3.3.1.2. Training Algorithm
As discussed in Chapter 1 with a context-free grammar, probabilities acting as parameters can initially be generated randomly, and then updated every time a new sentence is analyzed and added to the set. corpus. The training algorithm proposed by [79] aims to recalculate the parameter value after processing the input sentence. Like the context-free grammar, this algorithm relies on two parameters, the inner probability and the outer probability.

The probability in PrI ( L, R, l, r ) is the probability that words from L to R can be linked together such that the connections l and r are satisfied.
The outer probability Pro ( L, R, l, r ) is the probability that words outside the range L to R can be associated with each other such that the outer join requirements l and r are satisfied.
The inner probability is calculated recursively according to the relations:

According to the parsing algorithm in Figure 3.4, it is clear that PI ( wi , wi+1, NIL, NIL ) = 1 with 0 ≤ i ≤ n-1.
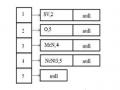
For example, With the linking grammar and the sentence “I bought a flower” mentioned above,
Maybe you are interested!
-
 Vietnamese linking grammar model - 18
Vietnamese linking grammar model - 18 -
 Vietnamese linking grammar model - 19
Vietnamese linking grammar model - 19 -
 Viterbi Type Algorithm To Find The Best Analysis
Viterbi Type Algorithm To Find The Best Analysis -
 Vietnamese linking grammar model - 22
Vietnamese linking grammar model - 22 -
 Development Situation Of Machine Translation In Vietnam
Development Situation Of Machine Translation In Vietnam -
 Language Difference Between Vietnamese And English
Language Difference Between Vietnamese And English
PrI ( 1, 4, NIL, NcNt3 ) = Pr (3, (McN)(NcNt3),→ | 1, 4, NIL, NcNt3 ) ×
PrI ( 1, 3, NIL, McN ) × PrI ( 3, 4, NIL, NIL )
with the values of the probabilities given in (3.1) :
PrI( 1, 3, NIL, McN) = Pr(2, ( )(McN), → | 1, 3, NIL, McN) ×
PrI (1, 2, NIL,NIL) × PrI (2, 3, NIL, NIL)
= 0.06 × 1 × 1 = 0.06
Pr ( 3, (McN)(NcNt3),→ | 1, 4, NIL, NcNt3 ) = 0.05
so, PrI (buy, flower, NIL, NcNt3) = 0.05 × 0.06 = 0.003 (3.5)
The probabilities outside PrO are calculated recursively: initially, for each d ∈ D(W0) there is left[d] = NIL, set
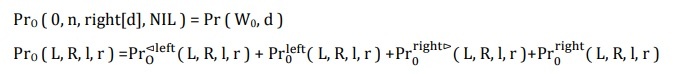
The probability is added to the 4 possible cases in the previous step (then R and L also play the role of W):
![Figure 3.22. Describe how to calculate probability Pr0 ⊲left(L, W, l ⊳, ⊲ left[D]) According 4](uploads/2021/08/16/luan-an-tien-si-cntt-mo-hinh-van-pham-lien-ket-tieng-viet-21-3.jpg)
![Figure 3.22. Describe how to calculate probability Pr0 ⊲left(L, W, l ⊳, ⊲ left[D]) According 5](uploads/2021/08/16/luan-an-tien-si-cntt-mo-hinh-van-pham-lien-ket-tieng-viet-21-4.jpg)
Figure 3.22. Describe how to calculate probability Pr0 ⊲left(L, W, l ⊳, ⊲ left[D])
![According to [79], Counts are calculated in the formulas from (3.6) to (3.9) below: The count(L, R, 6](uploads/2021/08/18/luan-an-tien-si-cntt-mo-hinh-van-pham-lien-ket-tieng-viet-21-5.jpg)
![According to [79], Counts are calculated in the formulas from (3.6) to (3.9) below: The count(L, R, 7](uploads/2021/08/18/luan-an-tien-si-cntt-mo-hinh-van-pham-lien-ket-tieng-viet-21-6.jpg)
According to [79], Counts are calculated in the formulas from (3.6) to (3.9) below:

The count(L, R, l, r) value is calculated in the analysis algorithm:

where δ is a function that takes 1 if l = NIL, 0 otherwise, match takes 1 if the two matches match, 0 otherwise. Notice match(c,NIL) = match(NIL,c) = 0.
The Pr(S) value stated in the above formulas is calculated according to the following formula:
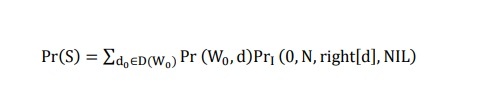
The values Count(L, R, l, r), Count(W, l, r) and Count(d, l, r) are calculated directly according to the connections and selections that appear in the corpus.