The outstanding debt to total assets ratio of the bank has increased steadily over the years, with the growth rate fluctuating between 9% - 11%, the lowest outstanding debt/total assets ratio of the bank in 2012 was 43.1% and the highest in 2017 was 70%. By 2018, the outstanding debt/total assets ratio was: 68.7%. Thus, it is clear that VPBank's annual income has a large contribution from credit activities. Also according to statistics, if comparing the total outstanding debt/equity value ratio of the bank each year, the average ratio is 8.53%. In order to match the growth rate of credit activities, the bank has adjusted to increase equity each year, the average equity growth rate is ~36.2%. In addition, VPBank's credit growth rate compared to the entire banking system is recorded as follows:
Table 3.3. VPBank's credit growth compared to the whole system
(unit:%)
Year
2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 09 February 2019 | |
Credit growth whole banking system row | 27.65 | 12 | 9.1 | 12.51 | 14.16 | 17.29 | 18.71 | 18.17 | 14 | 8.4 |
VPBank's credit growth | 60 | 15 | 26.8 | 42 | 49 | 49.1 | 23.8 | 26.2 | 17.3 | 14.7 |
Maybe you are interested!
-
![Pre-tax Profit of Bidv Tien Giang in the Period 2011-2015
zt2i3t4l5ee
zt2a3gsnon-credit services, joint stock commercial bank
zt2a3ge
zc2o3n4t5e6n7ts
At that time, the Branch had to set aside a provision for credit risks, which reduced the Branchs income.
Chart 2.2. Pre-tax profit of BIDV Tien Giang in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Billion VND
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
63.3
80.34
89.29
110.08
131.99
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Profit before tax
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
However, through chart 2.2, it can be seen that BIDV Tien Giangs profit is still increasing continuously, and its operating efficiency is currently leaking. This is a contribution of non-credit services, and this service segment will be increasingly focused on growth by BIDV Tien Giang to ensure the highest profit safety because credit activities have many potential risks. At the same time, focusing on developing non-credit services is consistent with one of the contents of restructuring the financial activities of credit institutions in the project Restructuring the system of credit institutions in the period 2011-2015 approved by the Prime Minister in Decision No. 254/QD-TTg dated March 1, 2012 [14]: Gradually shifting the business model of commercial banks towards reducing dependence on credit activities and increasing income from non-credit services.
2.2. Current status of non-credit service development at BIDV Tien Giang.
2.2.1. BIDV Tien Giang has deployed the development of non-credit services in recent times.
Along with the development of the Head Office, BIDV Tien Giangs products and services are constantly improved and deployed in a diverse manner to ensure provision for many different customer groups in the area: individual customers, corporate customers, and financial institutions. Typical services are as follows: Payment services, treasury services, guarantee services, card services, trade finance, other services: Western Union, insurance commissions, consulting services, foreign exchange derivatives trading, e-banking services,...
2.2.1.1. Payment services:
In accordance with the Prime Ministers Project to promote non-cash payments in Vietnam [15], banks in Tien Giang province have continuously developed payment services to reduce customers cash usage habits through card services and electronic banking services such as: salary payment through accounts, focusing on developing card acceptance points, developing multi-purpose cards, paying social insurance by transfer, paying bills through banks, etc.
Chart 2.3. Net income from payment services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
6000
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
0
3922 4065
4720 5084 5324
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from payment services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Along with the technological development of the entire system, BIDV Tien Giang has a payment system with a fairly stable transaction processing speed, bringing many conveniences to customers. The results of observing chart 2.3 show that the income from payment services that the Branch has achieved has grown over the years but the speed is not high and the products are not outstanding compared to other banks. Domestic payment products such as: Online bill payment, electricity bills, water bills, insurance premiums, cable TV bills, telecommunications fees, airline tickets, etc. bring many conveniences to customers. Regarding international payment, this is an indispensable activity for foreign economic activities, BIDV Tien Giang is providing international payment methods for small enterprises producing agriculture, aquatic food and seafood that have credit relationships with banks in industrial parks in Tien Giang province such as: money transfer, collection, L/C payment.
2.2.1.2. Treasury services:
BIDV Tien Giang always focuses on ensuring treasury safety and currency security, always complies with legal regulations, and minimizes risks in operations such as: counting and collecting money from customers, receiving and delivering internal transactions, collecting from the State Bank (SBV) or other credit institutions, receiving ATM funds, bundling money, etc. BIDV Tien Giangs treasury service management department is always fully equipped with modern machinery and equipment such as: money transport vehicles, fire prevention tools, money counters, money detectors, magnifying glasses, etc. to ensure absolute safety in treasury operations, immediately identifying real and fake money and other risks that may affect people and assets of the bank and customers. In addition, implementing regulation 2480/QC dated October 28, 2008 between the State Bank of Tien Giang province and the Provincial Police on coordination in the fight against counterfeit money, in the 3-year review of implementation, BIDV Tien Giang discovered, seized and submitted to the State Bank of Tien Giang province 475 banknotes of various denominations and was commended by the Provincial Police and the State Bank of Tien Giang province [17].
Chart 2.4. Net income from treasury services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
105 122
309 289 279
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from treasury services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
However, as shown in Figure 2.4, income from treasury operations is not high and fluctuates. Specifically, in the period 2011-2013, net income increased and increased most sharply in 2013, then in the period 2013-2015, there was a downward trend. This fluctuation is due to the fact that fees collected from treasury services are often very low and can even be waived to attract customers to use other services.
2.2.1.3. Guarantee and trade finance services:
BIDV Tien Giang, thanks to the advantages of the province and the favorable location of the Branch, has continuously focused on developing income from guarantee services and trade finance.
Chart 2.5. Net income from guarantee and trade finance services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
14000
12000
10000
8000
6000
4000
2000
0
5193 5695
2742 3420
8889
3992
11604 12206
5143 5312
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from guarantee services Net income from Trade Finance
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Through chart 2.5, we can see that BIDV Tien Giangs income from guarantee services and trade finance has grown over the years. The reason is: Among BIDV Tien Giangs corporate customers, the construction industry is the industry with the highest proportion of customers after the trading industry, this is a group of customers with potential to develop guarantee services. The second group of customers is corporate customers in the fields of agricultural production, livestock and seafood processing with high import and export turnover in the area.
are the target of trade finance development. In addition, BIDV Tien Giang also focuses on continuously developing these customer groups to increase revenue for many other products and services in the future.
2.2.1.4. Card and POS services:
As a service that BIDV Tien Giang has recently developed strongly, it can be said that this is a very potential market and has the ability to develop even more strongly in the future. Card services with outstanding advantages such as fast payment time, wide payment range, quite safe, effective and suitable for the integration trend and the Project to promote non-cash payments in Vietnam. Cards have become a modern and popular payment tool. BIDV Tien Giang early identified that developing card services is to expand the market to people in society, create capital mobilized from card-opened accounts, contribute to diversifying banking activities, enhance the image of the bank, bring the BIDV Tien Giang brand to people as quickly and easily as possible. BIDV Tien Giang is currently providing card types such as: credit cards (BIDV MasterCard Platinum, BIDV Visa Gold Precious, BIDV Visa Manchester United, BIDV Visa Classic), international debit cards (BIDV Ready Card, BIDV Manu Debit Card), domestic debit cards (BIDV Harmony Card, BIDV eTrans Card, BIDV Moving Card, BIDV-Lingo Co-branded Card, BIDV-Co.opmart Co-branded Card). These cards can be paid via POS/EDC or on the ATM system. In addition, with debit cards, customers can not only withdraw money via ATMs but also perform utilities such as mobile top-up, online payment, money transfer,... through electronic banking services.
In order to attract customers with card services, BIDV Tien Giang has continuously increased the installation of ATMs. As of December 31, 2015, BIDV Tien Giang has 23 ATMs combined with 7 ATMs in the same system of BIDV My Tho, so the number of ATMs is quite large, especially in the center of My Tho City, but is not yet fully present in the districts. Basic services on ATMs such as withdrawing money, checking balances, printing short statements,... BIDV ATMs accept cards from banks in the system.
Banknetvn and Smartlink, cards branded by international card organizations Union Pay (CUP), VISA, MasterCard and cards of banks in the Asian Payment Network. From here, cardholders can make bill payments for themselves or others at ATMs, by simply entering the subscriber number or customer code, booking code that service providers notify and make bill payments.
Chart 2.6. Net income from card services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
3500
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
687
1023
1547
2267
3104
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from card services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Through chart 2.6, it can be seen that BIDV Tien Giangs card service income is constantly growing because the Branch focuses on developing businesses operating in industrial parks, which are the source of customers for salary payment products, ATMs, BSMS. Specifically, there are companies such as Freeview, Quang Viet, Dai Thanh, which are businesses with a large number of card openings at the Branch, contributing to the increase in card service fees [25].
Table 2.6. Number of ATMs and POS machines in 2015 of some banks in Tien Giang area.
Unit: Machine
STT
Bank name
Number of ATMs
Cumulative number of ATM cards
POS machine
1
BIDV Tien Giang
23
97,095
22
2
BIDV My Tho
7
21,325
0
3
Agribank Tien Giang
29
115,743
77
4
Vietinbank Tien Giang
16
100,052
54
5
Dong A Tien Giang
26
97,536
11
6
Sacombank Tien Giang
24
88,513
27
7
Vietcombank Tien Giang
15
61,607
96
8
Vietinbank - Tay Tien Giang Branch
6
46,042
38
(Source: 2015 Banking Activity Data Report of the General and Internal Control Department of the Provincial State Bank [21])
Through table 2.6, the author finds that the number of ATMs of BIDV Tien Giang is not much, ranking fourth after Agribank Tien Giang, Dong A Tien Giang, Sacombank Tien Giang. The number of POS machines of BIDV Tien Giang is very small, only higher than Dong A Tien Giang and BIDV My Tho in the initial stages of merging the BIDV system. Besides, BIDV Tien Giang has a high number of cards increasing over the years (table 2.7) but the cumulative number of cards issued up to December 31, 2015 is still relatively low compared to Agribank, Vietcombank, Dong A (table 2.6).
div.maincontent .content_head3 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .p { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; margin:0pt; }
div.maincontent p { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; margin:0pt; }
div.maincontent .s1 { color: black; font-family:Courier New, monospace; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s2 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s3 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s4 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s5 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s6 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s7 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s8 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; }
div.maincontent .s9 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -2pt; }
div.maincontent .s10 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: 5pt; }
div.maincontent .s11 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s12 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -3pt; }
div.maincontent .s13 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s14 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 7.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s15 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s16 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s17 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s18 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -1pt; }
div.maincontent .s19 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s20 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -2pt; }
div.maincontent .s21 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10pt; }
div.maincontent .s22 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s23 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -3pt; }
div.maincontent .s24 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s25 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s26 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s27 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -6pt; }
div.maincontent .s28 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -1pt; }
div.maincontent .s29 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s30 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11pt; }
div.maincontent .s31 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11pt; }
div.maincontent .s32 { color: black; font-family:.VnTime, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s33 { color: black; font-family:Cambria, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s34 { color: black; font-family:Cambria, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s35 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s36 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s37 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s38 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s39 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 15pt; }
div.maincontent .s40 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; fo](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns=%22http://www.w3.org/2000/svg%22%20viewBox=%220%200%2075%2075%22%3E%3C/svg%3E) Pre-tax Profit of Bidv Tien Giang in the Period 2011-2015
zt2i3t4l5ee
zt2a3gsnon-credit services, joint stock commercial bank
zt2a3ge
zc2o3n4t5e6n7ts
At that time, the Branch had to set aside a provision for credit risks, which reduced the Branch's income.
Chart 2.2. Pre-tax profit of BIDV Tien Giang in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Billion VND
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
63.3
80.34
89.29
110.08
131.99
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Profit before tax
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
However, through chart 2.2, it can be seen that BIDV Tien Giang's profit is still increasing continuously, and its operating efficiency is currently leaking. This is a contribution of non-credit services, and this service segment will be increasingly focused on growth by BIDV Tien Giang to ensure the highest profit safety because credit activities have many potential risks. At the same time, focusing on developing non-credit services is consistent with one of the contents of restructuring the financial activities of credit institutions in the project "Restructuring the system of credit institutions in the period 2011-2015" approved by the Prime Minister in Decision No. 254/QD-TTg dated March 1, 2012 [14]: "Gradually shifting the business model of commercial banks towards reducing dependence on credit activities and increasing income from non-credit services".
2.2. Current status of non-credit service development at BIDV Tien Giang.
2.2.1. BIDV Tien Giang has deployed the development of non-credit services in recent times.
Along with the development of the Head Office, BIDV Tien Giang's products and services are constantly improved and deployed in a diverse manner to ensure provision for many different customer groups in the area: individual customers, corporate customers, and financial institutions. Typical services are as follows: Payment services, treasury services, guarantee services, card services, trade finance, other services: Western Union, insurance commissions, consulting services, foreign exchange derivatives trading, e-banking services,...
2.2.1.1. Payment services:
In accordance with the Prime Minister's Project to promote non-cash payments in Vietnam [15], banks in Tien Giang province have continuously developed payment services to reduce customers' cash usage habits through card services and electronic banking services such as: salary payment through accounts, focusing on developing card acceptance points, developing multi-purpose cards, paying social insurance by transfer, paying bills through banks, etc.
Chart 2.3. Net income from payment services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
6000
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
0
3922 4065
4720 5084 5324
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from payment services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Along with the technological development of the entire system, BIDV Tien Giang has a payment system with a fairly stable transaction processing speed, bringing many conveniences to customers. The results of observing chart 2.3 show that the income from payment services that the Branch has achieved has grown over the years but the speed is not high and the products are not outstanding compared to other banks. Domestic payment products such as: Online bill payment, electricity bills, water bills, insurance premiums, cable TV bills, telecommunications fees, airline tickets, etc. bring many conveniences to customers. Regarding international payment, this is an indispensable activity for foreign economic activities, BIDV Tien Giang is providing international payment methods for small enterprises producing agriculture, aquatic food and seafood that have credit relationships with banks in industrial parks in Tien Giang province such as: money transfer, collection, L/C payment.
2.2.1.2. Treasury services:
BIDV Tien Giang always focuses on ensuring treasury safety and currency security, always complies with legal regulations, and minimizes risks in operations such as: counting and collecting money from customers, receiving and delivering internal transactions, collecting from the State Bank (SBV) or other credit institutions, receiving ATM funds, bundling money, etc. BIDV Tien Giang's treasury service management department is always fully equipped with modern machinery and equipment such as: money transport vehicles, fire prevention tools, money counters, money detectors, magnifying glasses, etc. to ensure absolute safety in treasury operations, immediately identifying real and fake money and other risks that may affect people and assets of the bank and customers. In addition, implementing regulation 2480/QC dated October 28, 2008 between the State Bank of Tien Giang province and the Provincial Police on coordination in the fight against counterfeit money, in the 3-year review of implementation, BIDV Tien Giang discovered, seized and submitted to the State Bank of Tien Giang province 475 banknotes of various denominations and was commended by the Provincial Police and the State Bank of Tien Giang province [17].
Chart 2.4. Net income from treasury services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
105 122
309 289 279
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from treasury services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
However, as shown in Figure 2.4, income from treasury operations is not high and fluctuates. Specifically, in the period 2011-2013, net income increased and increased most sharply in 2013, then in the period 2013-2015, there was a downward trend. This fluctuation is due to the fact that fees collected from treasury services are often very low and can even be waived to attract customers to use other services.
2.2.1.3. Guarantee and trade finance services:
BIDV Tien Giang, thanks to the advantages of the province and the favorable location of the Branch, has continuously focused on developing income from guarantee services and trade finance.
Chart 2.5. Net income from guarantee and trade finance services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
14000
12000
10000
8000
6000
4000
2000
0
5193 5695
2742 3420
8889
3992
11604 12206
5143 5312
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from guarantee services Net income from Trade Finance
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Through chart 2.5, we can see that BIDV Tien Giang's income from guarantee services and trade finance has grown over the years. The reason is: Among BIDV Tien Giang's corporate customers, the construction industry is the industry with the highest proportion of customers after the trading industry, this is a group of customers with potential to develop guarantee services. The second group of customers is corporate customers in the fields of agricultural production, livestock and seafood processing with high import and export turnover in the area.
are the target of trade finance development. In addition, BIDV Tien Giang also focuses on continuously developing these customer groups to increase revenue for many other products and services in the future.
2.2.1.4. Card and POS services:
As a service that BIDV Tien Giang has recently developed strongly, it can be said that this is a very potential market and has the ability to develop even more strongly in the future. Card services with outstanding advantages such as fast payment time, wide payment range, quite safe, effective and suitable for the integration trend and the Project to promote non-cash payments in Vietnam. Cards have become a modern and popular payment tool. BIDV Tien Giang early identified that developing card services is to expand the market to people in society, create capital mobilized from card-opened accounts, contribute to diversifying banking activities, enhance the image of the bank, bring the BIDV Tien Giang brand to people as quickly and easily as possible. BIDV Tien Giang is currently providing card types such as: credit cards (BIDV MasterCard Platinum, BIDV Visa Gold Precious, BIDV Visa Manchester United, BIDV Visa Classic), international debit cards (BIDV Ready Card, BIDV Manu Debit Card), domestic debit cards (BIDV Harmony Card, BIDV eTrans Card, BIDV Moving Card, BIDV-Lingo Co-branded Card, BIDV-Co.opmart Co-branded Card). These cards can be paid via POS/EDC or on the ATM system. In addition, with debit cards, customers can not only withdraw money via ATMs but also perform utilities such as mobile top-up, online payment, money transfer,... through electronic banking services.
In order to attract customers with card services, BIDV Tien Giang has continuously increased the installation of ATMs. As of December 31, 2015, BIDV Tien Giang has 23 ATMs combined with 7 ATMs in the same system of BIDV My Tho, so the number of ATMs is quite large, especially in the center of My Tho City, but is not yet fully present in the districts. Basic services on ATMs such as withdrawing money, checking balances, printing short statements,... BIDV ATMs accept cards from banks in the system.
Banknetvn and Smartlink, cards branded by international card organizations Union Pay (CUP), VISA, MasterCard and cards of banks in the Asian Payment Network. From here, cardholders can make bill payments for themselves or others at ATMs, by simply entering the subscriber number or customer code, booking code that service providers notify and make bill payments.
Chart 2.6. Net income from card services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
3500
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
687
1023
1547
2267
3104
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from card services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Through chart 2.6, it can be seen that BIDV Tien Giang's card service income is constantly growing because the Branch focuses on developing businesses operating in industrial parks, which are the source of customers for salary payment products, ATMs, BSMS. Specifically, there are companies such as Freeview, Quang Viet, Dai Thanh, which are businesses with a large number of card openings at the Branch, contributing to the increase in card service fees [25].
Table 2.6. Number of ATMs and POS machines in 2015 of some banks in Tien Giang area.
Unit: Machine
STT
Bank name
Number of ATMs
Cumulative number of ATM cards
POS machine
1
BIDV Tien Giang
23
97,095
22
2
BIDV My Tho
7
21,325
0
3
Agribank Tien Giang
29
115,743
77
4
Vietinbank Tien Giang
16
100,052
54
5
Dong A Tien Giang
26
97,536
11
6
Sacombank Tien Giang
24
88,513
27
7
Vietcombank Tien Giang
15
61,607
96
8
Vietinbank - Tay Tien Giang Branch
6
46,042
38
(Source: 2015 Banking Activity Data Report of the General and Internal Control Department of the Provincial State Bank [21])
Through table 2.6, the author finds that the number of ATMs of BIDV Tien Giang is not much, ranking fourth after Agribank Tien Giang, Dong A Tien Giang, Sacombank Tien Giang. The number of POS machines of BIDV Tien Giang is very small, only higher than Dong A Tien Giang and BIDV My Tho in the initial stages of merging the BIDV system. Besides, BIDV Tien Giang has a high number of cards increasing over the years (table 2.7) but the cumulative number of cards issued up to December 31, 2015 is still relatively low compared to Agribank, Vietcombank, Dong A (table 2.6).
div.maincontent .content_head3 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .p { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; margin:0pt; }
div.maincontent p { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; margin:0pt; }
div.maincontent .s1 { color: black; font-family:"Courier New", monospace; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s2 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s3 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s4 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s5 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s6 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s7 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s8 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; }
div.maincontent .s9 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -2pt; }
div.maincontent .s10 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: 5pt; }
div.maincontent .s11 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s12 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -3pt; }
div.maincontent .s13 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s14 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 7.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s15 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s16 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s17 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s18 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -1pt; }
div.maincontent .s19 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s20 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -2pt; }
div.maincontent .s21 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10pt; }
div.maincontent .s22 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s23 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -3pt; }
div.maincontent .s24 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s25 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s26 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s27 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -6pt; }
div.maincontent .s28 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -1pt; }
div.maincontent .s29 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s30 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11pt; }
div.maincontent .s31 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11pt; }
div.maincontent .s32 { color: black; font-family:.VnTime, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s33 { color: black; font-family:Cambria, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s34 { color: black; font-family:Cambria, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s35 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s36 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s37 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s38 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s39 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 15pt; }
div.maincontent .s40 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; fo
Pre-tax Profit of Bidv Tien Giang in the Period 2011-2015
zt2i3t4l5ee
zt2a3gsnon-credit services, joint stock commercial bank
zt2a3ge
zc2o3n4t5e6n7ts
At that time, the Branch had to set aside a provision for credit risks, which reduced the Branch's income.
Chart 2.2. Pre-tax profit of BIDV Tien Giang in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Billion VND
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
63.3
80.34
89.29
110.08
131.99
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Profit before tax
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
However, through chart 2.2, it can be seen that BIDV Tien Giang's profit is still increasing continuously, and its operating efficiency is currently leaking. This is a contribution of non-credit services, and this service segment will be increasingly focused on growth by BIDV Tien Giang to ensure the highest profit safety because credit activities have many potential risks. At the same time, focusing on developing non-credit services is consistent with one of the contents of restructuring the financial activities of credit institutions in the project "Restructuring the system of credit institutions in the period 2011-2015" approved by the Prime Minister in Decision No. 254/QD-TTg dated March 1, 2012 [14]: "Gradually shifting the business model of commercial banks towards reducing dependence on credit activities and increasing income from non-credit services".
2.2. Current status of non-credit service development at BIDV Tien Giang.
2.2.1. BIDV Tien Giang has deployed the development of non-credit services in recent times.
Along with the development of the Head Office, BIDV Tien Giang's products and services are constantly improved and deployed in a diverse manner to ensure provision for many different customer groups in the area: individual customers, corporate customers, and financial institutions. Typical services are as follows: Payment services, treasury services, guarantee services, card services, trade finance, other services: Western Union, insurance commissions, consulting services, foreign exchange derivatives trading, e-banking services,...
2.2.1.1. Payment services:
In accordance with the Prime Minister's Project to promote non-cash payments in Vietnam [15], banks in Tien Giang province have continuously developed payment services to reduce customers' cash usage habits through card services and electronic banking services such as: salary payment through accounts, focusing on developing card acceptance points, developing multi-purpose cards, paying social insurance by transfer, paying bills through banks, etc.
Chart 2.3. Net income from payment services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
6000
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
0
3922 4065
4720 5084 5324
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from payment services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Along with the technological development of the entire system, BIDV Tien Giang has a payment system with a fairly stable transaction processing speed, bringing many conveniences to customers. The results of observing chart 2.3 show that the income from payment services that the Branch has achieved has grown over the years but the speed is not high and the products are not outstanding compared to other banks. Domestic payment products such as: Online bill payment, electricity bills, water bills, insurance premiums, cable TV bills, telecommunications fees, airline tickets, etc. bring many conveniences to customers. Regarding international payment, this is an indispensable activity for foreign economic activities, BIDV Tien Giang is providing international payment methods for small enterprises producing agriculture, aquatic food and seafood that have credit relationships with banks in industrial parks in Tien Giang province such as: money transfer, collection, L/C payment.
2.2.1.2. Treasury services:
BIDV Tien Giang always focuses on ensuring treasury safety and currency security, always complies with legal regulations, and minimizes risks in operations such as: counting and collecting money from customers, receiving and delivering internal transactions, collecting from the State Bank (SBV) or other credit institutions, receiving ATM funds, bundling money, etc. BIDV Tien Giang's treasury service management department is always fully equipped with modern machinery and equipment such as: money transport vehicles, fire prevention tools, money counters, money detectors, magnifying glasses, etc. to ensure absolute safety in treasury operations, immediately identifying real and fake money and other risks that may affect people and assets of the bank and customers. In addition, implementing regulation 2480/QC dated October 28, 2008 between the State Bank of Tien Giang province and the Provincial Police on coordination in the fight against counterfeit money, in the 3-year review of implementation, BIDV Tien Giang discovered, seized and submitted to the State Bank of Tien Giang province 475 banknotes of various denominations and was commended by the Provincial Police and the State Bank of Tien Giang province [17].
Chart 2.4. Net income from treasury services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
105 122
309 289 279
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from treasury services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
However, as shown in Figure 2.4, income from treasury operations is not high and fluctuates. Specifically, in the period 2011-2013, net income increased and increased most sharply in 2013, then in the period 2013-2015, there was a downward trend. This fluctuation is due to the fact that fees collected from treasury services are often very low and can even be waived to attract customers to use other services.
2.2.1.3. Guarantee and trade finance services:
BIDV Tien Giang, thanks to the advantages of the province and the favorable location of the Branch, has continuously focused on developing income from guarantee services and trade finance.
Chart 2.5. Net income from guarantee and trade finance services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
14000
12000
10000
8000
6000
4000
2000
0
5193 5695
2742 3420
8889
3992
11604 12206
5143 5312
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from guarantee services Net income from Trade Finance
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Through chart 2.5, we can see that BIDV Tien Giang's income from guarantee services and trade finance has grown over the years. The reason is: Among BIDV Tien Giang's corporate customers, the construction industry is the industry with the highest proportion of customers after the trading industry, this is a group of customers with potential to develop guarantee services. The second group of customers is corporate customers in the fields of agricultural production, livestock and seafood processing with high import and export turnover in the area.
are the target of trade finance development. In addition, BIDV Tien Giang also focuses on continuously developing these customer groups to increase revenue for many other products and services in the future.
2.2.1.4. Card and POS services:
As a service that BIDV Tien Giang has recently developed strongly, it can be said that this is a very potential market and has the ability to develop even more strongly in the future. Card services with outstanding advantages such as fast payment time, wide payment range, quite safe, effective and suitable for the integration trend and the Project to promote non-cash payments in Vietnam. Cards have become a modern and popular payment tool. BIDV Tien Giang early identified that developing card services is to expand the market to people in society, create capital mobilized from card-opened accounts, contribute to diversifying banking activities, enhance the image of the bank, bring the BIDV Tien Giang brand to people as quickly and easily as possible. BIDV Tien Giang is currently providing card types such as: credit cards (BIDV MasterCard Platinum, BIDV Visa Gold Precious, BIDV Visa Manchester United, BIDV Visa Classic), international debit cards (BIDV Ready Card, BIDV Manu Debit Card), domestic debit cards (BIDV Harmony Card, BIDV eTrans Card, BIDV Moving Card, BIDV-Lingo Co-branded Card, BIDV-Co.opmart Co-branded Card). These cards can be paid via POS/EDC or on the ATM system. In addition, with debit cards, customers can not only withdraw money via ATMs but also perform utilities such as mobile top-up, online payment, money transfer,... through electronic banking services.
In order to attract customers with card services, BIDV Tien Giang has continuously increased the installation of ATMs. As of December 31, 2015, BIDV Tien Giang has 23 ATMs combined with 7 ATMs in the same system of BIDV My Tho, so the number of ATMs is quite large, especially in the center of My Tho City, but is not yet fully present in the districts. Basic services on ATMs such as withdrawing money, checking balances, printing short statements,... BIDV ATMs accept cards from banks in the system.
Banknetvn and Smartlink, cards branded by international card organizations Union Pay (CUP), VISA, MasterCard and cards of banks in the Asian Payment Network. From here, cardholders can make bill payments for themselves or others at ATMs, by simply entering the subscriber number or customer code, booking code that service providers notify and make bill payments.
Chart 2.6. Net income from card services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
3500
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
687
1023
1547
2267
3104
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from card services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Through chart 2.6, it can be seen that BIDV Tien Giang's card service income is constantly growing because the Branch focuses on developing businesses operating in industrial parks, which are the source of customers for salary payment products, ATMs, BSMS. Specifically, there are companies such as Freeview, Quang Viet, Dai Thanh, which are businesses with a large number of card openings at the Branch, contributing to the increase in card service fees [25].
Table 2.6. Number of ATMs and POS machines in 2015 of some banks in Tien Giang area.
Unit: Machine
STT
Bank name
Number of ATMs
Cumulative number of ATM cards
POS machine
1
BIDV Tien Giang
23
97,095
22
2
BIDV My Tho
7
21,325
0
3
Agribank Tien Giang
29
115,743
77
4
Vietinbank Tien Giang
16
100,052
54
5
Dong A Tien Giang
26
97,536
11
6
Sacombank Tien Giang
24
88,513
27
7
Vietcombank Tien Giang
15
61,607
96
8
Vietinbank - Tay Tien Giang Branch
6
46,042
38
(Source: 2015 Banking Activity Data Report of the General and Internal Control Department of the Provincial State Bank [21])
Through table 2.6, the author finds that the number of ATMs of BIDV Tien Giang is not much, ranking fourth after Agribank Tien Giang, Dong A Tien Giang, Sacombank Tien Giang. The number of POS machines of BIDV Tien Giang is very small, only higher than Dong A Tien Giang and BIDV My Tho in the initial stages of merging the BIDV system. Besides, BIDV Tien Giang has a high number of cards increasing over the years (table 2.7) but the cumulative number of cards issued up to December 31, 2015 is still relatively low compared to Agribank, Vietcombank, Dong A (table 2.6).
div.maincontent .content_head3 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .p { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; margin:0pt; }
div.maincontent p { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; margin:0pt; }
div.maincontent .s1 { color: black; font-family:"Courier New", monospace; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s2 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s3 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s4 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s5 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s6 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s7 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s8 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; }
div.maincontent .s9 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -2pt; }
div.maincontent .s10 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: 5pt; }
div.maincontent .s11 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s12 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -3pt; }
div.maincontent .s13 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s14 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 7.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s15 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s16 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s17 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s18 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -1pt; }
div.maincontent .s19 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s20 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -2pt; }
div.maincontent .s21 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10pt; }
div.maincontent .s22 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s23 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -3pt; }
div.maincontent .s24 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s25 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s26 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s27 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -6pt; }
div.maincontent .s28 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -1pt; }
div.maincontent .s29 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s30 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11pt; }
div.maincontent .s31 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11pt; }
div.maincontent .s32 { color: black; font-family:.VnTime, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s33 { color: black; font-family:Cambria, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s34 { color: black; font-family:Cambria, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s35 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s36 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s37 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s38 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s39 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 15pt; }
div.maincontent .s40 { color: black; font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; font-style: normal; fo -
 General Comments on the Current Status of Credit Risk Management and Factors Affecting Credit Risk Management at Vpbank
General Comments on the Current Status of Credit Risk Management and Factors Affecting Credit Risk Management at Vpbank -
 Factors affecting credit growth at Vietnam's joint stock commercial banks - 1
Factors affecting credit growth at Vietnam's joint stock commercial banks - 1 -
 Credit risk management at Vietnam International Commercial Joint Stock Bank - Hanoi Branch - 12
Credit risk management at Vietnam International Commercial Joint Stock Bank - Hanoi Branch - 12 -
 Credit risk management for personal loans at Nam A Commercial Joint Stock Bank - Quang Ninh Branch - 13
Credit risk management for personal loans at Nam A Commercial Joint Stock Bank - Quang Ninh Branch - 13
(Source: Author's synthesis)
Looking at the above statistics table, it can be seen that VPBank's credit growth rate in the 5 years from 2012-2017 was always higher than the credit growth rate of the entire banking system. Especially in 2014 and 2015, the growth rate reached 49%. However, by the end of 2018, VPBank's credit growth rate decreased compared to the end of 2017, reaching only 17.3% but still higher than the industry average. The reason for such a sudden increase is that in 2014, VPBank established VPBank Finance Company (VPB FC) to expand and focus on the consumer credit network, so in the first 2 years after implementing this plan, VPBank's credit growth rate had such a leap. The plan to focus on the strategic segment of credit for individual customers of the bank has gradually brought positive business results to the bank. This
It is clearly shown that starting from 2017, 79% of VPBank's total operating income came from strategic segments. In 2018, despite a decline in credit growth rate due to strong competition from other commercial banks in VPBank's target strategic customer segment, this segment still contributed a large proportion to the total income of the segments at VPBank. Specifically as follows:
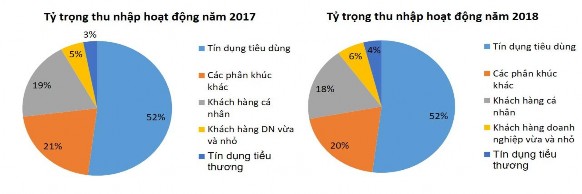
Unit: %
(Source: VPBank Annual Report 2018)
Figure 3.3. Contribution to total income of segments at VPBank in 2017-2018
According to statistics, in the first year of the third phase of the strategy (2018), 80% of operating income was contributed by the strategic segment. In which, FE credit, with its leading position in the consumer finance sector (accounting for 55% of Vietnam's market share), generated more than VND 16 trillion in revenue, contributing 52% to the total operating income of the entire bank. The KHCN segment continued to have a successful year with a growth rate of 22% compared to the previous year (accounting for 18% of VPBank's total revenue in 2018), demonstrating its spearhead role as a strategic segment. The Small and Medium Enterprise (SME) Customer segment recorded a TOI increase of 34% in this segment, thanks to its strong focus on the micro-SME sub-segment with simple unsecured loan products that created a breakthrough in margin interest, contributing 6% of the bank's total income. In 2018, the Small Business Credit Division had high growth in both total net revenue and loan scale thanks to the construction of a nationwide network to help small businesses receive timely financial support, accounting for 4% of the bank's total revenue. The satellite business segments of the Large Corporate Clients Division, the Financial Markets Division, the Financial Institutions Center and Transaction Banking... also
marking many positive changes, increasing income for the Bank, contributing 20% to revenue for the entire system.
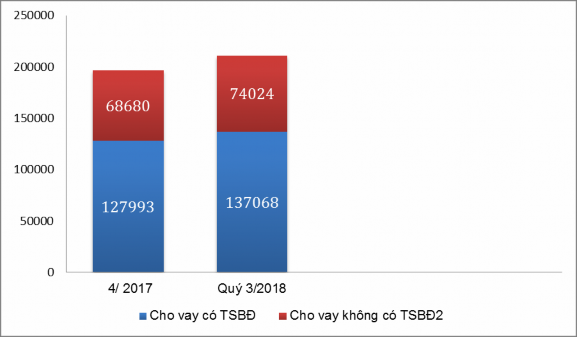
Unit: billion VND
Source: VPBank's business results report 09 months/2018
Figure 3.4. Loan structure by type
VPBank's loan structure at the time of Q4/2017 had a total outstanding loan balance of: VND 196,673 billion, of which VND 127,993 billion (accounting for 65.1% of total outstanding loan balance) was secured loans, unsecured loans were VND 72,096 billion (accounting for 34.9% of total outstanding loan balance). By the end of Q3/2018, these figures changed as follows: secured loans increased by VND 9,075 billion compared to Q4/2017, accounting for 64.9% of total outstanding loans at this time, unsecured loans also increased by VND 5,344 billion compared to Q4/2017, accounting for 35.1% of total outstanding loans. Thus, it is clear that unsecured loans (without collateral) account for a significant proportion of the loan structure at VPBank and if the bank does not have good measures to manage these loans, the risks arising from granting credit to unsecured customers are very high.
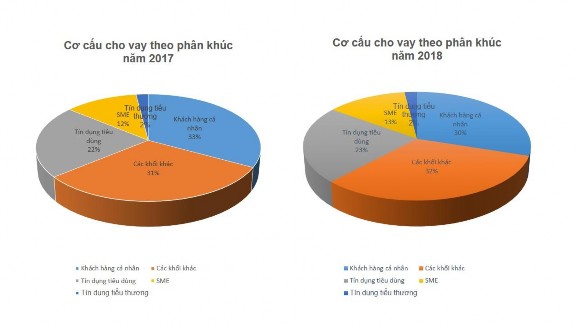
Unit: % (Source: VPBank Annual Report 2018)
Figure 3.5. Loan structure by segment
In general, at the end of 2018, VPBank continued to focus its business activities on four strategic segment pillars: Consumer Finance (FE credit); Individual customers: Production households and small traders; Corporate customers. This is reflected in VPBank's lending structure by segment. Specifically, at the end of 2018, the strategic customer segment accounted for 68% (equivalent to VND 150,934 billion) of the total outstanding loans of customers .
As mentioned above, VPBank's current business orientation is in the retail market, with the core customer segment being individuals, business households and small and medium enterprises. Therefore, the scale of lending to the household employment sector and the production of household consumer goods always accounts for the highest proportion in VPBank's total outstanding loans by sector. Specifically: On December 31, 2017, outstanding credit was VND 80,966 billion (accounting for 44.34% of total outstanding loans at this time), and on December 31, 2018, this proportion was VND 93,833 billion (accounting for 42.26% of total outstanding loans).
VPBank's business results in recent years have helped VPBank achieve its goal of becoming one of the largest non-state joint stock commercial banks in Vietnam. One of the important factors contributing to
Part of this success is the shift in focus to retail credit activities since 2012, which has brought great results to VPBank. Revenue from the individual customer segment, consumer finance and small and medium enterprises currently accounts for nearly 80% of the Bank's total revenue. In the period from 2012 to 2017, VPBank's credit growth has always been maintained at 36.2%, 2.4 times higher than the average growth rate of the banking industry in the same period. This is also the result of implementing a business strategy focusing on the retail market segment. By 2018, although VPBank's credit growth rate had declined, only at over 17% due to increasingly fierce competition among Vietnamese commercial banks in VPBank's strategic customer segment, VPBank's credit growth rate was still higher than the industry average in 2018 (14%).
3.2.1.2. Current status of credit risk at VPBank
In recent years, with a business strategy focusing on potential but risky segments (consumer credit, bonuses, etc.), VPBank has quickly joined the group of banks with the most effective operations in recent years and is aiming to become the leading retail bank in Vietnam... Some indicators to reflect credit risks at VPBank in recent years are as follows:
Table 3.4. Some indicators reflecting credit risk at VPBank
Unit: %
Target
06 month /2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |
Bad debt ratio | < 2 | 3.2 | 2.9 | 2.03 | 2.56 | 2.54 | 2.81 | <3 | 1.82 | 1.2 |
Provision rate preventive | 4.9 | 4.1 | 3.3 | 2.6 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | |
Credit growth rate | 7.33 | 17.3 | 16.96 | 24 | 27.6 | 40 | 42 | 26 | 16 | 66 |
Source: VPBank's annual report from 2010 - June 2019 [5]
VPBank's credit growth rate from 2010 to 2018 averaged ~34.3%. VPBank's bad debt ratio remained at 2.51%; overdue debt balance tended to increase gradually each year with an average growth rate of ~30.6%, and the average provisioning ratio increased by 2.2%. These figures all reflect the actual credit performance of VPBank from 2010 to June 2019: the credit growth rate has always been high compared to the industry average of ~ 16%, so the rate of RRTD is quite large, this is reflected in the bad debt ratio of VPBank in recent years at a level approaching 3% (the level prescribed by the State Bank), especially in 2018, the Bank's bad debt ratio was 3.2%, higher than the State Bank's regulations, this is completely consistent with the increase in the provisioning ratio in 2018 is completely reasonable. The reason for this RRTD is that the form of consumer credit (one of VPBank's main credit products) is quite risky, especially when the economy is entering a downward cycle.
3.2.2. Credit risk management model at VPBank
Since its establishment, VPBank has undergone structural and organizational changes to perfect the risk management model suitable for each stage of the business process. The credit risk management model at VPBank over the periods has always ensured compliance with the management, operation and business strategy requirements of the Bank. VPBank is implementing a centralized credit risk management model.
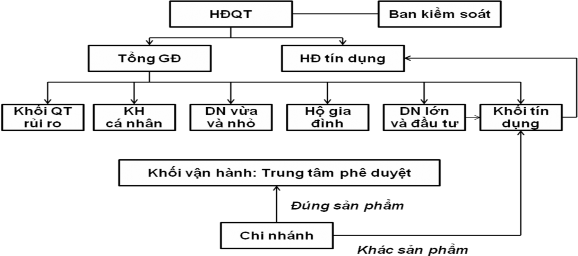
(Source: website VPBank.com.vn and author's synthesis)
Figure 3.6. Credit risk management model at VPBank
Functions and tasks of some departments in the RRTD management system at Vpbank:
Board of Control:
Supervise compliance with the provisions of law and VPBank's Charter in the management and operation of VPBank; be responsible before the law and the General Meeting of Shareholders for the performance of assigned tasks and powers; Be responsible for issues related to the internal audit department, the internal inspection and control system according to the regulations of the State Bank. Have the right to use independent consultants and the right to access, fully, accurately and promptly provide information and documents related to the management and operation of VPBank to perform assigned tasks. Currently, VPBank's Board of Supervisors has 03 members, of which 02 are full-time members, directly under the Board of Supervisors, which is the Internal Audit Division. Annual professional work: VPBank's Board of Supervisors periodically reviews VPBank's financial statements audited by an independent auditing unit; supervises the activities of VPBank's Board of Directors according to the criteria of functions and tasks as prescribed by law, VPBank's Charter, and the Resolution of the General Meeting of Shareholders.
QTRR Block:
As a unit under the VPBank Headquarters, established by the Board of Directors, under the direct management of the General Director and in charge of risk management activities throughout the VPBank system. Risk management includes credit risk, market risk and operational risk to ensure VPBank's business activities are safe and effective.
Organizational structure of risk management block:
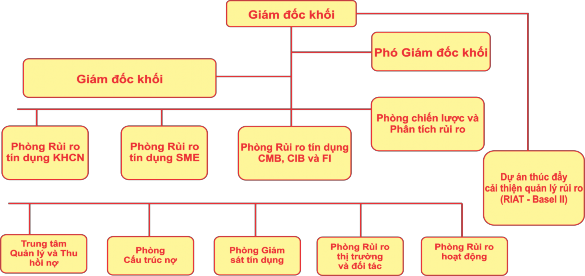
(Source: Regulations on organization and operation of Risk Management Block)
Figure 3.7. Organizational structure diagram of VPBank Risk Management Division
In the risk management block related to the credit sector, there are specialized functional departments in charge of: KHCN credit risk department, credit risk department
SME, CMB, CIB and FI credit risk department, debt management and collection center, debt structuring department, credit monitoring department, project board to promote risk management improvement (RIAT- Basel 2). These departments are responsible for the entire risk issues related to the customer segment they manage, acting as a bridge between the QTRR block and the individual customer, SME, CMB, CIB and FI blocks; consulting on risk aspects for credit products offered by these blocks; proposing and managing the quality of credit portfolios; building and managing the debt classification system and risk provisioning; participating in the development of regulatory documents guiding the management of problem loans across the VPBank system; submitting to competent authorities for approval financial solutions for problem loans; debt collection;… Credit monitoring department performs the function of monitoring high-risk group 1 debts according to VPBank's regulations in each period. Debt structuring department: acts as the focal point for receiving and appraising problem debt structuring plans and channeling financial solutions. Debt management and collection center: is the focal point for receiving debts that need to be channeled, appraising and evaluating channeling proposals of business units, monitoring credit and giving independent opinions on channeling proposals, developing debt collection plans, and reminding customers of debts. It can be seen that, with the current organizational structure of VPBank's Risk Management Division, RRTD management is very interested in and focused on development by the Executive Board.
Credit block:
As a unit under the General Director, the main function of the Credit Division is to appraise and approve credit for customers in the appraisal and approval stream of the Credit Division, to implement; advise and assist the Executive Board in managing and operating the entire system on re-appraisal operations; propose ideas to improve credit-related activities such as credit policies, credit appraisal, credit approval, etc. In addition, in order to manage credit risks most effectively, VPBank's Credit Division also established a post-loan control department to manage post-credit activities for each customer. The function and task of the Department is to inspect and supervise the bank's regulations and specific credit approval content of business units and related support units; promptly detect risks and coordinate with related professional departments to prevent and handle post-loan risks arising, etc.

![Pre-tax Profit of Bidv Tien Giang in the Period 2011-2015
zt2i3t4l5ee
zt2a3gsnon-credit services, joint stock commercial bank
zt2a3ge
zc2o3n4t5e6n7ts
At that time, the Branch had to set aside a provision for credit risks, which reduced the Branchs income.
Chart 2.2. Pre-tax profit of BIDV Tien Giang in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Billion VND
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
63.3
80.34
89.29
110.08
131.99
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Profit before tax
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
However, through chart 2.2, it can be seen that BIDV Tien Giangs profit is still increasing continuously, and its operating efficiency is currently leaking. This is a contribution of non-credit services, and this service segment will be increasingly focused on growth by BIDV Tien Giang to ensure the highest profit safety because credit activities have many potential risks. At the same time, focusing on developing non-credit services is consistent with one of the contents of restructuring the financial activities of credit institutions in the project Restructuring the system of credit institutions in the period 2011-2015 approved by the Prime Minister in Decision No. 254/QD-TTg dated March 1, 2012 [14]: Gradually shifting the business model of commercial banks towards reducing dependence on credit activities and increasing income from non-credit services.
2.2. Current status of non-credit service development at BIDV Tien Giang.
2.2.1. BIDV Tien Giang has deployed the development of non-credit services in recent times.
Along with the development of the Head Office, BIDV Tien Giangs products and services are constantly improved and deployed in a diverse manner to ensure provision for many different customer groups in the area: individual customers, corporate customers, and financial institutions. Typical services are as follows: Payment services, treasury services, guarantee services, card services, trade finance, other services: Western Union, insurance commissions, consulting services, foreign exchange derivatives trading, e-banking services,...
2.2.1.1. Payment services:
In accordance with the Prime Ministers Project to promote non-cash payments in Vietnam [15], banks in Tien Giang province have continuously developed payment services to reduce customers cash usage habits through card services and electronic banking services such as: salary payment through accounts, focusing on developing card acceptance points, developing multi-purpose cards, paying social insurance by transfer, paying bills through banks, etc.
Chart 2.3. Net income from payment services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
6000
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
0
3922 4065
4720 5084 5324
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from payment services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Along with the technological development of the entire system, BIDV Tien Giang has a payment system with a fairly stable transaction processing speed, bringing many conveniences to customers. The results of observing chart 2.3 show that the income from payment services that the Branch has achieved has grown over the years but the speed is not high and the products are not outstanding compared to other banks. Domestic payment products such as: Online bill payment, electricity bills, water bills, insurance premiums, cable TV bills, telecommunications fees, airline tickets, etc. bring many conveniences to customers. Regarding international payment, this is an indispensable activity for foreign economic activities, BIDV Tien Giang is providing international payment methods for small enterprises producing agriculture, aquatic food and seafood that have credit relationships with banks in industrial parks in Tien Giang province such as: money transfer, collection, L/C payment.
2.2.1.2. Treasury services:
BIDV Tien Giang always focuses on ensuring treasury safety and currency security, always complies with legal regulations, and minimizes risks in operations such as: counting and collecting money from customers, receiving and delivering internal transactions, collecting from the State Bank (SBV) or other credit institutions, receiving ATM funds, bundling money, etc. BIDV Tien Giangs treasury service management department is always fully equipped with modern machinery and equipment such as: money transport vehicles, fire prevention tools, money counters, money detectors, magnifying glasses, etc. to ensure absolute safety in treasury operations, immediately identifying real and fake money and other risks that may affect people and assets of the bank and customers. In addition, implementing regulation 2480/QC dated October 28, 2008 between the State Bank of Tien Giang province and the Provincial Police on coordination in the fight against counterfeit money, in the 3-year review of implementation, BIDV Tien Giang discovered, seized and submitted to the State Bank of Tien Giang province 475 banknotes of various denominations and was commended by the Provincial Police and the State Bank of Tien Giang province [17].
Chart 2.4. Net income from treasury services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
105 122
309 289 279
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from treasury services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
However, as shown in Figure 2.4, income from treasury operations is not high and fluctuates. Specifically, in the period 2011-2013, net income increased and increased most sharply in 2013, then in the period 2013-2015, there was a downward trend. This fluctuation is due to the fact that fees collected from treasury services are often very low and can even be waived to attract customers to use other services.
2.2.1.3. Guarantee and trade finance services:
BIDV Tien Giang, thanks to the advantages of the province and the favorable location of the Branch, has continuously focused on developing income from guarantee services and trade finance.
Chart 2.5. Net income from guarantee and trade finance services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
14000
12000
10000
8000
6000
4000
2000
0
5193 5695
2742 3420
8889
3992
11604 12206
5143 5312
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from guarantee services Net income from Trade Finance
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Through chart 2.5, we can see that BIDV Tien Giangs income from guarantee services and trade finance has grown over the years. The reason is: Among BIDV Tien Giangs corporate customers, the construction industry is the industry with the highest proportion of customers after the trading industry, this is a group of customers with potential to develop guarantee services. The second group of customers is corporate customers in the fields of agricultural production, livestock and seafood processing with high import and export turnover in the area.
are the target of trade finance development. In addition, BIDV Tien Giang also focuses on continuously developing these customer groups to increase revenue for many other products and services in the future.
2.2.1.4. Card and POS services:
As a service that BIDV Tien Giang has recently developed strongly, it can be said that this is a very potential market and has the ability to develop even more strongly in the future. Card services with outstanding advantages such as fast payment time, wide payment range, quite safe, effective and suitable for the integration trend and the Project to promote non-cash payments in Vietnam. Cards have become a modern and popular payment tool. BIDV Tien Giang early identified that developing card services is to expand the market to people in society, create capital mobilized from card-opened accounts, contribute to diversifying banking activities, enhance the image of the bank, bring the BIDV Tien Giang brand to people as quickly and easily as possible. BIDV Tien Giang is currently providing card types such as: credit cards (BIDV MasterCard Platinum, BIDV Visa Gold Precious, BIDV Visa Manchester United, BIDV Visa Classic), international debit cards (BIDV Ready Card, BIDV Manu Debit Card), domestic debit cards (BIDV Harmony Card, BIDV eTrans Card, BIDV Moving Card, BIDV-Lingo Co-branded Card, BIDV-Co.opmart Co-branded Card). These cards can be paid via POS/EDC or on the ATM system. In addition, with debit cards, customers can not only withdraw money via ATMs but also perform utilities such as mobile top-up, online payment, money transfer,... through electronic banking services.
In order to attract customers with card services, BIDV Tien Giang has continuously increased the installation of ATMs. As of December 31, 2015, BIDV Tien Giang has 23 ATMs combined with 7 ATMs in the same system of BIDV My Tho, so the number of ATMs is quite large, especially in the center of My Tho City, but is not yet fully present in the districts. Basic services on ATMs such as withdrawing money, checking balances, printing short statements,... BIDV ATMs accept cards from banks in the system.
Banknetvn and Smartlink, cards branded by international card organizations Union Pay (CUP), VISA, MasterCard and cards of banks in the Asian Payment Network. From here, cardholders can make bill payments for themselves or others at ATMs, by simply entering the subscriber number or customer code, booking code that service providers notify and make bill payments.
Chart 2.6. Net income from card services in the period 2011-2015
Unit: Million VND
3500
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
687
1023
1547
2267
3104
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Net income from card services
(Source: Report on the implementation of the annual business plan of the General Planning Department of BIDV Tien Giang [24])
Through chart 2.6, it can be seen that BIDV Tien Giangs card service income is constantly growing because the Branch focuses on developing businesses operating in industrial parks, which are the source of customers for salary payment products, ATMs, BSMS. Specifically, there are companies such as Freeview, Quang Viet, Dai Thanh, which are businesses with a large number of card openings at the Branch, contributing to the increase in card service fees [25].
Table 2.6. Number of ATMs and POS machines in 2015 of some banks in Tien Giang area.
Unit: Machine
STT
Bank name
Number of ATMs
Cumulative number of ATM cards
POS machine
1
BIDV Tien Giang
23
97,095
22
2
BIDV My Tho
7
21,325
0
3
Agribank Tien Giang
29
115,743
77
4
Vietinbank Tien Giang
16
100,052
54
5
Dong A Tien Giang
26
97,536
11
6
Sacombank Tien Giang
24
88,513
27
7
Vietcombank Tien Giang
15
61,607
96
8
Vietinbank - Tay Tien Giang Branch
6
46,042
38
(Source: 2015 Banking Activity Data Report of the General and Internal Control Department of the Provincial State Bank [21])
Through table 2.6, the author finds that the number of ATMs of BIDV Tien Giang is not much, ranking fourth after Agribank Tien Giang, Dong A Tien Giang, Sacombank Tien Giang. The number of POS machines of BIDV Tien Giang is very small, only higher than Dong A Tien Giang and BIDV My Tho in the initial stages of merging the BIDV system. Besides, BIDV Tien Giang has a high number of cards increasing over the years (table 2.7) but the cumulative number of cards issued up to December 31, 2015 is still relatively low compared to Agribank, Vietcombank, Dong A (table 2.6).
div.maincontent .content_head3 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .p { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; margin:0pt; }
div.maincontent p { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; margin:0pt; }
div.maincontent .s1 { color: black; font-family:Courier New, monospace; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s2 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s3 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s4 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s5 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s6 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s7 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s8 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; }
div.maincontent .s9 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -2pt; }
div.maincontent .s10 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: 5pt; }
div.maincontent .s11 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s12 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -3pt; }
div.maincontent .s13 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s14 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 7.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s15 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s16 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s17 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 9.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s18 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -1pt; }
div.maincontent .s19 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s20 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -2pt; }
div.maincontent .s21 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10pt; }
div.maincontent .s22 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s23 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -3pt; }
div.maincontent .s24 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -5pt; }
div.maincontent .s25 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s26 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s27 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -6pt; }
div.maincontent .s28 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -1pt; }
div.maincontent .s29 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s30 { color: black; font-family:Calibri, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11pt; }
div.maincontent .s31 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11pt; }
div.maincontent .s32 { color: black; font-family:.VnTime, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s33 { color: black; font-family:Cambria, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s34 { color: black; font-family:Cambria, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 10.5pt; vertical-align: -4pt; }
div.maincontent .s35 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 11.5pt; }
div.maincontent .s36 { color: black; font-family:Arial, sans-serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14pt; }
div.maincontent .s37 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s38 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 13pt; }
div.maincontent .s39 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; text-decoration: none; font-size: 15pt; }
div.maincontent .s40 { color: black; font-family:Times New Roman, serif; font-style: normal; fo](https://tailieuthamkhao.com/uploads/2022/06/06/dich-vu-phi-tin-dung-tai-ngan-hang-thuong-mai-co-phan-dau-tu-va-phat-8-1-120x90.png)



