INTRODUCTION
1. Reason for doing the topic
Like many countries in the world, Vietnam has attached great importance to nature conservation. As early as 1962, when the country was at war and faced many difficulties, the Government established the Cuc Phuong forbidden forest, now Cuc Phuong National Park - the first national park in Vietnam. Since the country's reunification, the Government has decided to establish more national parks and nature reserves. Up to the time of reviewing and re-planning three types of forests according to Directive No. 38/2005/CT-TTg of the Prime Minister, the special-use forest system includes 164 areas with a total natural area of 2,265,753.88 hectares, including 30 national parks with an area of 1,077,236.13 hectares; 69 nature reserves with an area of 1,099,736.11 hectares; 45 landscape protection areas, covering an area of 78,129.39 hectares and 20 scientific experimental research forests, covering an area of 10,652.25 hectares. The establishment of the special-use forest system is an important achievement of Vietnam in protecting the environment and natural resources of the country, making a positive contribution to the conservation of global biodiversity.
With the diversity of ecosystems and beautiful landscapes, special-use forests have great potential for tourism, which we have been exploiting in the direction of sustainable development of special-use forests by organizing the development of ecotourism. Cuc Phuong National Park and Xuan Thuy National Park are two National Parks with great potential and advantages for developing ecotourism, which is the priority development direction, the core of the development towards a sustainable financial mechanism of these Parks. A problem for the management of ecotourism in these two National Parks is: with the investment capital from the State Budget for management, it is necessary to identify priority areas for development in order to improve the efficiency of the value of financial capital. To answer this question, it is necessary to conduct specific studies based on the implementation results and orientation of ecotourism development in these two National Parks.
In order to provide scientific and practical arguments to contribute to improving the effectiveness of management and organization of ecotourism in Cuc Phuong National Park and Phu Quoc National Park.
Maybe you are interested!
-
 Assessing the current situation and proposing solutions for developing longan trees in Song Ma district, Son La province - 1
Assessing the current situation and proposing solutions for developing longan trees in Song Ma district, Son La province - 1 -
 Assessing the current situation and proposing solutions for developing longan trees in Song Ma district, Son La province - 11
Assessing the current situation and proposing solutions for developing longan trees in Song Ma district, Son La province - 11 -
 Assessing the current situation and proposing solutions for developing large-scale timber plantation in Phu Tho province - 11
Assessing the current situation and proposing solutions for developing large-scale timber plantation in Phu Tho province - 11 -
 Assessing the current situation and proposing solutions to improve the effectiveness of site clearance and resettlement at some projects in Thanh Tri district, Hanoi city - 14
Assessing the current situation and proposing solutions to improve the effectiveness of site clearance and resettlement at some projects in Thanh Tri district, Hanoi city - 14 -
 Assessing the current situation and proposing solutions for developing large-scale timber plantation in Phu Tho province - 17
Assessing the current situation and proposing solutions for developing large-scale timber plantation in Phu Tho province - 17
Xuan Thuy National Park, the master's thesis topic " Assessing the current situation and proposing solutions to improve the effectiveness of management and organization of ecotourism in Cuc Phuong and Xuan Thuy National Parks " has been selected for research and completion.
2. Research objectives of the thesis topic

* General objective: The topic aims to understand the difficulties in resources and benefit sharing in developing ecotourism in Cuc Phuong and Xuan Thuy National Parks, and propose solutions to improve the management and organization of ecotourism in these two National Parks.
* Specific objectives:
+ Summarize theoretical issues related to the development and organization of ecotourism activities in special-use forests.
+ Obtain general comments and assessments on the current status of management and organization of ecotourism in the studied National Parks.
+ Analyze and evaluate strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and challenges for the management and development of ecotourism in National Parks.
+ Determine the priority level for each area of ecotourism management and development in each National Park.
+ Propose some solutions to improve the effectiveness of management and organization of ecotourism, contributing to the conservation and sustainable development of Cuc Phuong and Xuan Thuy National Parks.
3. Research objects, scope and time
- Research object: activities, management mechanisms, and organization of ecotourism in special-use forests.
- Scope of research: research at two National Parks: Cuc Phuong and Xuan Thuy. Both of these National Parks have the potential to develop ecotourism with their own strengths in terms of location, high biodiversity and many scenic spots that attract tourists.
- Research period: evaluate the management and organization of ecotourism of two National Parks studied from 2011 to 2012.
4. Scientific and practical significance of the topic
- Scientific significance: The thesis initially presents the current status of ecotourism development in Cuc Phuong and Xuan Thuy National Parks. Ecotourism development is a new issue and is receiving attention from all levels and sectors; analyzes the advantages and disadvantages in developing ecotourism in the selected National Parks for research, especially management and organization.
- Practical significance : The thesis contributes to providing solutions to improve the effectiveness of ecotourism management and organization, contributing to the conservation and sustainable development of Cuc Phuong and Xuan Thuy National Parks.
5. Thesis structure
In addition to the introduction, conclusion and recommendations, the thesis is presented in the following 3 chapters:
- Chapter 1. Overview of research problem
- Chapter 2. Location, time, methodology and research methods.
- Chapter 3. Research results.
CHAPTER 1. OVERVIEW OF THE RESEARCH PROBLEM, ASSESSMENT OF THE CURRENT SITUATION AND PROPOSAL OF SOLUTIONS TO IMPROVE EFFICIENCY
MANAGEMENT AND ORGANIZATION OF ECO-TOURISM IN NATIONAL PARKS
1.1. Theoretical basis of ecotourism
1.1.1. Concepts of tourism and ecotourism
Since ancient times, tourism has been discussed a lot with different concepts. Traditional definitions only consider tourism as simply a vacation or a leisure trip. Nowadays, there are official research works on tourism with different definitions, but in general, these definitions include contents related to special forms of migration, how to use time at the destination and related socio-economic activities taking place there. Two American scholars, Mathieson and Wall, have summarized with the following definition: " Tourism is the temporary movement of people to places outside their usual residence and work areas, the activities carried out during their stay in those places, and the facilities created to satisfy their needs. "
Considering that tourism is not only the phenomenon of movement of residents but also everything related to that movement, Kaspar defines tourism as the whole of relations and phenomena that occur during the movement and stay of people in places other than their usual residence or workplace. We also see this idea in the view of Hunziker and Kraff: tourism is the sum of relations and phenomena that originate from the journey and temporary stay of individuals in places other than their usual residence and workplace.
In Vietnam, tourism is officially defined in the Tourism Ordinance [19] as follows: '' Tourism is a human activity outside of one's regular residence to satisfy the needs of sightseeing, entertainment, and relaxation within a certain period of time ''. In the Vietnam Tourism Law 2005 [21], the definition of tourism is adjusted as: "activities related to human trips outside of one's regular residence to satisfy the needs of sightseeing, learning, entertainment, and relaxation within a certain period of time" . Scholars compiling the Vietnam Encyclopedia have separated the two basic contents of tourism into two
separate part. The first meaning of this word is "a form of active sightseeing and recreation of people outside their place of residence for the purpose of: resting, entertaining, seeing scenic spots, historical relics, cultural and artistic works, ...". In the second meaning, tourism is considered "a comprehensive business with high efficiency in many aspects: improving understanding of nature, historical traditions and national culture, thereby contributing to increasing love for the country; for foreigners, it is friendship with their own people; in terms of economics, tourism is a very effective business sector; it can be considered a form of exporting goods and services on the spot".
Over time, along with the development of socio-economy, the trips become longer, the number of people who need to travel is constantly increasing. That increase has greatly affected the environment as well as tourism resources in the areas that visitors visit. Accordingly, a new type of tourism has appeared that can overcome the above problems, which is eco-tourism.
Ecotourism has its roots in nature tourism and outdoor tourism. The first ecotourists who flocked to Yellowstone and Yosemite National Parks centuries ago were the first ecotourists. The travelers who came to the Serengeti about half a century ago, the Himalayan adventurers who camped on Annapurna 25 years later, the thousands who came to photograph penguins in Antarctica, etc., were all ecotourists. Visitors are increasingly aware of the ecological impact they can have on natural values and on local concerns. Specialized organized tours - bird watching, nature walks, guided safaris, etc. - are increasingly ecotourism (David Western, 1999).
Nowadays, the world's trend is to consider ecotourism as a valuable resource. Ecotourism has become popular among nature lovers and is also considered a way to repay nature and increase the value of nature. In terms of content, ecotourism is a form of sightseeing and exploration, bringing tourists to relatively intact environments, to wild and unique natural areas to learn and research ecosystems and unique indigenous cultures, awakening in tourists the love and responsibility for conservation and development of nature and local communities.
However, the first definition of ecotourism was not until 1987 by Hector Ceballos - Lascurain: '' Ecotourism is travel to relatively undisturbed natural areas with the specific objectives of studying, appreciating and enjoying the scenery and wildlife, as well as the cultural manifestations (both past and present) discovered in these areas ''. According to Wood (1991): '' Ecotourism is travel to relatively undisturbed areas with the aim of learning about the history of the natural environment and culture without altering the integrity of the ecosystems while creating economic opportunities to support nature conservation and bring financial benefits to local people ''. In addition to the definitions of individuals, there are also definitions of organizations and associations such as the definition of the International Ecotourism Federation as follows: "Ecotourism is responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment and improves the welfare of local people" .
Most recently, definitions of ecotourism have been proposed in the works of David Bruce Weaver (2001) on the dictionary of ecotourism; of Ralf Buckley (2009) on the principles and practices of ecotourism; or of David Newsome et al. (2013) on ecotourism in protected areas. All of these works emphasize that ecotourism is a type of tourism development in a relatively unspoiled area, based on natural ecosystems and promoting community development.
In Vietnam, ecotourism is a new field that has been studied since the mid-1990s. At the workshop " Building a national strategy for developing ecotourism in Vietnam " (September 1999), a consensus was reached on the definition of ecotourism in Vietnam: " Ecotourism is a type of tourism based on nature and indigenous culture that educates the environment and contributes to conservation efforts and sustainable development with the active participation of local communities ". In the 2005 Tourism Law [21], ecotourism is defined as "a form of tourism based on nature, associated with local cultural identity with community participation for sustainable development" . The content of ecotourism is expanded in the definition: “Ecotourism is a type of tourism that takes specific, natural ecosystems as its target to serve tourists who love nature, travel, enjoy landscapes or study ecosystems. It is also a form of close and harmonious combination between economic development of tourism and introduction of
"national beauty as well as education, propaganda and protection, sustainable development of the environment and natural resources" (Le Huy Ba, 2000) [3].
Thus, from the first definition of ecotourism in 1987, until now, the perception of ecotourism has changed: from simply considering ecotourism as a tourism activity with little impact on the natural environment to a more positive view, according to which ecotourism is a type of tourism that is responsible for the environment, has a high educational and interpretive value about nature, contributes to conservation activities and brings benefits to the local community.
In short, in the world as well as in Vietnam, the concept of ecotourism is seen as tourism that selects the positive aspects of some types of tourism, and can be represented by a diagram combining the components of natural and indigenous cultural tourism, conservation-supporting tourism, environmentally-educated tourism, and community-supporting tourism. In which, ecotourism, no matter how it is defined, converges the following basic elements: (1) concern for nature and the environment; (2) responsibility to society and the community (Figure 1.1) .
NATURE TOURISM
INDIGENOUS CULTURE
TOURISM
TRAVEL BOOTS
CONSERVATION
TOURISM
TRAVEL WITH EDUCATION
ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION
TOUR SUPPORT
COMMUNITY
Figure 1.1. Ecotourism structure model “Source: Le Van Lanh, 1999 ”
1.1.2. The relationship of ecotourism with other types of tourism
Ecotourism is a type of tourism that not only relies on nature, but also includes learning and researching the indigenous culture of local communities. However, types of tourism based on nature such as resorts, sightseeing, adventure... mainly only bring people back to nature, while education and raising awareness
Raising awareness among tourists about nature and environment, local community culture is very rare and almost non-existent. However, if the activities of this type of tourism are associated with the implementation of the principles of ecotourism, including raising awareness so that tourists are responsible for the conservation of natural values and community culture, creating jobs and benefits for local people, then they themselves have transformed into a form of ecotourism.
DLST
Cultural tourism, historical tourism.
Other types of tourism (discovery tourism, community tourism, etc.)
Figure 1.2. The relationship between ecotourism, cultural tourism, historical tourism, and other types of tourism Le Huy Ba, 2006 ”
Ecotourism is closely related and interacts with tourism and ecology.
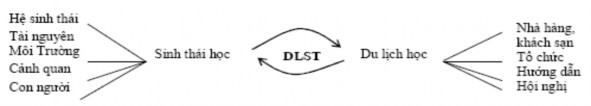
Figure 1.3. Ecotourism is made up of unity and
supplement of tourism and ecology “Source: Le Huy Ba, 2006 ”
1.1.3. Characteristics of ecotourism
The difference between ecotourism and other types of tourism is reflected in ensuring the following characteristics:
- Based on attractive natural areas and indigenous cultural elements : the subject of ecotourism is attractive natural areas, including unique indigenous cultural features.





