Commerce. This is the time limit for the seller to deliver the goods to the buyer from the effective date of the letter of credit. The delivery term is closely related to the validity period of the letter of credit. If the two parties agree to extend the delivery time by a few days, of course the bank opening the letter of credit must also understand that the validity period of the letter of credit is also extended accordingly. In practice, there are many cases where the delivery term is extended but the validity period remains the same.
h) Terms of goods:
The terms of the goods specify the provisions related to the goods, including the name of the goods, quantity and weight, price, quality specifications, packaging, markings, ....
i) The contents of transportation and delivery of goods:
Delivery conditions (FOB,CIF,C&F…), place of shipment, place of delivery, shipping and delivery methods… are recorded in the L/C. Normally, the terms of delivery depend on the exporter's supply capacity, the importer's ability to receive, the transport capacity of the means of transport, the goods must be delivered on the ship's deck. If it is found that the terms of delivery in the L/C cannot be fulfilled, the exporter can request an adjustment of the L/C.
Parties usually choose the standard Incoterms condition and must specify whether Incoterms 1990, 2000 or 2010.
j) Documents to be presented by the exporter:
The requirements for the preparation and presentation of documents need to be stated specifically and strictly in the L/C, stemming from the characteristics of the goods, the means of transport, the payment and credit, of the contractual nature and the legal sources relevant to the performance of that contract.
k) Payment commitment of the bank opening the letter of credit:
The commitment of the bank opening the L/C is the final content of the L/C, binding the responsibility of the bank opening the L/C to the beneficiary of this L/C. The commitment of the bank opening the L/C in the L/C forms is the same.
l) Other special conditions:
Other conditions may be listed such as to whom bank fees are charged, special conditions guiding the discounting bank, reference to the applicable UCP number, etc.
m) Signature of the bank opening the L/C:
L/C is actually a civil contract. Therefore, the person signing the L/C must also have the behavioral and legal capacity to enter into and perform a legal relationship. If sending by telex, swift, there is no signature, only based on L/C's testkey.
1.5.4.3 Classification of letters of credit.
(i) Irrevocable Letter of Credit:
Is a type of letter of credit where the bank opening the L/C is responsible for paying the exporter during the validity of the L/C, without the right to arbitrarily modify or cancel the letter of credit. Irrevocable type of L/C guarantees the interests of the exporter and is now commonly used. If the L/C is not specified, the default is irrevocable.
(ii) Confirmed irrevocable letter of credit:
Is an irrevocable letter of credit and is guaranteed by another more reputable bank to ensure the payment under that letter of credit together with the bank opening the L/C, that is, the confirming bank is responsible for payment. to the exporter if the bank opening the letter of credit fails to pay. With this L/C, the exporter's interests are more secure. When the exporter does not fully trust the bank opening the L/C, especially when the L/C value is relatively large, for assurance, the bank may confirm the request.
The bank opening the L/C must deposit in advance (in some cases, 100% of the L/C value must be deposited) and must pay a fee to the confirming bank. Normally, the bank opening the L/C will ask the advising bank to confirm the L/C (see Figure 1.4).
Bank notifies L/C
Figure 1.4: Confirmed irrevocable letter of credit
Bank opens L/CO
Foreigners
Exporters
Application for opening L/C (1)
L/C (2) Confirmation
I confirm
L/C (3)
Foreign trade contracts
L/C (4)
(iii) The Letter of Credit is irrevocable and non-recourse:
An irrevocable L/C in which the bank that opens the L/C after paying the exporter is not entitled to a refund under any circumstances. When using this type of L/C, the exporter when drawing the bill of exchange must write the sentence "no recourse to the drawer".
(iv) Revolving Letter of Credit:
An irrevocable type of L/C which stipulates that when the L/C is used up to its limit or after the L/C's delivery expires, it automatically restores its value to the same value and continues to do so until upon completion of the contract value. This type of cyclic L/C is applicable in cases where the exporter and the importer have a regular relationship and the subject matter of the purchase and sale does not change. When applying a revolving L/C, the importer benefits in two big points: no capital accumulation, reducing the cost of opening L/C. There are two types of revolving letters of credit:
+ Cumulative type: allows transferring the limit in the previous round to the next round and so on until the last round, that is, within the validity period of the L/C, the exporter if, for some reason, does not If the quantity is delivered in sufficient quantity, the value on the L/C will be delivered to the next round to make up for the previous missing part.
+ Non-cumulative type: does not allow to transfer the balance of the previous round to the next round.
In addition, revolving L/C can be divided into three cyclical methods: automatic revolving L/C, non-automatic cyclic L/C, semi-automatic revolving L/C.
(v) Back-to-back Letter of Credit:
An irrevocable letter of credit opened against another L/C as security. Under this L/C, the exporter based on the L/C opened by the importer, asks the bank to open a letter of credit for the other exporter to enjoy. Back-to-back letters of credit are often used in cases where the original L/C does not allow transfer or when the documents required under the original L/C do not match the documents of the second L/C and the intermediary. want to keep some information secret.
When applying a back-to-back L/C, the following conditions must be satisfied:
+ Two original and back-to-back letters of credit must be through a bank directly serving the exporter.
+ The original L/C value must be greater than or equal to the back-to-back L/C value. The intermediary import-export house enjoys this difference.
+ Original L/C must be opened earlier than back to back L/C.
(vi) Reciprocal Letter of Credit:
An irrevocable type of L/C which stipulates that it is only valid when another L/C corresponding to it is issued, that is, when the exporter receives the L/C issued by the importer, The corresponding L/C must be reissued for both L/Cs to be valid.
The type of reciprocal L/C is used when there is a relationship between the import and export parties of goods exchange or processing, raw materials, and finished products. In processing, L/C for imported finished products will be L/C at sight, L/C for raw materials is L/C with deferred payment.
(vii) Deferred payment letter of credit:
An irrevocable L/C in which the bank that opens the L/C or the bank that confirms the L/C commits to the beneficiary to pay the entire amount of the L/C by the specific time specified on the L/C. /C upon receipt of documents and without draft.
(viii) Letter of Credit with red clause:
A letter of credit with special terms, formerly written in red ink, whereby the L/C opener grants the exporter the right to release a certain amount of money prior to delivery. Therefore, this letter of credit is also known as an advance letter of credit.
(ix) Standby Letter of Credit:
To protect the interests of the importer, in the event that the exporter fails to deliver the goods according to the contract, the importer requires the exporter to open a standby letter of credit which stipulates that if the exporter fails to Under the contract, the bank opening the standby letter of credit will pay damages to the importer. This type of letter of credit is also implemented in accordance with UCP600 and ISP98.
(x) Letter of Credit with T/TR terms:
It is an ordinary letter of credit, but there are regulations that allow the bank serving the beneficiary after checking that the documents are consistent with the conditions specified in the L/C, then it is allowed to call for money from the open bank. L/C or a bank specified in the letter of credit. It is applicable in cases where two banks have an agency relationship with each other.
(xi) Transferable Letter of Credit:
An irrevocable type of L/C which stipulates the right to transfer part or all of the L/C value to one or more persons at the behest of the first beneficiary. However, the transfer is only allowed to be carried out once, it cannot be transferred at the request of the second beneficiary to any other subsequent beneficiary, that is, it is only allowed to be reassigned to another person when L. /C has no restrictions on transfer. In the event that the second party fails to deliver the goods or fails to deliver the goods correctly or the documents are not perfect, the first beneficiary shall be liable to the exporting party under the signed contract. Transfer costs are paid by the first beneficiary. This L/C is used when buying goods through agents or intermediaries. The transfer L/C must have the word “transferrable” written on the L/C.
1.5.5 Operation process of documentary credit method .
(See Appendix)
1.6 Advantages and disadvantages of documentary credit method.
(See Appendix)
1.7 Lessons learned from Vietnam.
From the 1980s onwards, in our country, Vietcombank held the monopoly on foreign trade payments. Other commercial banks may have financed the purchase, storage and processing of raw materials for export; After the goods are shipped, the relevant documents must be presented at Vietcombank to make an order to demand foreign money. The collected foreign currency is managed and exchanged at Vietcombank according to the foreign exchange management regime and the exchange rate, generating what is called the "right to use foreign currency" to import counter-trade goods and sell them at high prices. offset against loss due to export turnover at the official exchange rate.
The consequence of this policy is that import-export enterprises receive revenue from sales at Vietcombank, so it is easy to use them for other purposes (wrong purpose). It is very difficult for import-export enterprises to settle debts that are constantly hanging at "receivables payable" about "the right to use foreign currency", and at the same time it is difficult to repay loans from domestic credit institutions about the cost of producing goods that have been sold. Using capital for the wrong purpose can lead to business losses in the next cycle. Domestic credit institutions sponsor export goods, unable to close the credit cycle when export revenue cannot be managed (located at Vietcombank), so it is difficult to avoid bad debts.
In the early 1990s, when all the prescribed conditions were met, each domestic commercial bank was licensed to make international payments in turn , ending Vietcombank's monopoly position and at the same time ending the paradox in capital circulation. bank credit, return to normal operations for commercial banks.
Conclusion chapter 1.
Transactions between exporters and importers are conducted through banks using various payment methods such as money transfer, collection method and documentary credit method. The application of the payment method depends on the negotiation between the two parties and in accordance with the customs and laws in international payment and business.
Currently, the documentary credit payment method is increasingly widely used with the outstanding advantages of protecting the interests of both importers and exporters. Accordingly, the content of this chapter introduces the basic knowledge about documentary credit payment method such as concept, characteristics, content and role of documentary credit method; legal basis of documentary credit payments; types of letter of credit, documentary credit payment process. In addition, the advantages and disadvantages of documentary credit are also mentioned so that stakeholders can consider in choosing an appropriate payment method.
Based on the theory of documentary credit, the next part of the thesis presents the implementation of this method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam - Vung Tau Branch (Vietcombank Vung Tau) and advantages, problems as well as outstanding problems that need to be resolved.
CHAPTER 2: SITUATION OF INTERNATIONAL PAYMENT ACTIVITIES BY Documentary Credit Method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam - VUNG TAU BRANCH
2.1 Overview of Vietcombank
2.1.1 General introduction
- Vietnamese name: Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam;
- English name: Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam.
- Transaction name: Vietcombank.
- Abbreviated name: VCB.
- Head office: 198 Tran Quang Khai, Hoan Kiem District, Hanoi
- Network:
- 1 Head office in Hanoi;
- 1 Exchange; 71 branches and 269 transaction offices nationwide;
- 1 Training Center in Hanoi;
- 3 affiliated companies in Vietnam, 1 finance company in Hong Kong;
- 4 joint venture companies, 2 associate companies;
- Website: http://www.vietcombank.com.vn/
- Logos - Logos:

- Charter capital: 23,174,170,760,000 VND (as of December 31, 2011), in which, the largest shareholder of VCB is the State Bank of Vietnam (representing
state capital at VCB), holding 77.11% of charter capital. The strategic shareholder is Mizuho Corporate Bank Ltd. holds 15% of charter capital. Other shareholders (including domestic organizations and individuals, foreign organizations and individuals) hold 7.89% of VCB's charter capital (Figure 2.1).
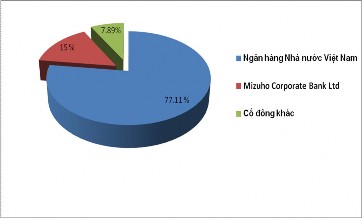
Figure 2.1: Vietcombank's shareholder structure
(Source: Website http://vietcombank.com.vn/Investors/CCCD.aspx)
2.1.2 The process of formation, development and achievements.
Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam (Vietcombank) officially operated on June 2, 2008 (according to the establishment and operation license of a joint stock commercial bank dated May 23, 2008 of the State Bank of Vietnam and the certificate of the State Bank of Vietnam). business registration issued by the Department of Planning and Investment of Hanoi for the first time on June 2, 2008) after the initial public offering on December 26, 2007.
Over nearly 50 years of construction and development, Vietcombank has always been a leading provider of full financial services in international trade; in traditional activities such as capital trading, capital mobilization, credit, project financing... as well as modern banking services such as foreign currency trading and derivative transactions, card services, and electronic banking. death….
Vietcombank is occupying a significant market share in Vietnam in many different business fields such as lending (about 10%), deposits (about 12%), international payment (about 23%), card payment (about 55%)….Vietcombank is also a pioneer in applying modern technology to automatically handle banking services and constantly offering electronic services to "bring the bank closer to customers" products" such as: Internet banking, VCB - Money (Home banking), SMS Banking, Phone banking....
From a specialized bank serving the external economy, Vietcombank today has expanded throughout the country, developing an Autobank system with 11,183 automatic teller machines and ATMs nationwide. , has relations with 1,300 correspondent banks in 100 countries and territories, opens NOSTRO accounts for major foreign currencies such as USD, EUR, GBP, JPY, CAD, AUD... at major financial institutions. With a wealth of experience and a team of professional staff, well-trained in finance, banking, market economy, foreign languages, able to adapt sensitively to the current business environment. Modern and highly integrated, Vietcombank has always been the first choice of large corporations, large domestic and foreign enterprises as well as more than 4 million individual customers.
2.2 Introduction of Vietcombank Vung Tau.
2.2.1 The process of formation and development.
Vietcombank Vung Tau was established on November 6, 1982 and is one of the first 5 first level branches under the Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam today.
Vietcombank Vung Tau succeeds the mission of the Foreign Exchange Department of Vung Tau (established in August 1977) under the State Bank of Vietnam.
Dong Nai consists of only 12 officers. In 1979, the Vung Tau Foreign Exchange Department became the International Payment Department under the State Bank of Vung Tau - Con Dao Special Zone (former), when the Vietnam-Soviet Petroleum Joint Venture Enterprise was established and operated in Vietnam. basis of the Intergovernmental Agreement with the former Soviet Union (now the Russian Federation) in June 1981.
In the face of the strong development of oil and gas exploration and production on the southern continental shelf, the work of the International Settlement Department is increasing, and the foreign payment business is expanding, leading to the establishment of the International Payment Department. of Vietcombank Vung Tau on November 6, 1982 with the initial number of 30 employees at the head office.
During the monopoly period of foreign operations, as the only foreign bank in the area, Vietcombank Vung Tau held almost the entire market share of international banking services. In the context of the economic embargo, international payments face many difficulties, but thanks to the application of payment operations through banks and international intermediary financial institutions abroad, the entire foreign currency revenue From exporting with sales of millions of USD per year and purchasing specialized oil and gas equipment, serving other necessary import and export payment needs of local units, always ensuring high safety, not being delayed or loss.
From the place of only international payments related to oil and gas, now the Branch is a large bank of Ba Ria - Vung Tau Province with a variety of services. Vietcombank Vung Tau promotes Vietcombank's advantages in modern banking services based on advanced technology. Continuously for 30 years since its establishment, the branch's capital has always increased at a high rate. In addition to import-export payment, Vietcombank Vung Tau has implemented supporting services such as foreign currency trading, voucher discounting, etc., both to meet the needs of business units and bring more profits to the bank. row.
In recent years, a series of foreign banks have entered Vietnam plus dozens of joint stock commercial banks in the area, creating a fierce competitive environment, reducing Vietcombank's market share.
Reality requires Vietcombank and Vietcombank Vung Tau to have a customer strategy, diversify services, improve service quality, especially international payment services, in order to promote advantages and limit disadvantages.
The staff of Vietcombank Vung Tau still maintain steady development every year. In particular, from 2002 to present, by marketing various new products of Vietcombank, applying flexible and flexible customer policies such as opening letters of credit without deposit, attractive preferential interest rates, etc. , quick procedures, timely funding for customers. Vietcombank Vung Tau constantly expands its scale and credit relationship to neighboring areas, performs well in international payment, brings practical efficiency.
Up to now, the branch has 168 officers and employees. Not only increasing in number, the branch's workforce is also mature in professional skills, especially with international experience and qualifications, ensuring timely acquisition of modern technical means in operation. banking services, especially supporting tools in Vietcombank's international banking service system such as: SWIFT payment system, retail banking system, electronic payment system, credit card payment, card payment ATM. The branch applies technology to deploy many management software such as: capital management and trading program, trade finance,... to better meet the increasing demands of customers and bring efficiency. best investment.
Vietcombank Vung Tau has become a reputable transaction center in the area, making a significant contribution to the construction and socio-economic development of the province. With the achievements Vietcombank Vung Tau has achieved,
received many certificates of merit and certificates of merit from the State Bank, the People's Committee of Ba Ria - Vung Tau province, the Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, the Prime Minister. Especially, in 2002, Vietcombank Vung Tau was honored to receive the Third Class Labor Medal. In 2007, on the occasion of the 25th anniversary of construction and growth, the collective of Vietcombank Vung Tau Branch was awarded the Second Class Labor Medal by the State President.
On June 1, 2008, the Bank of Vietnam officially transformed from a state-owned enterprise into a joint-stock enterprise with the name Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam (VCB Vietnam). Accordingly, Vung Tau Foreign Trade Bank branch also changed its operations to follow the model of a Joint Stock Commercial Bank with the name of "Vietnam Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade - Vung Tau Branch" (Vietcombank Vung Tau).
2.2.2 Operational network and organizational structure of Vietcombank Vung Tau. Vietcombank Vung Tau has 1 head office, 4 transaction offices (PGD) and 1 savings fund:
- Head office: No. 27 Tran Hung Dao, Ward 1, City. Vung Tau;
- Transaction Office No. 01: No. 30 Pham Hong Thai, Ward 6, City. Vung Tau;
- Transaction Office No. 02: No. 1 Ly Thuong Kiet, Phuoc Trung Ward, City. Ba Ria;
- Transaction Office No. 03: Phu My Town, Tan Thanh District;
- Le Loi Transaction Office: No. 27 Le Loi, Ward 4, City. Vung Tau;
- Savings counter (under the Sales and Service Department - Head office): 169 Nguyen Van Troi, Ward 4, City. Vung Tau .
The organizational structure of Vietcombank Vung Tau includes 01 Director, 02 Deputy Directors and 10 functional departments with the following main tasks:
+ The Director is responsible for operating and general management of all banking operations in accordance with the law, directly managing the administrative personnel, customers, internal control, capital and foreign currency trading, ...
+ Deputy Director 1: in charge of financial accounting, computers, business services, transaction offices...
+ Deputy Director 2: in charge of debt management, risk management, international payment, treasury, administrative work
Figure 2.1: Organizational model of Vietcombank Vung Tau
P. Debt Management
P. International Payment
P. Funds
Manager
Deputy Director 2
(Source: Administration and Human Resources Department - Vietcombank Vung Tau)
Deputy Director 1 | |||||
Internal check | P.Capital and business income | Human Resources Administration | P. Customers | ||
Maybe you are interested!
-
 Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 1
Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 1 -
 Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 2
Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 2 -
 Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 4
Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 4 -
 Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 5
Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 5 -
 Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 6
Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 6 -
 Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 7
Solution to complete international payment activities by documentary credit method at Joint Stock Commercial Bank for Foreign Trade of Vietnam, Vung Tau branch - 7
P. Plan | P. Kinh | PGD | PGD | PGD | PGD | P. Vi | |||||
maths | business | No.1 | No. 2 | No.3 | Pear | count | |||||
Finance | service | Profit |
Savings Counter
By the end of 2011, Vietcombank Vung Tau had 168 employees, of which 98 women - accounting for 58.33% and 70 men - accounting for 41.67% with an average age of 33 years old, were trained in theory, perception and expertise. professional skills to complete tasks well, in line with the current integration trend.