal the number or take advantage of it.
Use the card for the right purpose according to the regulations of the issuing bank.
Do not hand over the card and PIN to another person, the cardholder must bear the risk of card forgery to withdraw money or make payment.
Responsible for payment and refund of the used amount and interest to the issuing bank if using a credit card.
When the card is lost, it must be immediately reported to the issuing bank for timely management.
2.1.4.4 Card payment and (TT) banks and correspondent banks:
A bank that accepts card transactions as a means of payment through entering into card acceptance contracts with goods and service providers. By signing a contract, these goods and service suppliers will be accepted into the bank's card payment system, the bank will provide card reading devices, train staff on payment services card payments, management and processing of card transactions taking place at this location. In fact, many banks are both issuing banks and paying banks.
Maybe you are interested!
-
 Developing card services at Viet A Commercial Joint Stock Bank - 1
Developing card services at Viet A Commercial Joint Stock Bank - 1 -
 Criteria For Evaluating The Development Of Card Services In The Bank
Criteria For Evaluating The Development Of Card Services In The Bank -
 The Current Situation Of Card Service Development At Vietabank Compared To The Development Target
The Current Situation Of Card Service Development At Vietabank Compared To The Development Target -
 General Assessment Of The Development Of Card Services Of Vietabank
General Assessment Of The Development Of Card Services Of Vietabank
Card issuing banks are banks authorized by card issuers to perform card payment operations. If this bank accepts international card payments, it must be an official member or associate of an international card organization.
Card payment agent bank is a bank authorized by the Card Bank to perform a number of card payment acceptance services through a correspondent banking contract.
NHTT is responsible for:
Within 1 working day from receipt of payment receipt, payment must be made into CSCNT's account. When the card payment is in accordance with regulations, payment procedures must be carried out immediately with the issuing bank.
Responsible for providing equipment, payment invoices and billing statements; documents on how to access the card, check the card, the issuing bank's new notices on the payment limit change...etc for CSCNT.
2.1.4.5 Card acceptors
Are organizations or individuals providing goods and services that accept cards as a means of payment. After signing the contract, CSCNT must comply with the regulations on card payment of TTC. CSCNT is responsible for:
Only accept payment for cards with correct form prescribed by the TT and the issuing bank or the Card Association.
Only accept card payment after checking the technical safety regulations of the Commercial Bank and the issuing bank.
After delivering goods or providing services at the request of the cardholder, within the specified number of working days, the payment receipt must be submitted to the TTC or the correspondent bank to claim money. To overdue, if you encounter the above risk, you will not be responsible.
Regularly display the logos of the central bank or card organization
international.
2.1.4.6 Person responsible for payment
Applies to the issuance and payment of credit cards. This can be the main cardholder (if it is an individual card) or the organization or the company applying for the card (if it is a card authorized by the company for individuals to use). The person responsible for payment is obliged to pay all expenses arising from the cardholder's use of the card.
2.1.4.7 Card Center
As the central card management department - the representative of banks in direct external relations on card issuance, use and payment with international card organizations and other banks - responsible for operating the card business. issuance, licensing, tracing, card payment and risk management; It is also the center for card issuance and payment between branches in the bank's system.
2.2 Card service
2.2.1 Service concept
Service is a common concept, so there are many different definitions
About service:
According to Zeithaml & Britner (2000), services are behaviors, processes,
The way in which a job is done to create value for the customer to satisfy the needs and expectations of the customer.
According to Kotler & Armstrong (2004), services are activities or benefits that businesses can offer to customers in order to establish, strengthen and expand long-term relationships and cooperation with customers.
2.2.2 Service characteristics
A service is a special product that has its own characteristics that make it easy to distinguish from other tangible goods such as intangibility, heterogeneity, inseparability, and non-separability. can be stored.
Intangibility:
Intangibility of a service is a property that cannot be touched or grasped, has no specific shape like a tangible product, Goods have shape, size, color and even taste. Customers can review and evaluate whether it is suitable for their needs. On the contrary, the service is invisible, making the customer's senses not aware before
buy services. This is a big difficulty when selling a service compared to when selling a tangible good, because it is difficult for customers to try the service before buying, it is difficult to feel the quality, it is difficult to choose a service, and the service is difficult to advertise. fox. Therefore, services are more difficult to sell than goods.
The impact of intangibility on customers :
• It is difficult for customers to imagine the service
• It's difficult for customers to try before they buy
• It is difficult for customers to judge the quality
• It is possible to evaluate service quality through brands and prices
• Seek advice from acquaintances and salespeople
Inhomogeneity :
Services cannot be mass-provided, like the production of goods. This feature is also known as service differentiation. Accordingly, the performance of a service often differs depending on the way it is served, the service provider, the person serving, the time of performance, the area of service, the object of service and the location of the service. Fundamentally, service variability is also more likely and more frequent than non-conforming physical products, because services have a very high degree of human interaction. This feature makes service standardization more difficult to implement.
To overcome this drawback, enterprises can mechanize and automate in the service provision stage, and at the same time have a specific human resource management policy for service providers. However, contact with polite and welcoming service providers is also an attractive factor for customers. On the other hand, not every service can automate the provisioning process.
Inseparability:
The inseparability of services shows that it is difficult to divide services into two phases, the production phase and the use phase. Services are often created and used at the same time. This is not true of physical goods that are produced, stored, distributed through many intermediate stages of purchase and sale, and then consumed. For a commodity product, the customer only uses the product at the final stage, while for a customer service that accompanies it during or as part of the service creation process.
Impact of inseparability on customers:
• Customers must be present to enjoy the service
• Customers must go to the service location
• Influenced by the service delivery process, the service provider's attitudes, and the environment in which the service delivery occurs .
Impact of inseparability on business:
• Difficult to achieve economies of scale
• Difficult to achieve uniformity in quality (depends on service provider)
• Difficult to balance between service supply and demand
• The relationship between the customer and the service provider has a great influence on the customer's perception of service quality.
Non-storability:
Services cannot be stored, stored and sold like other goods, the process of supply and consumption occurs at the same time at the time of using the service.
Non-transferable property
When purchasing a product, the customer transfers ownership and becomes the owner of the goods he has purchased. When buying a service, a customer is only entitled to use the service and enjoy the benefits that the service brings for a certain period of time only.
This feature affects distribution policy in service marketing, in which wholesalers and retailers cannot transfer ownership. They are merely participants in the service delivery process. And of course, they have an influence on service quality. Thus, the issue of training, support, consulting, inspection and evaluation of distribution intermediaries is a necessary factor to ensure service quality.
2.2.3 Concept of card service:
If manufacturing enterprises create tangible goods (rice, rice, machinery and equipment, etc.), commercial banks produce intangible goods, or rather services. The bank's products have immaterial characteristics, are always passive, and depend on customers. The difficult thing is to process the authorizations according to the customer's wishes and requirements, the quality of banking products and services is reflected in the ability to complete the customer's authorization in the shortest time, accurately and safely. and convenience, especially for currency payment services.
Currently, there is no specific and exact concept for card service, but this is also a type of service that belongs to the group of retail services, also known as personal services of a modern bank. closely linked and developed with electronic banking services (e-banking) and e-commerce (e-commerce).
Debit card service can be understood as including all banking products provided to customers when using cards such as payment for goods and services, withdrawal, money transfer, balance inquiry, etc. Card service is the ultimate goal that customers need in a card, card service also has all the common features of the service.
Main activities of bank card service:
- Top-up: cardholders can top-up their accounts directly at the Bank, transfer money from other banks.
- Withdrawal: at the Bank, through the ATM system, at the Bank's cash advance points or allied banks
- Transfer: via any bank account, pay business transactions, service bills (electricity, water, telephone...)
- Receive transfer: from domestic and foreign banks, receive salary, bonus..
- Payment for goods and services: at stores, commercial centers, supermarkets, restaurants - hotels...
- Direct or automatic payment of electricity and water bills, top up mobile phones, buy prepaid cards...
Card service classification
Classification by support tools: card services at ATM, POS, internet. Customers can use different card services at different support tools.
Classification by territory: card services are performed domestically and abroad. Only international cards can use card services abroad.
Typical integrated service: is a preferential service of a bank associated with a certain organization for customers when using a combination of two services of that bank and that organization. This is a service that is becoming more and more popular, it is more attractive to customers because of the extra attractiveness that the second provider brings.
2.3 Card classification
Diagram 2.1: Card classification scheme
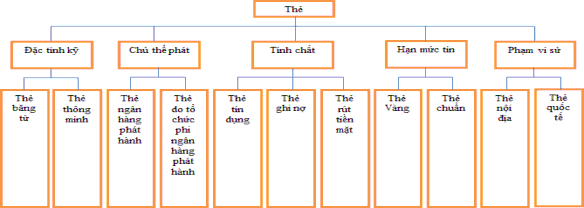
Source: Viet A Joint Stock Commercial Bank Card Process
2.4 Benefits and risks of using card services
2.4.1 Benefits of using card services
2.4.1.1 For cardholders:
Flexibility, convenience and safety:
When using the card, the cardholder has been provided by the bank with a payment service with high security and great convenience. With more and more card payment facilities, ATMs becoming more and more popular, the card will be an ideal payment tool for cardholders.
Customers do not face many risks when carrying large amounts of cash. Using a credit card or payment card ensures the ability to spend in multiple foreign currencies, regardless of the foreign currency of any country.
Currently, with advanced technology, ATMs are not only used to withdraw money, but it becomes a miniature bank with all functions and utilities: deposit, direct withdrawal, transfer to all banks. , pay bills, services, taxes, fees... buy prepaid cards for mobile phones, Internet... ATM systems are installed in most cities, some hotels, restaurants, supermarkets, etc. large department stores, including universities and this will allow users to withdraw money from many places when needed.
Cardholders can withdraw money, transfer money... at any time without having to go to the bank.
Credit granted:
For credit cards, the Bank provides credit in advance to customers to pay for goods and services without being charged any interest within the specified time, customers have been helped by the bank to expand their payment capacity. his math. In addition, when the customer has a balance on the account, if the customer does not use it, this balance will enjoy the interest rate on demand deposit.
Time saving:
Using the card is very simple and fast. Within a few minutes the user's command will be executed. And they can easily withdraw the amount they want.
Thanks to the form of payment via card of many workers, employees have a habit of depositing money into an account that is both profitable and safe.
Easily control spending:
Another benefit is that card users can let their relatives use their accounts via supplementary cards and can limit spending of extra cards for easy control.
2.4.1.2 For the Bank:
Above all, banks are the beneficiaries of card issuance and payment activities. This manifests itself in the following ways:
Increase capital for the Bank: In the process of card issuance and payment, banks have a low-cost capital mobilization channel from cardholders' account balances and card-accepting establishments.
Increase revenue from fees: trade discounts, cash withdrawal fees, payment agent fees, annual fees, ... the bank will get a relatively stable revenue.
Expanding the area of operations: placing ATMs or contacting
New card-accepting establishments are useful in places where opening a branch is expensive.
Joining the global service chain: After profits, the ability to provide global services is the biggest benefit for the bank, creating conditions for the bank to participate in the globalization process and integrate with the international community. economic.
Promoting diversification and modernization of banking services: The birth of the card enriches banking services, banks have the opportunity to develop other services such as transactions and online payment by card.
2.4.1.3 For merchants that accept cards
Increase business efficiency, Help CSCNT recover capital quickly.
By giving credit in advance to customers, the bank has helped customers spend beyond their means, this is a push on customers' purchasing power and this will make the consumption of goods. services of establishments accepting card payments increased.
In addition, for some establishments, accepting payments by bank cards is also a condition to enjoy the bank's incentives on credit, payment services...
Card transactions are paid immediately to CSCNT's account, with less risk of theft than checks or cash. In addition, the CSCNT avoids the phenomenon of customers using counterfeit money.
When accepting cards, merchants have the ability to minimize the costs of cash management such as preservation, counting, depositing into an account at the bank...
Shorten transaction time with customers
2.4.1.4 For the economy:
Reducing the volume of cash in circulation: As an alternative means of payment for cash, checks, etc., the card's first role is to reduce the volume of cash in circulation. Implement measures to "stimulate demand" of the State
Contributing to financial transparency, supporting the state's macro management: Because all transactions are done through banks.
Rapidly increasing the volume of circulation and payments in the economy because most transactions are done online.
Minimizing the risks of using cash and social evils related to using cash. Reducing the cost of issuing and printing new money,…
2.4.2 Some risks in the process of using card services:
* Fake issuance information or customer insolvency:
Due to not carefully verifying customer information, the bank may issue a card to registered customers with fake information. And so, the bank can be at risk when customers are unable to pay.
* Fake card
This is the biggest and most dangerous type of risk today that card organizations are very interested in. This is the case of organizations or individuals forging based on information obtained from card transactions or from cards that have been stolen or lost.
* Card stolen, lost
In card circulation, this situation is very likely to happen to customers and banks. In case the card is lost, the cardholder does not promptly notify the bank, leading to the card being taken advantage of by others, causing fake transactions and causing losses to customers.
* The cardholder did not receive the card sent by the bank
The bank sent the card to the cardholder by post, but in transit the card was stolen and used without the cardholder knowing that the card was sent to him.
* Cardholder's account is taken advantage of
This risk arises at the time the bank renews or reissues the card. Issuing bank receives notification of customer address change and requests to send card to new address. Due to not checking the authenticity of the information, the bank sent the card to a new address at the request of the customer, but this is not the request of the real cardholder.
* Risk of using a lost card
In some cases, the cardholder informs the issuing bank that the card has been lost, but then uses it while the card has not yet been included in the list of banned cards, the cardholder uses it by signing the invoice. slightly different from the signature on the card. There are also cases where the cardholder replaces the signature with a blank signature tape and re-signs it with a completely different signature from the old one. When paying, the cardholder will sign with a new signature. Thus, cardholders can avoid the responsibility of paying for transactions
* Risk of overuse
The customer intentionally uses the card at different CSCNTs with a payment rate lower than the payment limit but the total limit is higher than the allowed payment limit. This is only discovered when the TT Bank checks the invoices sent by CSCNT and the bank can bear the risk when the cardholder becomes insolvent. Cardholders can also take advantage of the card's global payment nature to collude with other people, handing the card over to that person for use in different countries with the cardholder's forged signature, and refusing to pay when being denied by the issuing bank. claim money.
* Create fake magnetic tape
This is a type of card forgery using high technology, based on customer information on magnetic tapes of card payment establishments, criminal organizations use encryption software and create magnetic tapes. fake on the card and make the transaction.
* Merchant staff prints multiple invoices for one card payment
Taking advantage of card payment invoices: The cause of this risk is that CSCNT staff deliberately printed out many sets of payment invoices of one card, but only delivered one set of invoices for the cardholder to sign to complete the transaction. Translate. After that, the staff of CSCNT forged the signature of the cardholder to submit payment invoices to the TT Bank.
* Risks in banking technology, information technology
In the current situation when the transaction volume and the number of cards have reached a huge number, the processing process requires a lot of support and depends greatly on equipment, especially automatic processing equipment. Therefore, the level of science and technology, machinery, equipment, telecommunications networks, etc. has a great impact on risks.
* ATM system is often overloaded, card transactions fail during processing.
In recent years, although the ATM card market has developed rapidly, the number of ATM cards issued is still very low compared to the market potential. In theory, ATMs operate 24 hours a day, but at present, they have not been implemented. presently. In addition, the system of card-accepting points is relatively small, which makes customers afraid to use cards.
2.5 Business process of card issuance and payment
2.5.1 Card issuance process:
Legal Basis
Card issuance and payment must be based on the law of the country where the card is issued, specifically the regulations on card issuance and payment issued by the State Bank. In addition, if the bank deploys an international card, the card issuance and payment must be approved by the international card organization through the contract signed between the bank and international card organizations, and at the same time comply comply with applicable laws and regulations of international card organizations.
Based on these bases, each issuing bank will have its own regulations on card issuance and payment prescribed by the General Director of the bank.
Card Issuance Process
- Marketing information activities to bring card products to the market
- Design and organize white card purchases
- Issuing card: this is considered one of the most basic operations to create a finished card product of the bank:
Figure 2.2: Card issuance process
(2)
(3)
Receiving records
Profile appraisal
Cardholder
(first)
(6)
Card delivery
Card stamping, Pin printing
Customer classification
(5) (4)
Source: Card issuance process at Viet A Commercial Joint Stock Bank
(1) The customer goes to the bank to request a card issue
(2) Receipt of card issuance documents: Customers go to the bank to complete some necessary procedures and present some other relevant documents.
(3) Appraisal of documents: Based on the customer's profile, the appraisal department examines the profile and makes a decision to approve the card issue or refuse it.
(4) Customer classification: If the review of the card issuance dossier is completely valid, the bank can conduct customer classification. For a debit card, it is simpler because the customer already has an account at the bank. As for credit cards, banks must conduct customer classification to have an appropriate credit policy.
(5) Embossed card and PIN, card packaging: With each issuing bank's own technique, embossed necessary information about the cardholder on the card such as card number, validity period, bank code... Simultaneously encrypt and format the personal identification number (PIN) for the cardholder. Pack the card and PIN in separate envelopes to send to the branch bank or directly to the cardholder.
(6) Handing over the card to the customer: Before handing over the card, the bank must activate the card for the customer. When the bank delivers the card and PIN, the cardholder is required to keep his PIN secret. In all cases of loss of money due to disclosure of PIN, the cardholder must be responsible.
After handing the card to the customer, the card issuance task is over. The time from the customer's request for card issuance to the receipt of the card is usually no more than 6 days.
2.5.2 Card payment process:
When a customer presents a card to buy goods and services, the CSCNT must see if the payment amount exceeds the limit set by the TT Bank. In case the payment amount is larger than the limit, the CSCNT must apply for a license. Considering current international cards, Amex card has the largest limit, followed by MasterCard, JCB and finally Visa. Normally, when accepting card payments, CSCNT must perform the following tasks:
Step 1 : Check the authenticity of the card, card number; cardholder authentication; Is the transaction limit paid or does it require a license?
Step 2 : Make 04 payment invoices
Step 3 : Return the card to the cardholder with the same payment invoice, the payment CSCNT keeps one copy of the invoice to save as a document when there is a dispute (usually kept for 1 year), the remaining 2 invoices are re-submitted for NHTT