Finally, the security and privacy of the airline website have a significant positive effect on customer satisfaction in using HKGR. This clearly reflects that online users are very concerned about security and privacy when they visit airline websites. In addition, the issue of security and privacy is also a global phenomenon. The four corresponding items include: personal security protection, safe payment methods, assurance and security respectively. Customers are concerned about security and privacy for various reasons, from spam attacks to online identity theft. With the layered security system, i.e. firewalls provided by airlines, customers will be satisfied when booking and providing confidential information to suppliers (Chang et al., 2013). Vietjet Air or Jetstar partner with financial companies or banks to provide secure transactions whereby one-time passwords are given to any customer who wants to purchase services online or pay via a higher protection banking link such as Napas. The safer the customer feels, the more successful HKGR is.
2.7. Research model
A series of new reports from international aviation conferences were collected and studied in detail. This is the foundation for building the report. Furthermore, direct contact with HKGR travel agents and ground handling services and HKGR operators at Tan Son Nhat International Airport was also conducted to demonstrate the impacts of tourism 4.0 on customer satisfaction in Vietnam. Thanks to previous relationships due to having worked in the aviation industry, the surveyor approached Jetstar Pacific sales channel managers, Bamboo Airways representatives, and Vietnam Airlines chief flight attendants to propose support in answering questions. The questions in the questionnaire were carefully and reasonably selected based on available theory.
Compared with the SERVQUAL model, the E-QUAL model is suitable for this research topic because the topic is closely related to IoT in the era of industry 4.0 and
digital technology in understanding customer satisfaction. The reasons given by Ojasalo (2010) why E-QUAL is the most suitable model are as follows:
- The interaction of service providers with customers is done via the Internet.
- Communication in electronic services can be personalized.
- Customers can proactively adjust services
Expected
The relationship between expectations and actual experience (yes/no)
Quality of service
-Service provision is not limited by time (24/7) and geographical distance. However, to build a suitable model, it is necessary to select the most necessary and suitable factors, so the model is formed after receiving information from experts and through other suitable theses.
Real experience
Figure 2.7.1. The compact SERVQUAL model of Parasuraman et al. (2008)
Kuo et al. (2009) suggested that modern and easy-to-use e-commerce websites and applications make consumer transactions easier and that attracts consumers to revisit or repurchase more, leading to customer satisfaction. Alpar et al. (2001) identified two attributes of e-service quality that determine customer satisfaction: convenience (speed of response, navigation assistance, use of new technologies); and information content (quantity, quality, accuracy, customization of information). This indicates that the more user-friendly the application or website is, the more likely customers are to engage in online shopping.
The E-QUAL model built from 2001 to 2016 by researchers is summarized in the following table:
Table 2.7. Summary and comparison of factors affecting digital service quality
Author
Year | Factor | |
Bressolles and associates | 2007 | Convenience (ease of use) Information source Design Reliability Security/trustworthiness Personalization |
Mills and Associates | 2003 | Convergence Distinctiveness Trust. |
Zehir and associates | 2016 | Efficiency System availability Feasibility Security |
Kuo and associates | 2009 | Beautiful interface Easy to use |
Alpar and associates | 2001 | Convenience Information content |
Parasuraman Zeithaml and Malhotra | 2008 | Effective Complete Availability Privacy Responsiveness Contact |
Maybe you are interested!
-
 Model system to assess the suitability of Vietnam's population-economic development process - 21
Model system to assess the suitability of Vietnam's population-economic development process - 21 -
 Building a Research Model of Factors Affecting Agribank's Brand Value
Building a Research Model of Factors Affecting Agribank's Brand Value -
 Psychological Structure - Typical Model of Thach Lam's Prose.
Psychological Structure - Typical Model of Thach Lam's Prose. -
 Organizational Structure of Management Apparatus: The Organizational Model and Operation of the Nghe An Provincial People's Credit Fund is Shown in Diagram 3.1. Below.
Organizational Structure of Management Apparatus: The Organizational Model and Operation of the Nghe An Provincial People's Credit Fund is Shown in Diagram 3.1. Below. -
 Evaluation of SHB's Business Performance After Merger According to Camel Model
Evaluation of SHB's Business Performance After Merger According to Camel Model
Convenience
Accessibility
Customer satisfaction
Quality of 4.0 tourism application
The survey model for the topic is a combination of research on SERVQUAL and E-QUAL Model, selecting overlapping variables, used in previous research articles, reading through research articles to select and create the E-QUAL model as below:
Personalization
Security and privacy
Figure 2.7.2: Research model in the article
2.8. Research hypothesis
H1 . There is a positive relationship between convenience and customer digital satisfaction with the Travel 4.0 application in travel experiences with HKGR
H2 . There is a positive relationship between accessibility and customers' digital satisfaction with the Travel 4.0 application in their travel experience with HKGR
H3 . There is a positive relationship between personalization and customer satisfaction with the application of Travel 4.0 in travel experience with HKGR
H4 . There is a positive relationship between security/ confidentiality and customer satisfaction with the Travel 4.0 application in travel experiences with HKGR
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1. Objectives of the topic
The objective of the thesis is to examine the impact of the application of tourism 4.0 on customer satisfaction in using the services of HKGR airlines. In addition, the purpose of the article is to determine the expectations of customers for HKGR airlines. Thus, the quantitative method has been applied to clarify the questions in the questionnaire sent to the respondents.
The topic is formed based on two (02) main objectives:
Determine tourists' awareness of 4.0 tourism applications of HKGR airlines.
Assess the impact of tourism 4.0 on the "digital satisfaction" of Vietnamese tourists.
From the above two objectives, the report will analyze the requirements that HKGR airlines should do to achieve Vietnam's high "digital satisfaction" in traveling.
3.2. Survey subjects
The main subjects of this survey are customers using airline services in Vietnam in three cities: Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City and Vung Tau City, mainly customers using HKGR services. The answers from these respondents are considered objective and fair, based on practical experience.
3.3. Research sampling plan
According to Silverman (2013), quantitative research requires sufficient samples to allow for valid and reliable statistical conclusions to be drawn about the results. Therefore, developing a sampling plan will help determine the specific number of respondents needed.
Krejcie and Morgan (1970) indicated that the relevant sample size for knowing the opinions of 100,000 experienced guests was 384 respondents. The relevant number
important for analysis because it can determine the possibility of using smaller groups of respondents to make inferences about larger groups. As such, it saves costs for the research and minimizes alpha error (differences that do not exist in the total sample.
Table 3.3. TABLE OF ALLOCATION OF NUMBER OF QUESTIONNAIRE FORM (NUMBER OF SAMPLES) USED FOR SURVEY
Source: Krejcie & Morgan (1970)
N
S | N | S | N | S | N | S | N | S | |
10 | 10 | 100 | 80 | 280 | 162 | 800 | 260 | 2800 | 338 |
15 | 14 | 110 | 86 | 290 | 165 | 850 | 265 | 3000 | 341 |
20 | 19 | 120 | 92 | 300 | 169 | 900 | 269 | 3500 | 246 |
25 | 24 | 130 | 97 | 320 | 175 | 950 | 274 | 4000 | 351 |
30 | 28 | 140 | 103 | 340 | 181 | 1000 | 278 | 4500 | 351 |
35 | 32 | 150 | 108 | 360 | 186 | 1100 | 285 | 5000 | 357 |
40 | 36 | 160 | 113 | 380 | 181 | 1200 | 291 | 6000 | 361 |
45 | 40 | 180 | 118 | 400 | 196 | 1300 | 297 | 7000 | 364 |
50 | 44 | 190 | 123 | 420 | 201 | 1400 | 302 | 8000 | 367 |
55 | 48 | 200 | 127 | 440 | 205 | 1500 | 306 | 9000 | 368 |
60 | 52 | 210 | 132 | 460 | 210 | 1600 | 310 | 10000 | 373 |
65 | 56 | 220 | 136 | 480 | 214 | 1700 | 313 | 15000 | 375 |
70 | 59 | 230 | 140 | 500 | 217 | 1800 | 317 | 20000 | 377 |
75 | 63 | 240 | 144 | 550 | 225 | 1900 | 320 | 30000 | 379 |
80 | 66 | 250 | 148 | 600 | 234 | 2000 | 322 | 40000 | 380 |
85 | 70 | 260 | 152 | 650 | 242 | 2200 | 327 | 50000 | 381 |
90 | 73 | 270 | 155 | 700 | 248 | 2400 | 331 | 75000 | 382 |
95 | 76 | 270 | 159 | 750 | 256 | 2600 | 335 | 100,000 | 384 |
Note: “N”: Overall size
“S” : Sample size
3.4. Data collection method
The analysis of the thesis is based on the results collected from the questionnaire. Since the thesis is a quantitative research, the use of SPSS analysis system is necessary. Data collection can be done with both primary and secondary data. The methods have been carefully considered to ensure the lowest cost and time saving (Creswell, 2007).
For primary data, in line with the objectives and data collection tools, self-reporting technique was adopted to achieve the desired results. The reasons for using questionnaires were because of the appropriate number of respondents, time saving, convenience and cost effectiveness. Within four months, the study was conducted accurately, therefore, the survey with questionnaires was considered the most suitable primary tool. The questionnaire included both closed (Yes/No) and open-ended questions. The combination of the two types of questions allowed respondents to feel comfortable answering as well as allowed for better quality information to be obtained.
In the questionnaire, Likert scale was used because it requires respondents to rate specific statements on a scale from 1 to 5, corresponding to strongly disagree to strongly agree (Silverman, 2013). Using Likert scale is easy to handle and it creates a sense of understanding for the respondents, and the respondents can choose neutral when they are uncertain about the decision.
The range of Likert scale is important because it can create a questionnaire that is friendly to the respondents. There are two different Likert scales: odd and even. The study used odd Likert scale instead of even. The advantage of odd Likert scale includes the idea of neutrality (Laerhoven et al., 2004). Moreover, in case of sensitive topics, it is more suitable to answer at the midpoint. Among odd Likert scales (3,5,7,9,11), the 5-range scale is considered the most suitable choice, easy for the respondents to answer and evaluate. For secondary data, information from articles and reviews from other studies was used a lot with the underlying theories from textbooks. Internet sources were used to read and understand the necessary information and compare with the latest version of the data.
The study was conducted by collecting relevant reports and collecting feedback through questionnaires for relevant research subjects. The questionnaires were made in paper and online at a ratio of 30:70 and sent to the research subjects for implementation. The number of questionnaires was divided into two phases: a pilot questionnaire consisting of 54 questionnaires, and an official questionnaire consisting of 400 questionnaires both online (website link) and offline (paper questionnaires) distributed in 3 cities: Hanoi Capital, Ho Chi Minh City, and Vung Tau City. The exclusion of Da Nang from the list is due to the complicated developments of the CoVid-19 epidemic in this Central province.
3.5. Question design
Mills et al. (2003) in their study on measuring customer satisfaction with online travel services demonstrated that their model has all the elements to analyze the factors affecting digital satisfaction: Convergence, Discrimination and Trust.
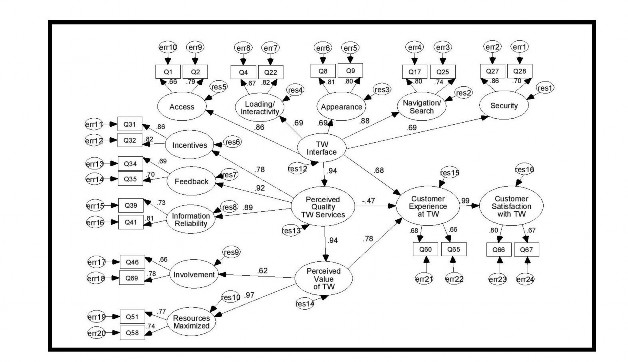
Figure 3.5.2: Mills and Morrison's Digital Satisfaction Model (2003) Bressolles et al. (2007) identified variables to study service quality in the digital age and applied the study of variables to be able to determine the





