2.4.1 Scoring model of corporate credit society at LienVietPostBank’s branch
LienVietPostBank’s corporate credit system is basically based on the legal guidance framework of the State Bank such as Decision No. 57/2002/QD-NHNN dated January 24, 2002 on pilot implementation of the enterprise credit analysis and socialization project. ; Decision No. 473/QD-NHNN dated 28/04/2004 on the implementation of the project of analysis of credit society at CIC; Decision No. 1253/QD-NHNN dated June 21, 2006 on permission to perform the business of corporate credit and replaces Decision No. 473/QD-NHNN dated April 28, 2004.
At LienVietPostBank, the scoring of corporate credit rating is carried out in accordance with Official Letter No. 2277B/2008/QD-LienVietPostBank dated December 15, 2008 provisionally regulating the internal credit rating system of corporate customers and later on Official letter No. 353/2010/QD-LienVietBank dated February 5, 2010 regulating the internal credit rating system of corporate customers (official version). The sequence of steps to score the corporate credit score at the branch includes:
| Step 1 Gather information | -> | Step 2 Determine the line of business | -> | Step 3 Determine the size of the business | -> | Step 4 Scoring Financial CT | -> | Step 5 Scoring Non-TC | -> | Step 6 Summarize Scores & Ratings |
Maybe you are interested!
-
 The Role Of Credit Rating S In Risk Management
The Role Of Credit Rating S In Risk Management -
 Similarities Between Edward I. Altman’S Credit Score Model And Standard & Poor’S Credit Rating
Similarities Between Edward I. Altman’S Credit Score Model And Standard & Poor’S Credit Rating -
 Lessons From Experience In Credit Relationship For Lienvietpostbank
Lessons From Experience In Credit Relationship For Lienvietpostbank -
 Second Case Study: The Enterprise Is Classified As Bbb And Has Incurred Overdue Debt
Second Case Study: The Enterprise Is Classified As Bbb And Has Incurred Overdue Debt -
 Objectives Of Improving The Credit Rating System Of Lienvietpostbank’S Corporate Customers
Objectives Of Improving The Credit Rating System Of Lienvietpostbank’S Corporate Customers -
 Completing the credit rating system of corporate customers at Lien Viet Post Commercial Joint Stock Bank - 9
Completing the credit rating system of corporate customers at Lien Viet Post Commercial Joint Stock Bank - 9
Step 1: Collect information. Information collected is divided into five groups:
– General information: Information about the organizational structure; List of major shareholders and members of the Board of Directors; Information about customer development history; Information on personnel policy, executive team; Business strategy orientation.
Legal information: Decision of establishment; Business certificates; Enterprise’s regulations; License; Decision appoint; Documents related to investment decisions, loans, business of enterprises, …
– Financial information: financial statements for two consecutive years before and up to the latest time; Business plan, current year financial and forecast for the following years (if any), …
– Market and business information: Information about products and services; Information on industries and business fields; Information about key competitors; Information about input providers; Information about output partners; Government and local policies related to the field of production and business, …
– Relationship information with credit institutions.
Step 2: Determine the customer’s industry and business field
The determination of the customer’s business line and field is for the purpose of properly referencing the standard values established according to the characteristics of each industry or field.
Determining business lines based on production and business activities of corporate customers. Production and business activities are the activities with the highest proportion of revenue, or the industry with the most potential for development. Classification of client enterprises according to five main industry groups presented in Table I.2 of Appendix I, including: Agriculture, forestry, fishery; Light industry; Trade in Services; Capital construction investment; Heavy industry.
Step 3: Determine the size of business customers
Determining the size of the business based on four criteria: Net annual revenue, Equity, Total assets, Average number of employees in the year. Accordingly, the size of enterprises is divided into three types of large-scale, medium-sized and small-sized as presented in Table I.1 of Appendix I.
Step 4: Scoring financial indicators
On the basis of industry and size, using Tables I.03, I.04, I.05, I.06, I.07 of Appendix I corresponding to the main business lines of the enterprise to score points. finance. Calculation of financial indicators is presented in Table 2.2 (Page 36). The financial indicators are evaluated according to the guiding framework of the State Bank of Vietnam and the industry statistical coefficients have been adjusted to match the credit information of LienVietPostBank, each evaluation criterion has five corresponding standard ranges: five score levels 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 (Initial Score). The weighted score is the product of the original score and the corresponding weight. The principle of scoring each indicator is that the actual index closest to any value will be scored according to that value; if the actual index is between two values, the lower grade is taken (lower scale).
Table 2.2: Guidelines for calculating some financial analysis criteria in LienVietPostBank’s corporate credit scoring
| STT | Only title | Single taste | Cong formula | Notes |
| I | Only Liquidity spending | |||
| first | Short solvency term | time | Current Assets/Short Liabilities term | |
| 2 | Solvency fast | time | (Money + Short-term investment + Receivable) / Short-term debt | |
| II | Only growth target | |||
| 3 | Growth revenue | % | (Year’s net sales now – Net sales last year) / Net sales last year x 100% | |
| 4 | Profit growth rate profit | % | (Profit before tax this year – Profit before tax last year) / Profit before tax last year x 100% | |
| III | Only profitability target | |||
| 5 | Net profit margin | % | Profit after tax / Net Revenue x 100% | |
| 6 | ROA | % | Profit after tax / Total assets x 100% | |
| 7 | ROE | % | Profit after tax / Capital owner x 100% | |
| IV | Only Sponsorship Target | |||
| 8 | Self-funding coefficient | % | Equity / Total capital x 100% | |
| DRAW | Only activity target | |||
| 9 | Accounts Receivables Turnover collect | ring | Net Revenue / Amounts average short-term receivables | No payables It is difficult to claim enterprises that have not yet made provision |
| ten | Inventory turnover | ring | Cost of Goods Sold / Inventory average warehouse | Cost of goods sold? including depreciation |
| 11 | Working capital turnover | ring | Net Revenue / Finance average short-term assets | |
| twelfth | Efficient use of assets | Time | Net Revenue / Total asset |
(Source: Lien Viet Post Commercial Joint Stock Bank)
Step 5: Scoring non-financial indicators
Scoring of non-financial indicators includes four groups with thirty-two indicators, each of which has five standard values, corresponding to five points of 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 (Initial score). ) as shown in Tables I.8, I.9, I.10, I.11 of Appendix I. The total non-financial scores are aggregated according to Table 2.3.
Table 2.3: Weighted scores of LienVietPostBank’s non-financial indicators
| Number | Non-financial factors | Proportion |
| 01 | Management qualifications and internal environment | 20% |
| 02 | Factors outside the business | 10% |
| 03 | Relations with CIs | 35% |
| 04 | Operational characteristics of the business | 35% |
Step 6: Summarize points, rank and approve the results
The aggregate score is the total score of the indicators. The weights of the indicator groups are presented in Table 2.4.
Table 2.4: Weighted scores of financial and non-financial criteria for scoring LienVietPostBank’s corporate credit
| STT | Group target | Billion important |
| first | Financial indicators | 40% |
| 2 | Non-financial indicators | 60% |
| total | 100% |
(Source: Lien Viet Post Commercial Joint Stock Bank)
Based on the total score achieved in the end multiplied by the weight, businesses are credit society according to nine grades corresponding to increasing risk level from AAA (lowest risk) to C (high risk level). best) as shown in Table 2.5.
Table 2.5: LienVietPostBank’s corporate credit system symbology
| Total score | Rank | hit business rating price |
| 90-100 | AAA | Strong potential, ability to manage good management, efficient operations, growth prospects, goodwill. Low risk Best. Prioritize to meet maximum credit needs with preferential interest rates Unsecured loans may apply. Strengthen relationship with client. |
| 80-89.9 | AA | work efficiently, good prospects, good will. Low risk. Prioritize to meet maximum needs credit with preferential interest rates, can apply for loans without assets guaranteed. Strengthen relationships with customers. |
| 70-79.9 | A | work efficiently, relatively good financial situation, guaranteed repayment ability, goodwill. Risks low risk. Prioritize meeting credit needs. Does not require high security measures loan guarantee. |
| 60-69.9 | BBB | Works efficiently, yes development prospects. There are some financial and management constraints. Risk medium. Credit can be extended. Limit the application of preferential conditions. Thoroughly evaluate the economic cycle and the effectiveness of long-term lending. |
| 50-59.9 | BB | Low efficiency operation. Financial potential and average management capacity. Medium risk. May struggling when adverse economic conditions persist. Limited credit expansion, focus only on short-term credit and require adequate collateral. |
| 40-49.9 | REMOVE | The efficiency is not high and prone to fluctuations. Risk. |
| 30-39.9 | CCC | Low efficiency operation, financial capacity is not guaranteed, management level is poor. Risk. In danger of losing capital. Credit restrictions. |
| 20-29.9 | CC | Losing and less likely resilience, poor financial position, and unsecured debt repayment capacity. Risk very high. There is a high chance of not being able to recover the loan. |
| <20 | OLD | Losing for many years, financial unhealthy, weak management. Especially risky. There are many possibilities loans cannot be recovered. |
(Source: Lien Viet Post Commercial Joint Stock Bank)
2.4.2 Periodical summary of corporate credit society at the head office of LienVietPostBank
Lien Viet Post Bank’s Head Office approves credit relationships every 6 months on March 31 and September 30 every year for corporate customers who have established credit relationships with other banks. Branch. The scoring of corporate credit is based on the score of three parts including: Financial indicators as presented in Table 2.2 (Page 36), Indicators reflecting the debt situation (including: Solvency interest, Bank loan balance/Equity, Unqualified debt situation) and non-financial indicators as shown in Tables I.8, I.9, I.10, I.11 of Appendix I.
The total credit score multiplied by the weight is converted to nine categories of risk, increasing from AAA (lowest risk) to C (highest risk) as shown in Table 2.5 ( Page 38).
Based on official periodic credit results, LienVietPostBank’s Head Office will coordinate with branches to propose appropriate credit policies for respective corporate customers.
2.5 Research on some actual credit rating situations of corporate customers at a branch of LienVietPostBank
The objective of this study is to improve the credit system in the direction of enhancing the ability to predict risks leading to credit risk, so the study will only focus on analyzing credit records that have been rated high and relatively low. high, i.e. belonging to groups from BBB, A, AA to AAA (ratings are assessed as low risk and can be prioritized for credit extension) but in fact have incurred bad debts (current or existing debts). overdue, or the debt has been restructured within the six-month period up to the time of the study) or has a tendency to bad debt (Increasing the maximum possible withdrawal to repay the due principal and interest; or resolved; new loans near the maturity of the old loans).
According to the above criteria, the topic will select credit records belonging to the group of corporate customers that have a credit relationship with LienVietPostBank. Due to limited data sources and information security reasons for the bank, the study only accesses and presents the data source from a branch of LienVietPostBank in Ho Chi Minh City. From a group of twenty-seven corporate customers, through classifying accessible credit records, the study selected two credit profiles that meet the above criteria, including: A joint stock company with The ranking result up to the second quarter of 2011 is A and a joint stock company has the rating of the second quarter of 2011 as BBB as shown in Table 2.6. Due to the requirement to ensure the confidentiality of customer and bank information, this study will not specify the name of the business used in the research process, in addition, some sensitive information is omitted. The high rate of records with bad debts in the sample does not completely reflect the actual situation because at the time of the study, the economy is subject to many fluctuations due to the influence of inflation, high interest rates and tight monetary policy of the country. Government. Moreover, the study only selected a sample that was not too random (there were specific selection criteria from the beginning such as: having been credit union in 2010 and up to 2011, having a credit relationship at LienVietPostBank, and giving priority. select records with outstanding balances at many credit institutions).
Table 2.6: Classification and bad debt of the researched business group
| STT | Group customer | Numbers quantity | bad debt | Yes bad debt trends |
| first | Grade A | 11 | first | 2 |
| 2 | Rating BBB | 11 | 3 | 3 |
| 3 | Rating BB | 2 | first | |
| 4 | Rated NO | first | first | |
| 5 | Not rated yet | 2 | ||
| Total plus | 27 | |||
(Source: LienVietPostBank’s access data collection)
2.5.1 Case study first: The enterprise has been rated A but tends to incur overdue debt
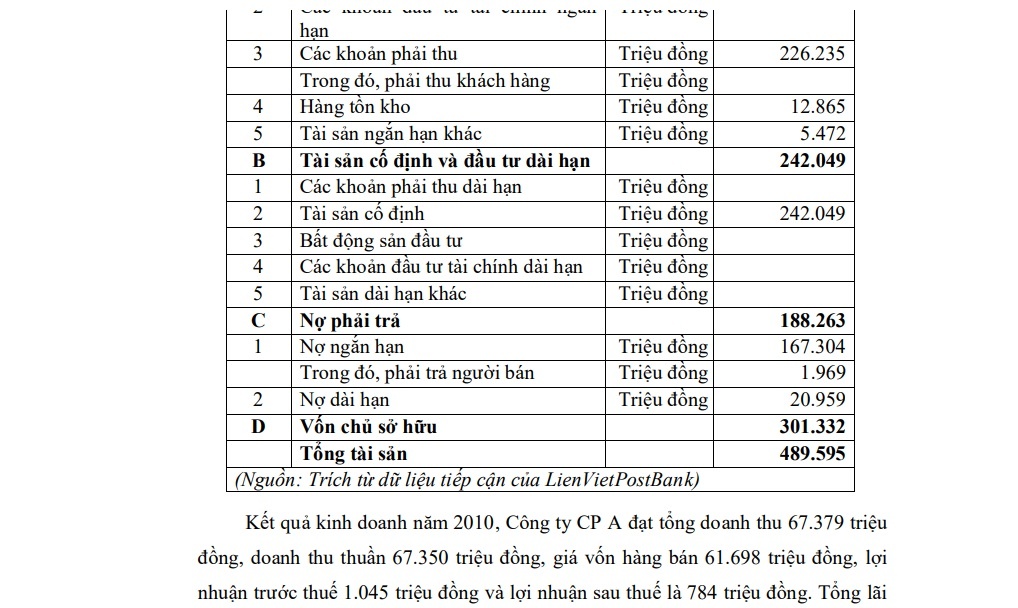
Enterprises in the form of joint stock companies, medium-sized, doing business in the field of brick and tile production (tunnel kilns), artificial quartz stone production, building materials trading and civil construction . The basic figures on the financial position of this enterprise (hereinafter referred to as JSC A) at the time of rating are presented in Table 2.7.
Table 2.7: Summary of the 2010 balance sheet of JSC A
| STT | Only title | Single calculus | Numbers money |
| A | Tai> movable property | Million VND | 247,546 |
| first | Money and Accounts cash equivalents | Million VND | 2,972 |
| 2 | Financial investments short-term main | Million VND | |
| 3 | Receivables | Million VND | 226,235 |
| Of which, payable client | |||
| 4 | Inventory | Million VND | 12.865 |
| 5 | Other current assets | Million VND | 5,472 |
| B | Tai> fixed assets and long-term investments | Million VND | 242.049 |
| first | Long receivables term | Million VND | |
| 2 | Fixed assets | Million VND | 242.049 |
| 3 | Investment real estate | Million VND | |
| 4 | Financial investments long-term main | Million VND | |
| 5 | Other long-term assets | Million VND | |
| C | Debt payable | Million VND | 188.263 |
| first | Short-term debt | Million VND | 167,304 |
| In which, must pay people sell | Million VND | 1,969 | |
| 2 | Long-term liabilities | Million VND | 20,959 |
| D | Capital owner | 301.332 | |
| Total assets | 489,595 |
(Source: Extracted from LienVietPostBank’s outreach data)
Business results in 2010, Joint Stock Company A achieved total revenue of VND 67,379 million, net revenue of VND 67,350 million, cost of goods sold VND 61,698 million, profit before tax of VND 1,045 million and profit after tax of VND 784 million. . Total interest paid to banks is 1,058 million VND.






